Sigmoid Colectomy: Open Technique
Wayne A.I. Frederick
Tolulope Oyetunji
Shiva Seetahal
DEFINITION
A sigmoidectomy is the resection of the sigmoid colon to the level of the rectosigmoid junction. The extent of the lymphadenectomy will be determined by the indication (benign vs. malignant disease).
Focal segmental sigmoid resection for benign disease can be accomplished by dividing the vessels close to the bowel wall, without the need for a high pedicle transection. A complete sigmoidectomy (described in this chapter) includes transection of the inferior mesenteric artery (IMA) at its origin and resection of the proximal superior rectal artery (SRA) and sigmoidal branches.
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Indications for sigmoidectomy include the following:
Sigmoid colon polyps and cancer
Diverticular disease (i.e., complicated diverticulitis, perforation, fistulae, etc.)
Other indications include sigmoid volvulus, ischemic or infectious colitis, and trauma.
PATIENT HISTORY AND PHYSICAL FINDINGS
Most patients with early-stage colon cancer are asymptomatic, found on colonoscopy performed for screening purposes or secondary to a positive fecal occult blood test.
Late-stage colon cancer can present with abdominal pain, unexplained weight loss, melena, iron deficiency anemia, or a change in bowel habits. Obstructive symptoms are typically secondary to circumferential tumors.
Patients with uncomplicated diverticulitis report episodic pain in the left lower quadrant associated with fever, changes in bowel habits, and/or bloating.
The spectrum of symptomatology for complex diverticulitis can be as benign as those for uncomplicated diverticulitis but can progress to localized or even generalized peritonitis.
Patients with neoplastic or inflammatory erosion into adjacent organs, such as the bladder or vagina, can present with pneumaturia, fecaluria, or fecaloid vaginal discharge.
A thorough family history of colon or rectal cancer, polyps, and/or other malignancies should be elicited.
The physical examination should include the following:
Focused abdominal exam, including notation of abdominal scars
Digital rectal exam, focused on assessment of sphincter function
Rigid proctoscopy for all patients with sigmoid polyps or cancer reported by endoscopy to be within 20 cm from the anal verge. This will allow for confirmation of the site of the lesion, which oftentimes may not coincide with the endoscopy report. This information may alter the surgical and oncologic approach.
Rigid proctoscopy should not be performed in patients presenting with acute diverticulitis or perforation to avoid worsening of a microperforation by air insufflation.
IMAGING AND OTHER DIAGNOSTIC STUDIES
Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA): The baseline preoperative result and postsurgical control must be obtained as an assessment for complete tumor resection. On the other hand, the absolute presurgical value is an independent variable for survival.
Abdominal computed axial tomography is the most sensitive and specific test for detection of intraabdominal metastases.
Chest computed axial tomography is the most sensitive and specific test to detect mediastinal and lung metastases. It is also helpful in diverticulitis cases to evaluate for the extent of diverticular disease and for the possible presence of peridiverticular abscess, stricture, and/or fistula.
Total colonoscopy: Regardless of the primary localization of the tumor, every patient should have a complete colonoscopy study whenever possible, because 2% to 9% of the patients may have synchronous tumors. The colonic enema with double contrast may be used in those patients in whom the colonoscopy is not possible.
SURGICAL MANAGEMENT
Preoperative Planning
The patient should be mechanically bowel prepped the day before surgery with the GoLYTELY solution.
The nil per os (NPO) status is then effective after midnight.
The necessary radiologic and laboratory examination should be verified and reviewed accordingly.
Patient should be consented appropriately for the procedure.
We typically do not place preoperative stents for patients undergoing sigmoid colectomy for resolved diverticulitis. However, if there is any concern regarding potential difficulty in identification of the ureter, stenting should be considered.
Appropriate intravenous antibiotic prophylaxis is given on induction.
Consideration should be given to intravenous steroid supplementation if the patient is steroid dependent.
Subcutaneous low-molecular-weight heparin is given on induction.
A preoperative briefing with the entire surgical team is conducted. Items discussed include patient identification, type of surgery, type of anesthesia, expected events during the surgery, the need for blood components, prophylactic antibiotic, surgical devices availability, and potential adverse events and their prevention.
TECHNIQUES
PATIENT POSITIONING AND OPERATING TEAM SETUP
The patient should be placed in a standard supine position for induction of anesthesia.
Following induction and securing of the endotracheal tube, a Foley catheter should be inserted.
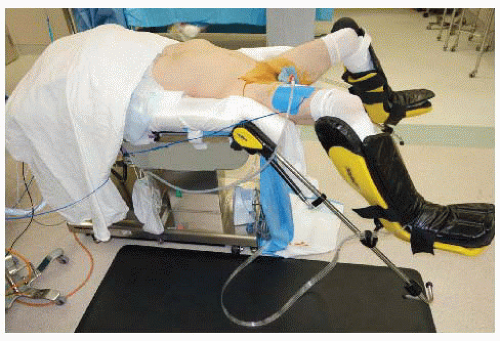
The patient is then placed in a low lithotomy position (FIG 1). Special care should be given to the positioning of the patient’s legs in the stirrup devices; adequate padding and symmetrical positioning can minimize nerve injury.
The arms should ideally be tucked at the sides with appropriate padding to afford the surgeons adequate space during the procedure and to prevent neurovascular injuries.
Once the patient has been positioned and secured to the operating table, the rectum should be irrigated with saline solution using a piston syringe to evacuate remnant stool and bowel prep fluid.
The patient can then be cleaned and draped. The drape should have a cut-out section to allow for easy access to the perineum without disrupting the sterile field of the abdomen.
The surgeon stands to the patient’s right side, with his or her assistant standing to the patient’s left side and with the scrub nurse standing to the surgeon’s right side. A second assistant, if available, stands between the patient’s legs (FIG 2).
LAPAROTOMY, INSPECTION, AND SURGICAL FIELD PREPARATION
A midline incision from the umbilicus to the pubis is usually sufficient to begin the procedure. Additional access can be gained by extending the incision cranially toward the xiphoid process as necessary. Care should be taken to stay within the midline of the rectus sheath (linea alba) on opening.
In patients with previous abdominal surgery, adherent bowel can complicate entry into the peritoneal cavity and meticulous dissection may be warranted. If possible, it might be easier to gain access into the abdomen by going above the previous scar where adhesions may be less tenuous.
Upon entry into the peritoneal cavity, moist laparotomy pads placed around the wound edges can serve as wound protectors to reduce the likelihood of wound infection.
A self-retaining retractor (e.g., a Balfour or Bookwalter retractor) can then be placed for adequate exposure.
A careful and thorough examination of the abdominal cavity is critical. Evidence of metastatic disease or carcinomatosis must be appreciated before proceeding with the procedure. If present, these significantly impact both management and prognosis.
The colon should be palpated in cases involving tumors to verify the position of the disease and assess the extent of resection. In procedures for diverticular disease, the state of the entire colon should be investigated, as this may impact the optimal scope of resection.
Following inspection, if the decision is made to proceed, the small bowel should be eviscerated and packed to the right upper quadrant using a moist laparotomy pad or a moist towel to better facilitate exposure.
LATERAL TO MEDIAL MOBILIZATION OF THE LEFT COLON AND IDENTIFICATION OF THE LEFT URETER
Once this has been confirmed, the supplying vessels and lymph basins should then be identified. Sigmoid colectomy usually entails resection of the sigmoid artery branches coming off of the IMA and the left colic artery with the accompanying lymph nodes that reside within that basin. The IMA or the left colic artery should be carefully identified along with the path of planned resection along the mesentery; the extent of the planned resection along the length of the sigmoid will dictate the degree to which the left colon must be mobilized.
The patient is placed on a Trendelenburg position with the left side up to facilitate exposure.
Mobilization of the colon is facilitated by retracting the sigmoid colon toward the midline.
Using a combination of electrocautery and blunt dissection, release the lateral attachments of the sigmoid and descending colon by transecting the line of Toldt (FIG 3).
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree