Pseudomesotheliomatous Adenocarcinoma
Key Facts
Terminology
Malignant epithelial neoplasm of lung origin growing along pleural surface
Etiology/Pathogenesis
Has been linked to the following
Tobacco use
Asbestos exposure
Iron exposure
Stone dust exposure
Clinical Issues
Cough
Shortness of breath
Chest pain
Weight loss
Pleural effusion
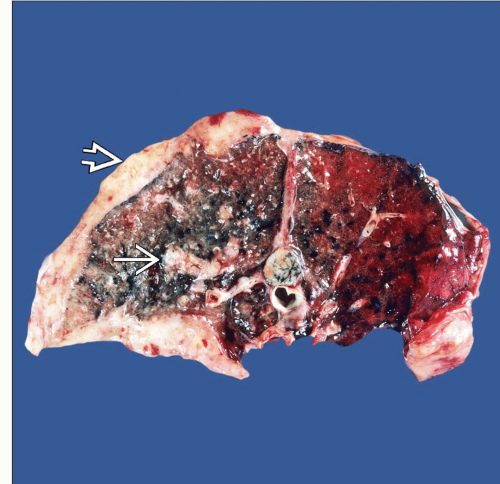
Macroscopic Features
Thickening of pleura
Encasement of lung parenchyma
Tumor growth along pulmonary septum
Discrete peripheral intrapulmonary tumor
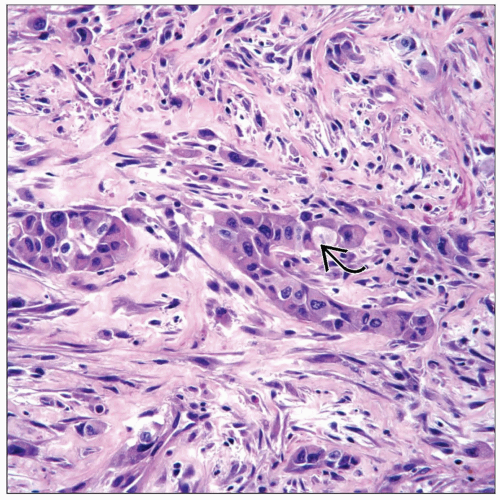
Microscopic Pathology
Glandular formation
Desmoplastic reaction
Papillary pattern in some cases
Top Differential Diagnoses
Mesothelioma, epithelioid type
Immunohistochemistry: Carcinomatous epitopes positive (CEA-M, TAG72, MOC-31, CD15, TTF-1)
TERMINOLOGY
Definitions
Malignant epithelial neoplasm of lung origin growing along pleural surface
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Environmental Exposure
Has been linked to the following
Tobacco smoke
Asbestos exposure
Iron exposure
Stone dust exposure
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Tumor of rare occurrence
Age
Majority of patients are > 50 years old
Gender
Tumor may be more common in men
Presentation
Cough
Shortness of breath
Chest pain
Weight loss
Pleural effusion
Treatment
Adjuvant therapy
Chemotherapy
Prognosis
Poor with survival of < 18 months
IMAGE FINDINGS
General Features
Tumor mimics radiographic findings of mesothelioma
MACROSCOPIC FEATURES
General Features
Thickening of pleura
Encasement of lung parenchyma
Tumor growth along pulmonary septum
Discrete peripheral intrapulmonary tumor
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
Histologic Features
Glandular formation
Desmoplastic reaction
Papillary pattern in some cases
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree