Renal Medullary Carcinoma
Yimin Ge, MD
Key Facts
Terminology
Rapidly growing medullary tumor associated almost exclusively with sickle cell trait
Clinical Issues
Predominantly young black males
Very aggressive; mean survival: 4 months
Cytopathology
Single cells, small loose clusters, or tubular pattern
Uniformly high-grade cells with scant cytoplasm
Hyperchromatic nuclei with irregular contours and prominent central nucleoli
Occasional cytoplasmic granules or vacuoles
Ancillary Tests
Positive for AE1/AE3 and CEA
Top Differential Diagnoses
Wilms tumor, yolk sac tumor, other high-grade malignancies
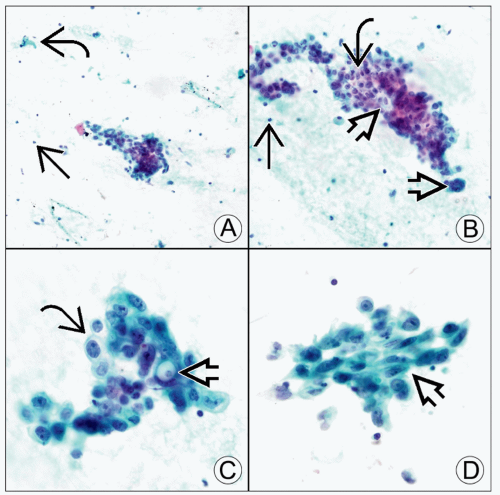 (A) Pap-stained fine-needle aspiration of renal medullary carcinoma shows a loosely cohesive group of high-grade tumor cells, stromal fragments
 , and inflammatory cells , and inflammatory cells  . (B) Medium magnification demonstrates high nuclear:cytoplasmic ratio, round to oval nuclei, and prominent central nucleoli . (B) Medium magnification demonstrates high nuclear:cytoplasmic ratio, round to oval nuclei, and prominent central nucleoli  . Pap stain shows gland-like structures . Pap stain shows gland-like structures 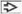 and background neutrophils and background neutrophils  . (C) High magnification of Pap stain reveals clear cytoplasm . (C) High magnification of Pap stain reveals clear cytoplasm  with occasional cytoplasmic vacuoles with occasional cytoplasmic vacuoles 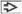 . (D) The nuclei are moderately pleomorphic with irregular contours and focal spindle morphology . (D) The nuclei are moderately pleomorphic with irregular contours and focal spindle morphology 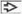 on Pap stain. on Pap stain.Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel
Full access? Get Clinical Tree
 Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

|