Solid Pseudopapillary Neoplasm
Gene Landon, MD
Key Facts
Clinical Issues
Typically in young females, in body/tail of pancreas
Cytopathology
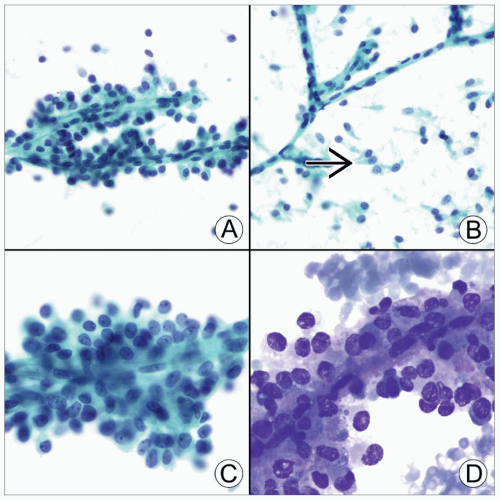
Pseudopapillae with tumor cell layer(s) arranged around capillaries
± metachromatic myxoid or hyaline stromal pericapillary layer
Bland nuclei ± longitudinal grooves
Long, slender cytoplasmic processes
Intracytoplasmic hyaline globules
Ancillary Tests
PAS-D(+) hyaline globules
Positive for β-catenin (nuclear), β-1-antitrypsin, CD10, vimentin, PR, CD56, CD99 (paranuclear dot-like pattern); synaptophysin and keratin both (+/-)
Top Differential Diagnoses
Pancreatic endocrine neoplasm
Acinar cell carcinoma
TERMINOLOGY
Definitions
Low-grade malignant neoplasm of uncertain cellular derivation
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology and Presentation
Uncommon, 1-2% of pancreatic exocrine tumors
Female predominance, rare in men
Most patients in 20s and 30s, but wide age range
Vague abdominal pain, anorexia, weight loss, nausea, vomiting
May have palpable abdominal mass
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree