Smooth Muscle Tumors of the Pleura
Key Facts
Clinical Issues
Incidence
Exceedingly rare tumors in pleura
Tumor affects individuals in wide range of ages (20-70 years)
Symptoms
Chest pain
Empyema
Asymptomatic
Macroscopic Features
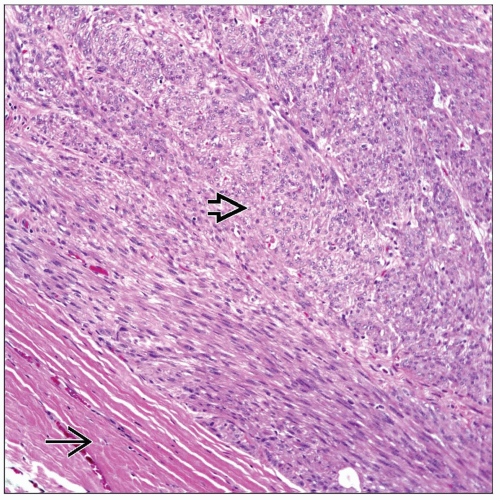
Pleural-based tumors
Diffuse involvement of pleura can occur
Microscopic Pathology
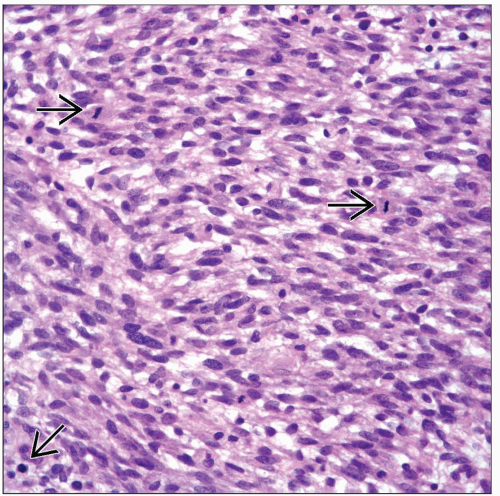
Spindle cell proliferation
Fascicular pattern
Variable mitotic activity
Necrosis
Top Differential Diagnoses
Solitary fibrous tumor (SFT)
Shows positive staining for CD34 and Bcl-2
Shows different growth patterns in the same tumor
Peripheral nerve sheath tumor (PNST)
May show positive staining for S100 protein
Would be most unusual for PNST to show positive staining for desmin &/or smooth muscle actin
Desmoid tumor
Spindle cell proliferation of desmoid tumor is fibroblastic
Would be unusual to show strong positive staining for desmin or smooth muscle actin
TERMINOLOGY
Synonyms
Leiomyoma, leiomyosarcoma
Definitions
Spindle cell tumor with muscle differentiation
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Exceedingly rare tumors in pleura
Age
Tumor affects individuals in wide range of ages (20-70 years)
Gender
No apparent gender predilection
Presentation
Chest pain
Empyema
Asymptomatic
Treatment
Surgical approaches
Complete surgical resection
Adjuvant therapy
In high-grade tumors, chemotherapy may be considered
Prognosis
Depends on grade of tumor
Higher grade tumors have poor prognosis
MACROSCOPIC FEATURES
General Features
Pleural-based tumors
Diffuse involvement of pleura can occur
Firm, white, and homogeneous surface
Areas of hemorrhage &/or necrosis may be present
Size
Between 10-18 cm
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
Histologic Features
Spindle cell proliferation
Fascicular pattern
Variable mitotic activity
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree