Pelger-Huët Anomaly
Kathryn Foucar, MD
Key Facts
Terminology
Nuclear hyposegmentation of neutrophils and other granulocytic cells producing
Bilobed (pince-nez) nuclei
Mononuclear (Stodtmeister) nuclei
Familial and acquired forms
Etiology/Pathogenesis
Autosomal dominant familial PHA
Mutations in lamin β-receptor (LBR) gene at 1q41-43
Results in defects in scaffolding proteins that control shape of nuclear membrane
Nuclear hypolobation results from reduced levels of LBR protein
All granulocytic lineages affected
Neutrophil function normal
Numerous medications linked to acquired, nonneoplastic PHA
Chronic infections can cause acquired PHA
Clonal myeloid neoplasms linked to acquired PHA
Clinical Issues
1 per 5,000 population for familial PHA
Microscopic Pathology
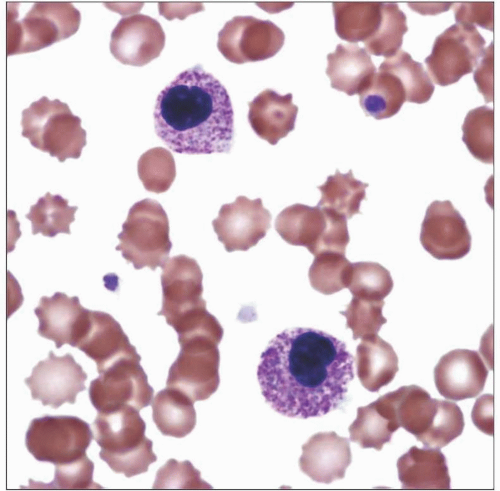
Bilobed or monolobated nuclei of neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils
≥ 70% of neutrophils are hyposegmented with increased nuclear clumping
Neutrophils show normal cytoplasmic granularity
Other lineages usually normal in familial PHA
Multilineage abnormalities common in acquired, clonal PHA
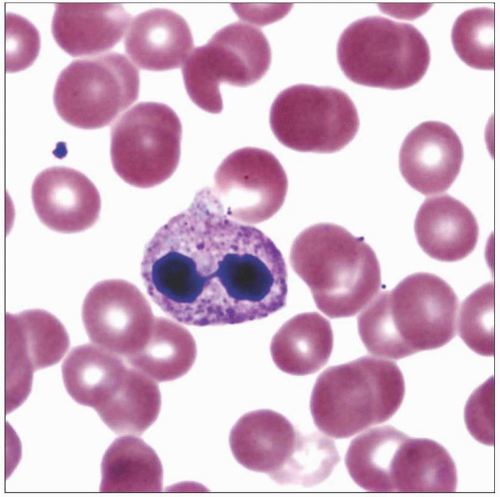 This blood smear shows a neutrophil with a hyposegmented nucleus in acquired PHA in a patient on numerous medications. Note that the cytoplasm is normal. |
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Pelger-Huët anomaly (PHA)
Definitions
Nuclear hyposegmentation of neutrophils and other granulocytic cells resulting in either bilobed (pincenez) or mononuclear (Stodtmeister) morphology
Familial and acquired forms
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Multifactorial Causes
Autosomal dominant familial PHA
Numerous medications linked to acquired, nonneoplastic PHA
Sulfasoxazole
Sulfonamides
Mycophenolate mofetil
Myelosuppressive agents
Colchicine
Ganciclovir
Valproic acid
Paclitaxel
Other medications
Chronic infections can cause acquired PHA
HIV
Tuberculosis
Mycoplasma pneumonia
Influenza
Malaria
Clonal myeloid neoplasms linked to acquired PHA
Myelodysplasia (MDS)
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML)
Myelodysplastic/myeloproliferative neoplasms
Neutrophils are component of neoplastic clone
Pathogenesis of Familial PHA
Autosomal dominant
Mutations in lamin β-receptor (LBR) gene at 1q41-43
Results in defects in scaffolding proteins that control shape of nuclear membrane
Nuclear hypolobation results from reduced levels of LBR protein
All granulocytic lineages affected
Neutrophil function normal
Neutrophil migratory defect linked to soft tissue infections
Pathogenesis of Acquired Secondary, Nonneoplastic PHA
Unknown
Pathogenesis of Acquired, Clonal PHA in Myeloid Neoplasms
Possible acquired mutations in LBR
Possible apoptotic defect with resulting dense, nonsegmented nuclei
Possible acquired clonal 17p deletion linked to prominent PHA
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
1 per 5,000 population for familial PHA
Highly variable for acquired PHA dependent upon cause
Age
Present at birth in familial PHA
Wide age range for acquired PHA dependent upon cause
Gender
No gender predilection except for HIV-associated acquired PHA, which is more common in males
Ethnicity
No ethnic predilection
Presentation
Incidental finding in familial PHA
Clinical findings variable in acquired PHA dependent on underlying cause
Laboratory Tests
Complete blood count (CBC) with differential
Normal hematopoietic parameters in familial PHA
Abnormal granulocyte morphology

Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree