Skin
Staci Bryson, MD
Key Facts
Embryology
Dermis
Originates from somatic mesoderm and dermomyotome population of somites
Elastin and collagen fibers produced at week 11
Epidermis
Forms from ectoderm
Simple epithelium present by week 4
Superficial periderm forms by week 7
Intermediate layer forms from stratum germinativum by week 11
Periderm cells are replaced by epidermal cells by week 21
All adult layers are formed by birth
Melanocytes
Melanoblasts migrate from neural crest to basal layer by week 8
Adnexa
Hair follicles form from downgrowths of stratum germinativum during weeks 9-12
Sebaceous glands form as buds from hair follicle root sheath
Arrector pili muscles form from surrounding mesoderm
Eccrine sweat glands form as solid epidermal downgrowths into dermis by week 20
Macroscopic Anatomy
Skin remains thin with visible vessels until week 17
Vernix caseosa forms white protective covering
Formed from desquamated periderm cells, sebum, lanugo hairs, and amniotic cells
Epidermal ridges form from downgrowths of stratum germinativum into dermis
Arise during weeks 13-17 of development
Palmar surfaces of hands and fingers, plantar surfaces of feet and toes
Give rise to unique pattern of whorls, e.g., fingerprints
Microscopic Anatomy
Definitive layers of skin are not present until week 21 of development
Dermis
Contains collagen and elastic fibers in ground substance of mucopolysaccharides and mucoproteins
Contains adnexal structures, nerves, blood vessels
Cellular composition is a mix of fibroblasts, mast cells, macrophages, lymphocytes, and dermal dendrocytes
Stratum germinativum
Basal layer
Cuboidal cells with high nucleus:cytoplasmic ratios
Produces other keratinocytes
Intermediate layer
Layers of cells between stratum germinativum and periderm
Lacks spiny bridge of stratum corneum
Present from week 11 of development until definitive layers form (week 21)
Periderm
Earliest layer of squamous cells that keratinize and desquamate
Stratum spinosum
Several layers of cells
Cells are larger and have more cytoplasm than stratum germinativum
Progressive maturation with cells becoming increasingly flat and eosinophilic toward surface
Cells are attached by spiny bridges
Stratum granulosum
1-3 cell layers thick
Cells contain intensely basophilic keratohyaline granules
Stratum corneum
Cornified or horny layer
Definitive keratinizing and desquamating layer
“Basket weave” pattern of multiple polyhedral cells without nuclei
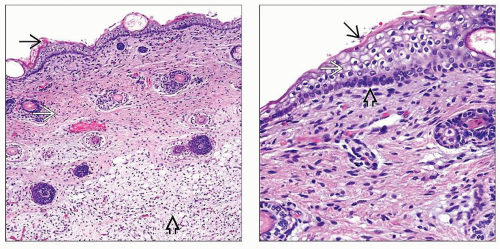 (Left) Overview of the skin at 20 weeks gestation shows the basic layers: Epidermis
 , dermis , dermis  , and subcutis , and subcutis 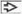 . Note the relatively thin epidermis without rete ridges and the relative paucity of fat in the subcutis. (Right) At 20 weeks gestation, the skin lacks the definitive layers of the epidermis. The superficial layer is the periderm . Note the relatively thin epidermis without rete ridges and the relative paucity of fat in the subcutis. (Right) At 20 weeks gestation, the skin lacks the definitive layers of the epidermis. The superficial layer is the periderm  with an underlying intermediate layer with an underlying intermediate layer  and a basal layer, the stratum germinativum and a basal layer, the stratum germinativum  . .Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel
Full access? Get Clinical Tree
 Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

|