Sarcoidosis and Other Immune-Related Conditions
Michael J. Thrall, MD
Key Facts
Clinical Issues
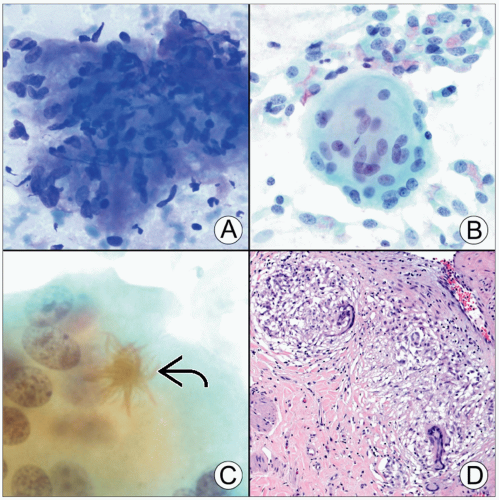
Sarcoidosis is a granulomatous disease most often involving lung and mediastinum
Rheumatoid nodules may form in the lung or pleura
Eosinophilic pneumonia is diagnosed by the presence of markedly increased eosinophils
Cytopathology
Multinucleated giant cells and epithelioid histiocyte aggregates are typical of sarcoidosis
Rheumatoid nodules may shed concerning epithelioid histiocytes with bizarre morphology
Ancillary Tests
Fungal and mycobacterial stains to rule out organisms are essential in granulomatous diseases
Top Differential Diagnoses
Granulomatous inflammation due to infectious etiologies
Other granulomatous responses
CLINICAL ISSUES
Sarcoidosis
Granulomatous disease most often involving lung and mediastinum
Etiology is unknown
Diagnosis of exclusion requiring elimination of known infectious and other causes of granuloma formation
Elevated angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) levels in serum may aid diagnosis
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree