Papillary Adenoma
Satish K. Tickoo, MD
Victor E. Reuter, MD
Key Facts
Terminology
Small epithelial proliferations with papillary, tubular, or tubulo-papillary configuration; ≤ 5 mm
Etiology/Pathogenesis
Trisomy 7 and 17, and loss of Y chromosome very frequently observed
Clinical Issues
Incidence of 7-40% in autopsy studies
Higher incidence in patients with chronic renal disease, particularly acquired cystic disease of kidney
Reported incidence of 7% in nephrectomy specimens resected for other tumors
More often seen in kidneys harboring papillary RCC, compared to other types of renal tumors
Macroscopic Features
Appear as well-circumscribed grayish-white to yellow nodules
By definition, all tumors are 5 mm or less in diameter
Microscopic Pathology
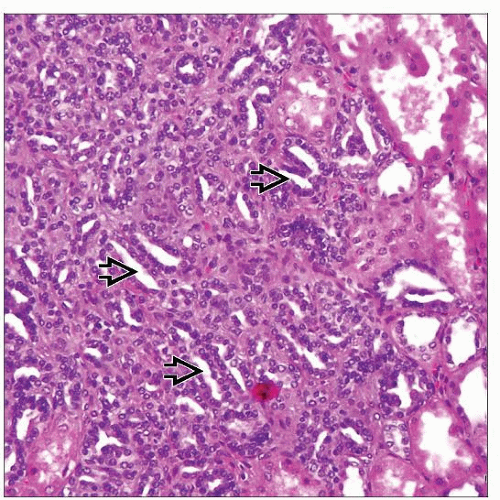
Resembles papillary RCC (usually type 1)
Have papillary, tubular, or tubulopapillary architecture; usually with low-grade nuclei
Ancillary Tests
Most are CK7 and AMACR positive; CD10 often shows luminal staining pattern
Top Differential Diagnoses
Papillary renal cell carcinoma
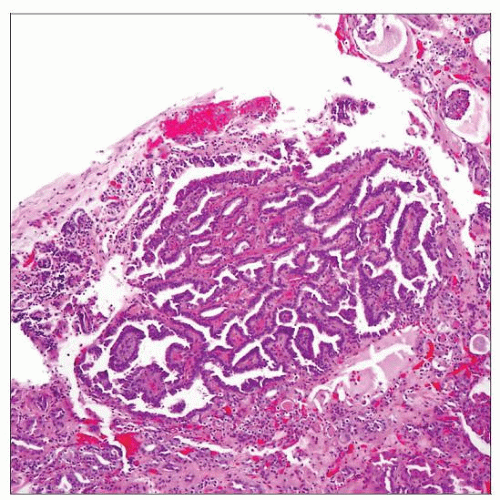 Papillary adenomas show papillary &/or tubular architectural features, similar to that seen in larger papillary renal cell carcinomas. By definition, these are 5 mm or less in maximum diameter. |
TERMINOLOGY
Synonyms
Chromophil adenoma, renal cortical adenoma
Definitions
Small epithelial proliferations with papillary, tubular, or tubulo-papillary configuration; ≤ 5 mm
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Genetic Features
Trisomy 7 and 17, and loss of Y chromosome very frequently observed
Such changes also frequent in papillary RCC
In addition to gains of chromosomes 7, 17 and loss of Y chromosome, gains of chromosomes 12, 16, and 20 also frequently present
Progressive gains of these specific chromosomes do not appear to correlate with transition from adenoma to papillary carcinoma
Frequent association with papillary RCC has raised the question of adenomas representing intrarenal metastases from papillary RCC
Loss of heterozygosity assays on multiple tumors in each kidney have shown discordant allelic loss patterns between tumors
Thus, likelihood of adenomas representing intrarenal metastases from papillary RCC is very low
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
7-40% in autopsy studies
Frequency increases with age (10% < 40 years old vs. 40% > 70 years old)
Higher incidence in patients with chronic renal disease, particularly acquired cystic disease of kidney
Incidence > 30% in acquired cystic disease of kidney
Reported incidence of 7% in nephrectomy specimens resected for other tumors
Actual incidence is likely higher because of retrospective nature of study that did not specifically target to find papillary adenomas
Presentation
Incidental finding in kidneys removed for larger tumors or other causes, and at autopsy
More often seen in kidneys harboring papillary RCC, compared to other types of renal tumors
> 25% of kidneys with papillary RCC also show papillary adenomas
Adenomas more likely to be multifocal in kidneys with papillary RCC, compared to other tumor subtypes
When papillary adenomas bilateral and multifocal (numerous), called “renal adenomatosis”
Treatment
Surgical approaches
Determined by the other presenting lesions (tumor or nontumorous condition)
Prognosis
Considered to be putative precursor of papillary RCC
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree