Nonproliferative and Proliferative Changes in Breast
Savitri Krishnamurthy, MD
TERMINOLOGY
Synonyms
Nonproliferative breast changes are also referred to as fibrocystic changes (FCC)
Definitions
Nonproliferative breast changes
Commonly encountered constellation of benign breast changes, including
Cysts
Apocrine metaplasia
Stromal fibrosis
Adenosis
Proliferative breast changes
Usual ductal hyperplasia (UDH)
Represents benign intraductal proliferation without atypia
Atypical ductal hyperplasia (ADH)
Clonal intraductal proliferation with architectural and cytologic features approaching those seen in low-grade ductal carcinoma in situ
EPIDEMIOLOGY
Age Range
Most commonly noted in women 30-50 years of age
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Hormonal Effects
Responsiveness of breast tissue to monthly changes in estrogen and progesterone levels
Clinical factors associated with increased risk of benign breast disease
Late age at menopause
Estrogen replacement therapy
Nulliparity
Low body mass index
Family history of breast cancer
Tamoxifen is associated with 28% reduction in prevalence of benign breast changes
CLINICAL IMPLICATIONS
Clinical Presentation
Symptoms related to menstrual cycle
Premenstrual pain
Palpable nodularity in bilateral breasts but no symmetrical findings
Tenderness and breast pain
Prognosis
Nonproliferative changes
4% lifetime risk of invasive carcinoma
Proliferative disease without atypia
Associated with 1.5-2x increased risk for developing cancer
5-7% increased lifetime risk of invasive cancer
ADH is a marker of increased risk for developing invasive carcinoma and a nonobligate precursor of carcinoma
Associated with 4-5x increased relative risk or with 13-17% lifetime risk of invasive carcinoma
Cancer risk is approximately equal in both breasts
Usually increased risk in women with positive family history of cancer
Imaging Findings
Mammographic findings
May present as ill-defined densities or clustered, indeterminate calcifications
Cysts can present as rounded densities mimicking other benign tumors such as fibroadenoma and papilloma
CYTOPATHOLOGY
Nonproliferative Changes
Low cellularity
Few clusters of benign ductal epithelial cells with associated myoepithelial cells and apocrine cells
Few naked nuclei, foamy histiocytes, and small fragments of fibrocollagenous tissue in background
Nuclei are regular with smooth nuclear membranes, fine nuclear chromatin, and inconspicuous nucleolus
Cysts
Aspiration of fluid, which can be yellow, brown, or milky in appearance; lesion collapses following aspiration
Few clusters of ductal cells, apocrine cells, and foamy histiocytes distributed in background of proteinaceous material
Aggregated proteinaceous material can be present as extracellular globules of varying sizes
Liesegang rings including slightly faceted concretions of proteinaceous material with laminations
Fragments of calcifications including birefringent calcium oxalate crystals can be present
Ductal epithelial cells and apocrine cells can demonstrate reactive/degenerative atypia with large round or elongated nuclei with prominent nucleolus and abundant cytoplasm
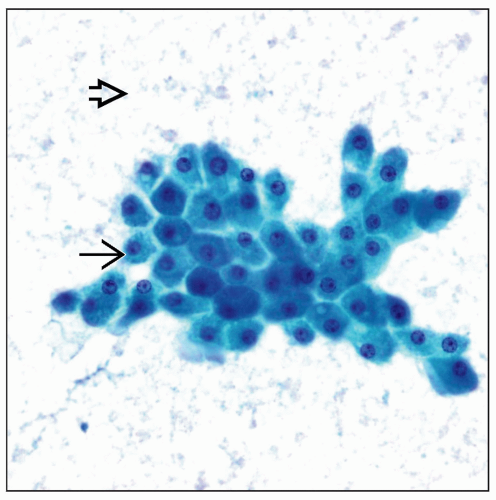
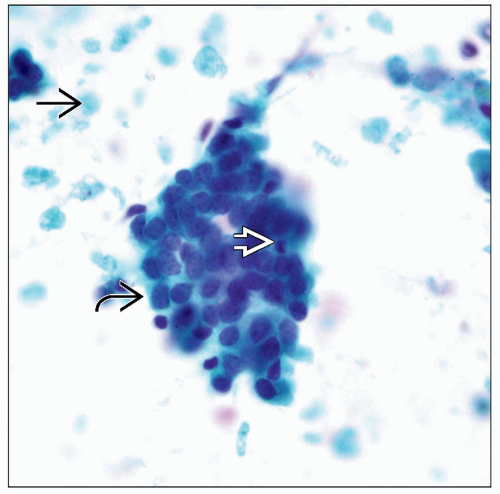
Proliferative Breast Changes Without Atypia
Cellularity is variable (usually moderate)
Moderate or large-sized fragments of cohesive ductal epithelial cells associated with other findings similar to nonproliferative breast changes
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree