Primary Cutaneous Mucinous Carcinoma
Senait W. Dyson, MD
David Cassarino, MD, PhD
Key Facts
Terminology
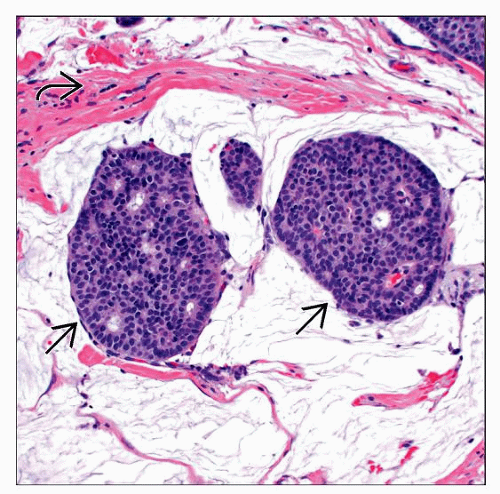
Malignant tumor with characteristic histology of epithelial islands “floating” in pools of mucin
Clinical Issues
Very rare tumor, commonly on eyelids
Slow-growing, asymptomatic, solitary, reddish papule, ulcer, or cyst
Up to 36% local recurrence and up to 15% metastasis to regional lymph nodes or distant metastasis
Microscopic Pathology
Well-circumscribed, dermal-based tumor with occasional extension to subcutaneous or deeper tissue
Strands of fibrous tissue divide tumor into different compartments
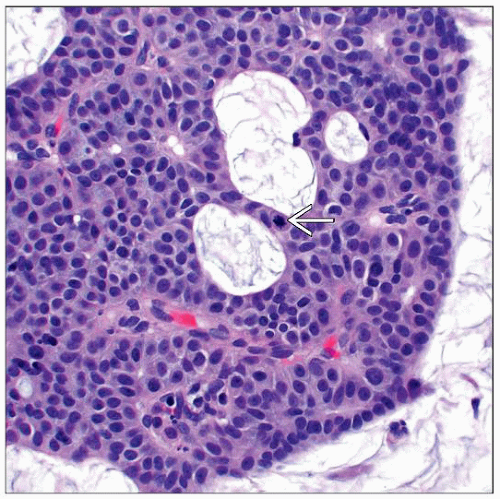
Within compartments, epithelial cells in nests and cords appear to float in large pools of mucin
Ancillary Tests
CK5/6 and p63 are typically positive and favor cutaneous primary
CK7 is typically positive, CK20 negative
ER, PR, and GCDFP-15 are often positive but not useful in excluding metastatic breast carcinoma
Top Differential Diagnoses
Metastatic mucinous carcinoma (MMC)
Mucinous breast carcinoma
Mucinous colonic carcinoma
Other primary cutaneous tumors with mucin
Basal cell carcinoma
Adenoid cystic carcinoma
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Primary cutaneous mucinous carcinoma (PCMC)
Synonyms
Mucinous carcinoma, mucinous eccrine carcinoma, mucinous eccrine adenocarcinoma
Definitions
Malignant cutaneous tumor with classic histology of epithelial islands “floating” in pools of mucin
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Gender
Men affected more often than women
Presentation
Very rare tumor
Occurs in adults and elderly
Commonly on face, with higher incidence on eyelids
Slow-growing, asymptomatic, solitary, reddish papule, ulcer, or cyst
Treatment
Surgical approaches
Wide local excision, ± dissection of regional lymph nodes
Mohs micrographic surgery
Antiestrogen drugs have been tried for patients with estrogen receptor (ER) positive tumors
Chemotherapy and radiation have not been helpful in recurrent tumors
Prognosis
Up to 36% local recurrence and up to 15% metastasis to regional lymph nodes or distant metastasis
MACROSCOPIC FEATURES
Size
0.5-7 cm; rare larger lesions
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
Histologic Features
Highly distinct low-power histologic appearance
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree