Portal Venous Obstruction
Laura Webb Lamps, MD
Key Facts
Etiology/Pathogenesis
Can occur at any level of portal venous system
Extrahepatic: Portal trunk or large tributaries, usually caused by thrombosis
Intrahepatic: Intrahepatic portal venules, often no specific cause determined
Sequelae depend on location, cause, time course, and extent of blockage
Microscopic Pathology
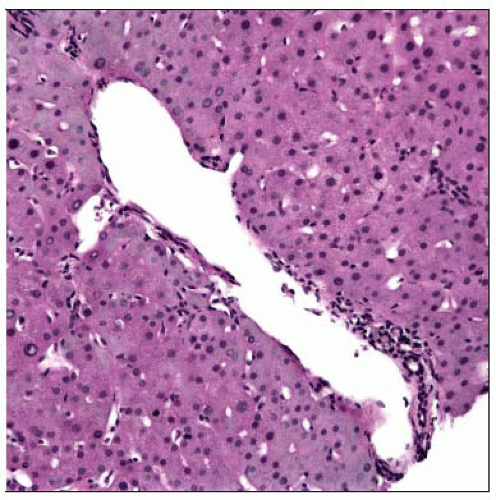
Often irregularly distributed, may be missed in small biopsy specimens
Dilated portal venules
Multiple collateral venules
Herniation of venules into parenchyma
Portal fibrosis
TERMINOLOGY
Synonyms
Idiopathic portal hypertension
Many cases of idiopathic portal hypertension probably represent undetected portal vein thrombosis
Noncirrhotic portal hypertension
Definitions
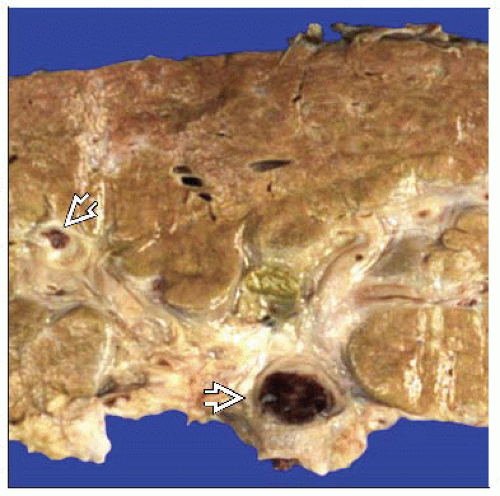
Changes resulting from mechanical obstruction of lumen of portal vein
Extrahepatic
Obstruction of portal trunk or main tributaries
Usually diagnosed by imaging studies
Inconsistent changes seen in liver biopsy
Many causes including tumors, thrombi, intraabdominal inflammation, congenital vascular anomalies, venous outflow obstruction, compression
Intrahepatic
Obstruction of portal venules within liver
Lesion(s) may not be apparent on noninvasive imaging studies
Suggestive changes may be seen on liver biopsy
May result from propagation of large portal vein thrombosis or emboli
Specific cause often not identified
Can be secondary to other conditions including congenital hepatic fibrosis, sarcoidosis, schistosomiasis, and any type of cirrhosis
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree