Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia
Bruce M. Wenig, MD
Key Facts
Terminology
Multisystem disease caused by ultrastructural defects of respiratory cilia and sperm tails
Etiology/Pathogenesis
Usually inherited as autosomal recessive trait
Clinical Issues
Sinusitis, otitis media, and mucopurulent rhinorrhea often striking, occurring in virtually all patients
Chronic bronchitis, recurrent pneumonia, and atelectasis are common
Macroscopic Features
Nasal cavity biopsy is usually most easily obtained specimen
Ancillary Tests
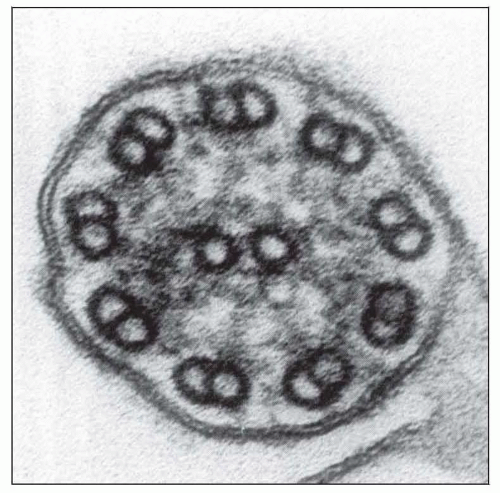
Absence of dynein arms is most confidently diagnosable structural anomaly
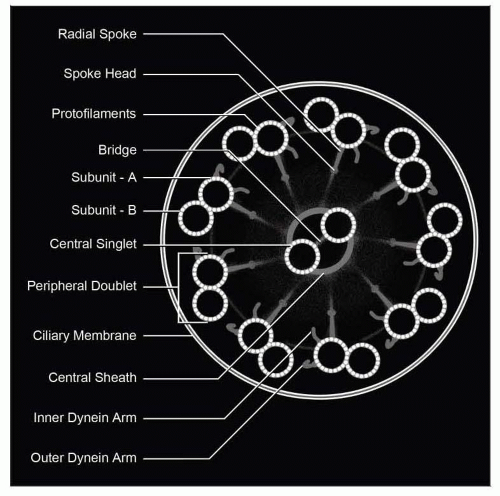 Schematic cross section shows a ciliary axoneme (main body of the organellum) detailing the normal ciliary structures, including single central couplet and 9 pairs of peripheral doublets. |
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Primary ciliary dyskinesia (PCD)
Synonyms
Immotile cilia syndrome
Definitions
Multisystem disease caused by ultrastructural defects of respiratory cilia and sperm tails
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Genetic
Majority are inherited as autosomal recessive trait
Different genes are involved in different patients and genetic mutations include
DNAI1 (chromosome 7p21), DNAH5 (chromosome 5p15-5p14), DNAH11 (chromosome 7p21)
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree