Protothecosis
Gretchen Frieling, MD
Chad Jessup, MD, MS
Martin Mihm, MD
Key Facts
Terminology
Rare algal infection caused by organisms of genus Prototheca
Etiology/Pathogenesis
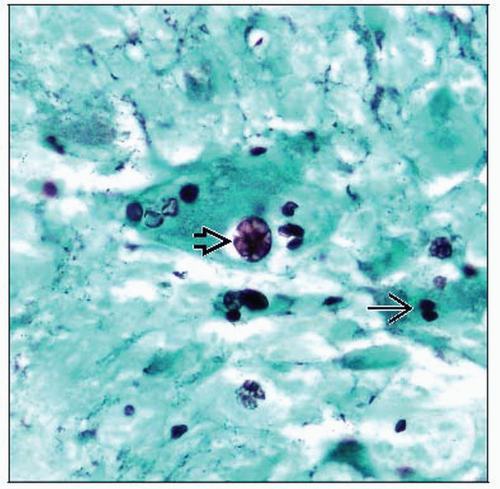
Principle defense thought to be neutrophilic response, through engulfing and eradication of organisms
Clinical Issues
Infection usually results from traumatic, inconspicuous inoculation in an immunocompromised host
Microscopic Pathology
Pan-dermal chronic granulomatous reaction with superimposed mixed inflammatory infiltrate composed of lymphocytes, plasma cells, occasional eosinophils and scattered neutrophils
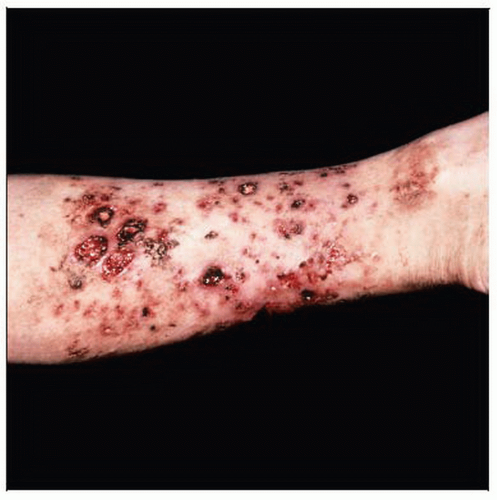 Erythematous plaques, vesiculobullous and ulcerative lesions with purulent discharge and crusting, are distributed on the calf. (Courtesy P. Hillesheim, DO.) |
TERMINOLOGY
Definitions
Exceedingly rare, indolent infection caused by achlorophyllic algae of genus Prototheca, primarily affecting immunocompromised individuals
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Infectious Agents
Prototheca spp. is an achlorophyllic and ubiquitous algae
First described in 1964, it has been isolated from soil, water, animal, and food items
Found universally, except in Antarctica
Prototheca wickerhamii is species responsible for majority of infections in humans
Pathogenesis Unclear
Principle defense thought to be neutrophilic response, through engulfing and eradication of organisms
Patients with neutrophilic defects may be at increased risk of disease progression
CLINICAL ISSUES