|
Extramammary Paget Disease |
High-Grade Penile Intraepithelial Neoplasia (PeIN) |
Age |
Adults. Sixth to eighth decades |
Younger adults |
Location |
Scrotum and scrotal penile junction most common locations |
Shaft, glans, and perimeatal region |
Symptoms |
Pruritus, pain |
None |
Signs |
Erythematous, eczematous, or ulcerated plaque-like lesion with well-defined borders |
Flat to slightly raised plaque |
Etiology |
Unknown in majority of cases. Occasionally arise in association with underlying colorectal, urogenital, or skin adnexal carcinoma |
High-risk HPV related to undifferentiated (basaloid) PeIN (most cases) and differentiated PeIN (˜50% of cases) |
Histology |
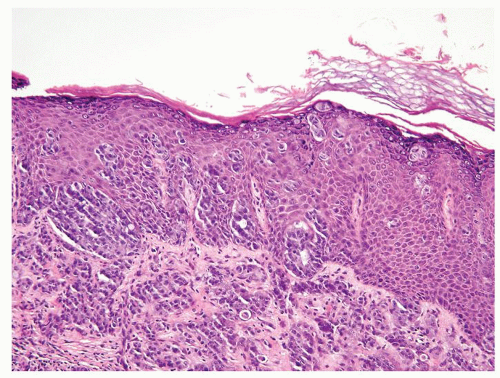
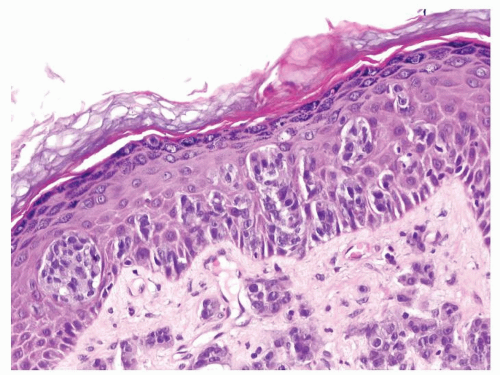
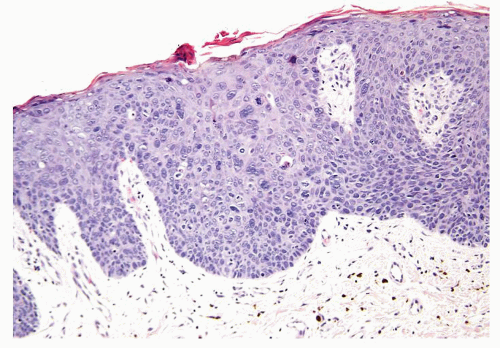
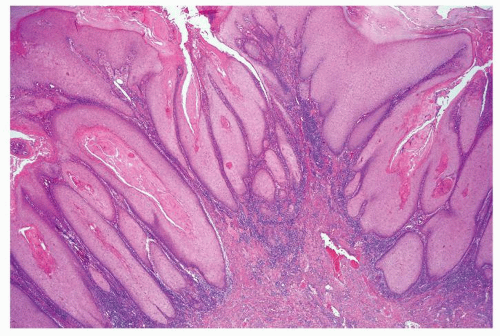
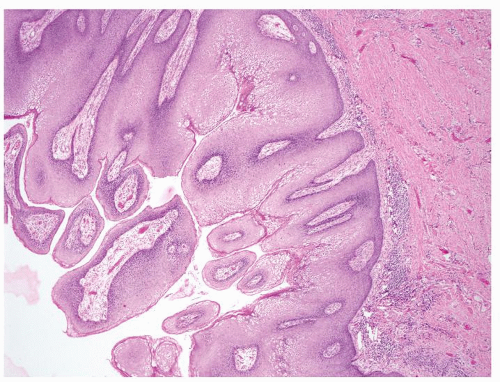
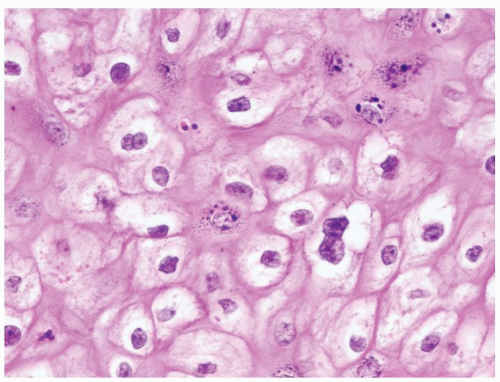
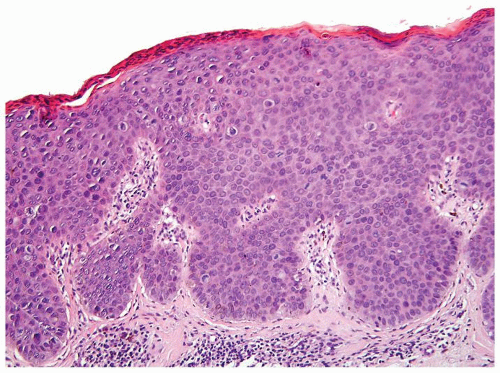
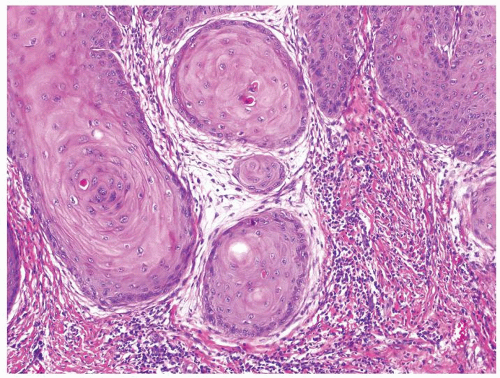
Scattered more loosely cohesive atypical cells and cell clusters with abundant pale vacuolated cytoplasm in a background of normal epithelial cells (Figs. 5.1.1 and 5.1.2)
Nuclei large vesicular with prominent nucleoli
Vacuolated pale cytoplasm with mucinous material occasionally discernible
Many suprabasally located and separated from basement membranes by normal basal cells. Tends to cluster at tips of the rete ridges
Lacks basaloid appearance
Dyskeratotic cells not seen. May see mitoses and apoptosis
Invasion into dermis or lamina propria occasionally encountered
Associated hyperkeratosis, parakeratosis, and papillomatosis commonly present
|
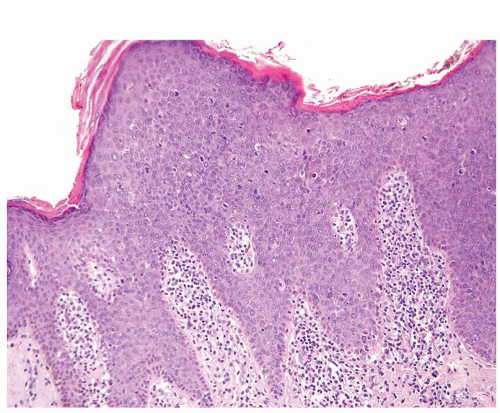
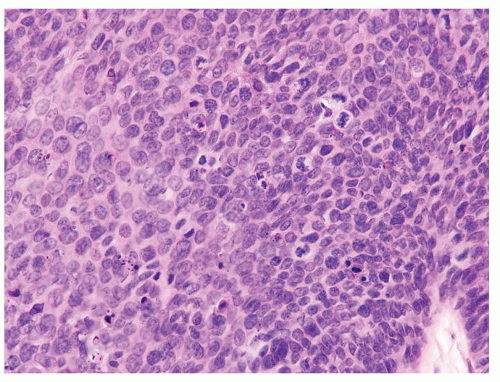
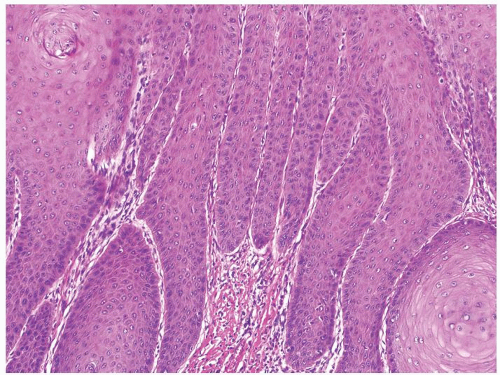
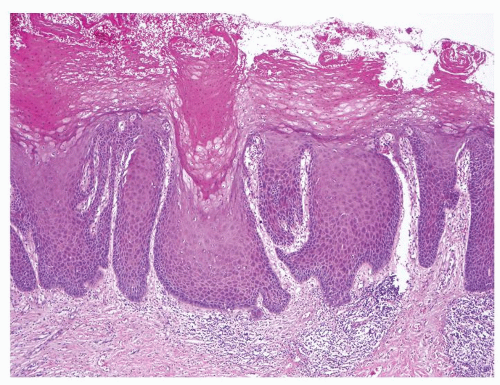
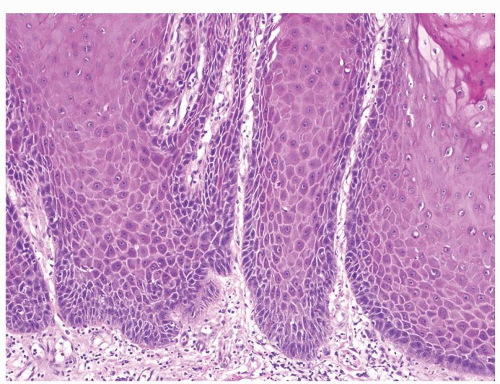
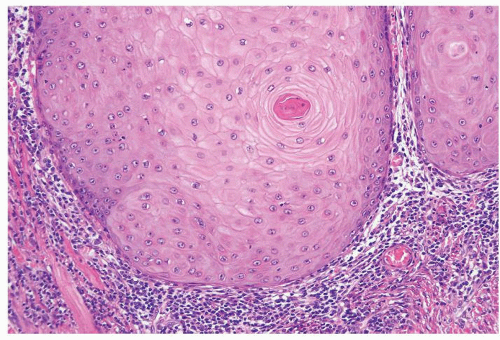
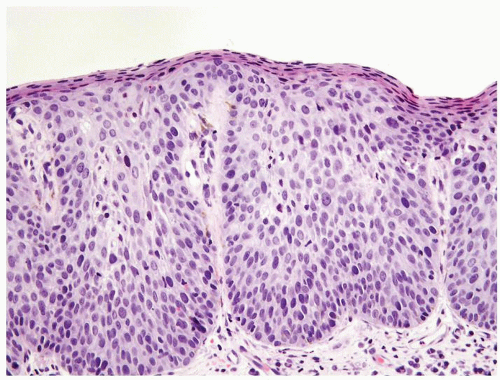
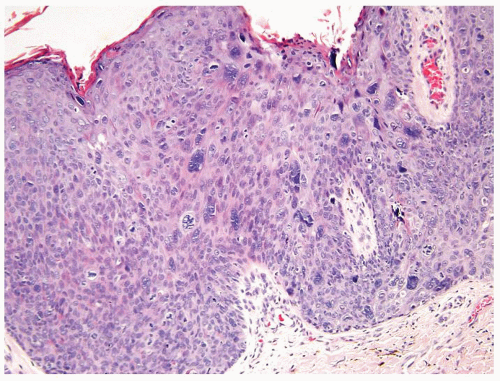
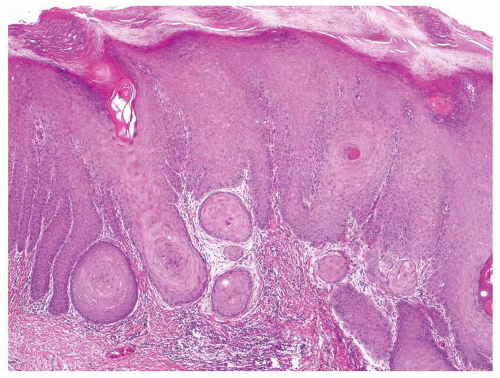
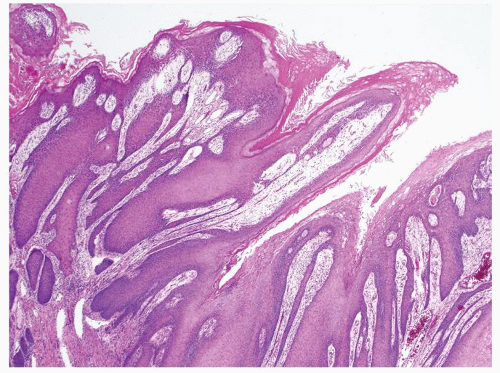
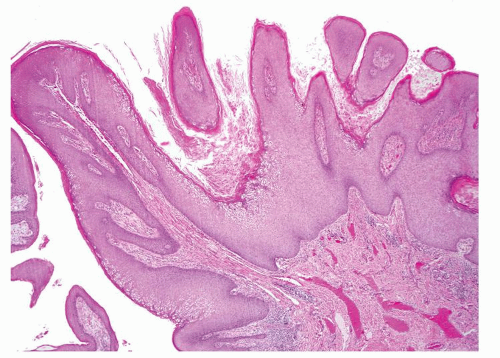
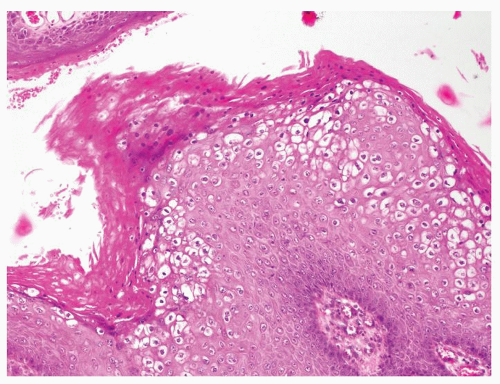
Full-thickness cohesive atypical neoplastic cells
Nuclei typically not as pleomorphic in undifferentiated PeIN (Figs.5.1.3, 5.1.4, 5.1.5, 5.1.6) compared to differentiated PeIn (Figs. 5.1.7 and 5.1.8)
Cytoplasm eosinophilic identical to normal squamous cells
No sparing of the basal cell layer
Basaloid PeIN with smaller cells with high N/C ratio
Mitoses, individually keratinized dyskeratotic cells and apoptotic bodies seen
Invasion into dermis absent by definition
Associated surface hyperkeratosis and parakeratosis commonly present
|
Special studies |
Intracytoplasmic mucin on histochemical stains
CEA+, CK7+, HER2+, CAM5.2+
Negative for high-risk HPV using in situ hybridization (ISH)
|
Intracytoplasmic mucin not demonstrable on histochemical stains
Typically CEA-, CK7-, HER2-, CAM5.2-
High-risk HPV can be detected using ISH
|
Treatment |
Wide local excision of the skin and subcutaneous tissues. Sentinel lymph node biopsy and/or regional lymphadenectomy warranted for invasive Paget disease |
Complete conservative excision |
Prognosis |
If noninvasive, favorable prognosis. Invasion with 2-y overall survival rate approaching 50%. Depth of invasion and lymphovascular involvement prognostic |
Excellent |