Paragonimiasis
Key Facts
Terminology
Synonyms: Pulmonary distomiasis, lung fluke disease, parasitic hemoptysis, tojil (earth-borne disease), and gregarinosis
Infectious condition caused by trematode
Etiology/Pathogenesis
Raw or partially cooked crab or crayfish
Contaminated drinking water
Infectious agent; most common in humans are
Paragonimus westermani (Asia)
Paragonimus mexicanus (Latin America)
Clinical Issues
Infection can involve
Lung
Brain
Skin/subcutis
Laboratory results
Eosinophilia
Treatment
Surgical resection
Alternative treatment
Praziquantel
Bithionol
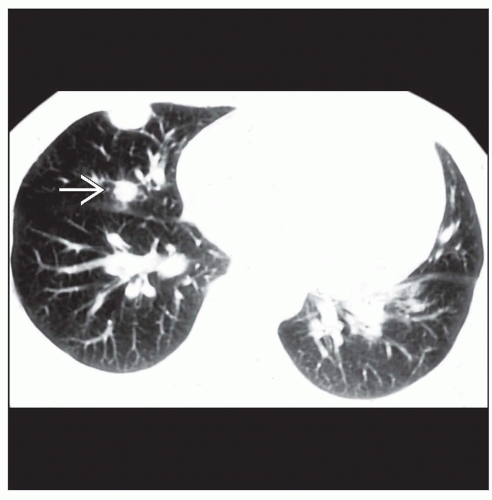
Image Findings
Pulmonary mass
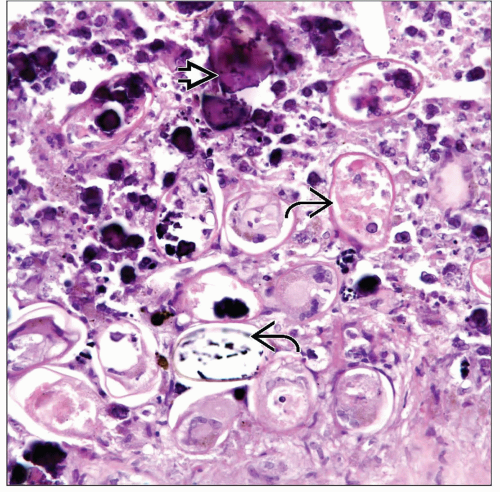
Microscopic Pathology
Identification of parasite or eggs
Granulomatous reaction
Necrosis
TERMINOLOGY
Synonyms
Pulmonary distomiasis, lung fluke disease, parasitic hemoptysis, tojil (earth-borne disease), and gregarinosis
Definitions
Infectious condition caused by trematode
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Environmental Exposure
Raw or partially cooked crab or crayfish
Contaminated drinking water
Infectious Agents
Although there are numerous species of Paragonimus, most common in humans is
Paragonimus westermani (Asia)
Paragonimus mexicanus (Latin America)
Requires 7 different phases in life cycle
Requires 3 hosts to complete life cycle
Incubation period is ˜ 70 days
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Worldwide distribution
Age
More common in younger patients
Gender
Males appear to be more commonly infected
Ethnicity
No ethnic predilection
Site
Infection can involve
Lung
Brain
Skin/subcutis
Presentation
Symptoms
Abdominal pain
Diarrhea
Nausea
Vomiting
Fatigue
Fever
Cough
Night sweats
Chest pain
Hemoptysis
Hydropneumothorax
Asymptomatic
Laboratory Tests
Eosinophilia
Treatment
Surgical approaches
Surgical resection
Drugs
Praziquantel
Bithionol
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree