Primary Biliary Cirrhosis
Matthew M. Yeh, MD, PhD
Key Facts
Terminology
Idiopathic chronic cholestatic autoimmune liver disease in which intrahepatic bile ducts are progressively destroyed by nonsuppurative inflammation
Clinical Issues
Middle-aged to elderly women
Insidious onset with pruritus
Fatigue, jaundice, associated autoimmune disorders
Positive antimitochondrial antibodies (AMA)
Minority of cases are AMA(-)
Elevation of GGT, alkaline phosphatase, bilirubin
Ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) is treatment of choice
Microscopic Pathology
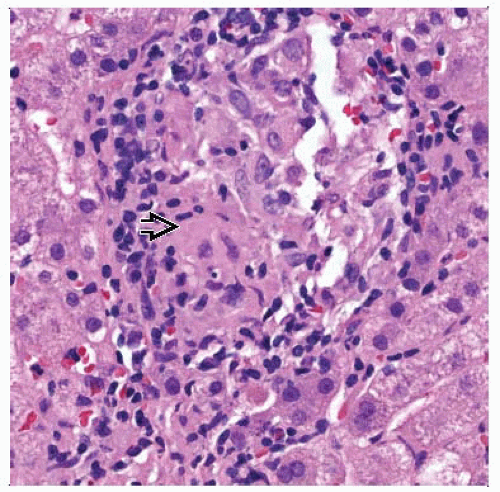
Florid duct lesion
Bile duct injury
Bile ductular reaction
Chronic cholestasis
Portal-based fibrosis
Copper stain highlights accumulated copper in hepatocytes (copper is normally excreted in bile)
Top Differential Diagnoses
Primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC)
Secondary biliary obstruction
Drug-induced chronic cholestasis
Sarcoidosis
Autoimmune hepatitis
Some patients have autoimmune hepatitis-PBC overlap syndrome with features of both
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC)
Definitions
Chronic cholestatic autoimmune disease in which intrahepatic bile ducts are progressively destroyed by nonsuppurative inflammation
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Unknown
Most likely multifactorial
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Up to 30/100,000 in Scandinavia and parts of North America
Much more prevalent among individuals of North European descent
Distinctly rare in Asians
Age
Middle-aged to elderly (40-60 years old)
Gender
Predominantly women (F:M = 9:1)
Presentation
Insidious onset with pruritus (most common), fatigue, jaundice, associated autoimmune disorders
Laboratory Tests
Positive antimitochondrial antibodies (AMA)
Elevation of GGT &/or alkaline phosphatase
Elevated bilirubin
Elevated IgM
Mildly elevated transaminases
Treatment
Surgical approaches
Liver transplantation
Drugs
Ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA)
Prognosis
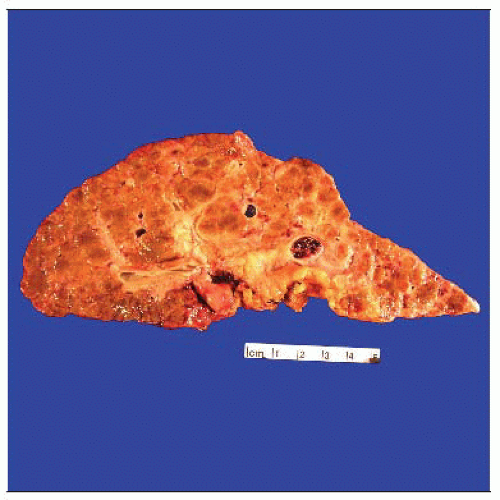
Chronic, progressive disease
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
Histologic Features
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree