Psoriasis
Cary Chisholm, MD
Key Facts
Terminology
Synonym: Psoriasis vulgaris
Clinical Issues
Incidence
1-3% of the population is affected
Age
Mean age of presentation: 25-35 years
Presentation
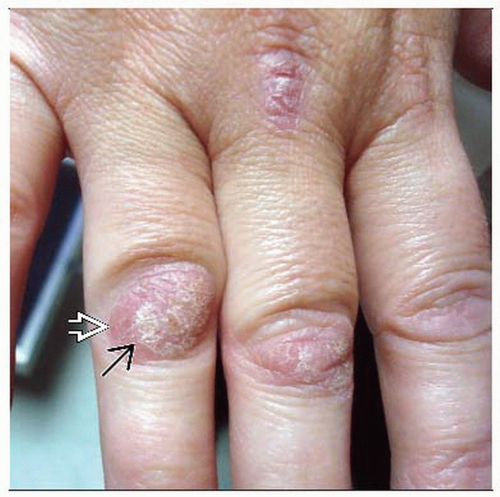
Sharply demarcated erythematous plaques and patches
Overlying silvery white scale
Auspitz sign: Pinpoint bleeding occurs when scale is removed
Site
Extensor surfaces of the extremities, scalp, trunk, nails, and buttocks
Microscopic Pathology
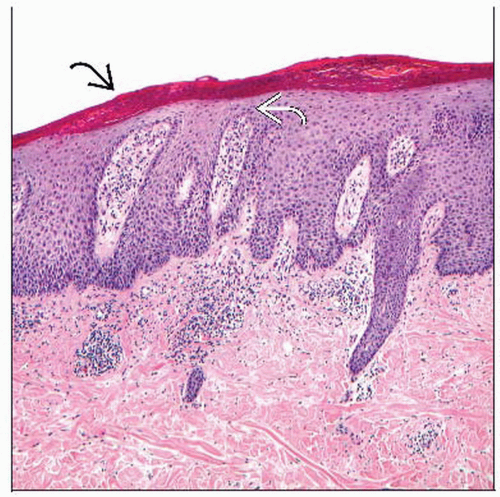
Epidermis
Confluent parakeratosis
Regular psoriasiform hyperplasia with thinning over dermal papillae
Neutrophils migrating through epidermis over dermal papillae
Neutrophil collections in the corneal (Munro microabscesses) and spinous (spongiform pustules of Kogoj) layers
Dermis
Dilated vessels in papillary dermis
± RBC extravasation
Denser perivascular activated lymphocytes, Langerhans cells, and neutrophils
TERMINOLOGY
Synonyms
Psoriasis vulgaris
Definitions
Prototype of psoriasiform dermatoses
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Environmental/Lifestyle Associations
Stress
Comorbidities of metabolic syndrome
Obesity, hypertension, diabetes mellitus, dyslipidemia, cardiovascular disease
Some organisms
Viruses: HPV5, HPV36, and HIV
Bacteria: Streptococcus pyogenes, Staphylococcus aureus
Fungi: Malassezia spp., Candida albicans
Trauma
Koebner reaction: Present in 1/3 of cases
Medications
Particularly β-blockers, ACE-inhibitors, clonidine, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, anti-malarials, and some β-lactam antibiotics
Genetic
Extremely complicated and ever evolving
Polygenic, but more common in monozygotic than dizygotic twins
HLA-Cw6
Psoriasis vulgaris, guttate psoriasis
Earlier disease onset
Penetrance only 10-15%
Interleukin (IL)-23α subunit, IL-12/23 shared β subunit, IL-23 receptor subunit
Critical role in mounting a T-cell response
Other gene products that interact with these subunits are also implicated
IL-4 and IL-13 polymorphisms
Important role in forming and mediating effects of the Th2 T-cell subset
Also leads to downregulation of Th1 T cells
Downstream signaling mediators of tumor necrosis factors (TNF)
TNIP1 and TRAF3IP2
Immunological
Very complex; a detailed explanation is beyond the scope of this chapter
T cells are recruited to the superficial dermal vessels
CD4(+) T cells mostly remain in the dermis
CD8(+) T cells infiltrate the epidermis
Dermal dendritic cells exacerbate CD4 T-cell recruitment and cytokine cascade
Plasmacytoid dendritic cells produce interferon (IFN)-α
Langerhans cells stimulate IL-22 producing T cells
Myeloid dendritic cells produce TNF-α, produce and stimulate multiple cytokines, stimulate T cells, and increase IFN-γ
Increase in cytokines causes keratinocyte proliferation and epidermal hyperplasia
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
1-3% of the population is affected
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree