Radial Scar/Complex Sclerosing Lesion
Savitri Krishnamurthy, MD
Key Facts
Clinical Issues
Most radial sclerosing lesions are microscopic findings detected following investigation of mammographically found density lesions
Risk factor for subsequent development of breast carcinoma
Both in situ and invasive carcinomas can occur in association with radial sclerosing lesions
Cytopathology
Variable cellularity with clusters of benign ductal epithelial cells of varying sizes ± hyperplasia, associated with few naked bipolar nuclei, fragments of elastoid, and fibrocollagenous tissue in background
Cytologic findings are very similar to fibrocystic changes
Top Differential Diagnoses
Tubular carcinoma
 (A) Pap-stained FNA smear of a radial scar shows an elastoid stromal fragment
 . (B) Pap-stained FNA smear of a radial scar shows small clusters of benign ductal epithelial cells . (B) Pap-stained FNA smear of a radial scar shows small clusters of benign ductal epithelial cells  with associated myoepithelial cells with associated myoepithelial cells  including a few naked bipolar nuclei in the background including a few naked bipolar nuclei in the background  . (C) Pap-stained FNA smear of a radial scar shows a tubular fragment that mimics the neoplastic glands of tubular carcinoma. (D) Pap-stained FNA smear shows a tubular fragment that is composed of benign ductal epithelial cells . (C) Pap-stained FNA smear of a radial scar shows a tubular fragment that mimics the neoplastic glands of tubular carcinoma. (D) Pap-stained FNA smear shows a tubular fragment that is composed of benign ductal epithelial cells 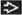 and myoepithelial cells and myoepithelial cells  without the rigid edges of the tubular glands of tubular carcinoma. without the rigid edges of the tubular glands of tubular carcinoma.Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel
Full access? Get Clinical Tree
 Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

|