Nodules Resembling Granulomas
Some lesions may grossly or microscopically mimic granulomas and enter into their differential diagnosis. These lesions include rheumatoid nodules and nodules arising in malakoplakia.
Part 1 Rheumatoid Nodules
Abida K. Haque
Mary L. Ostrowski
Patients with rheumatoid arthritis can develop rheumatoid lung disease, manifested as rheumatoid nodules. However, other types of lung lesions, such as diffuse interstitial pneumonia, pulmonary vasculitis, pleuritis, and pulmonary fibrosis indistinguishable from usual interstitial pneumonia, are also seen with or without the typical necrobiotic nodules similar to those seen in the subcutaneous tissues. The prevalence of lung involvement in rheumatoid arthritis varies from 16% in clinical surveys to 60% in open lung biopsies.
Histologic Features
The rheumatoid nodule is a granulomatous lesion with central fibrinoid necrosis, surrounded by a distinct layer of palisading histiocytes, and an outermost layer of lymphocytes, plasma cells, and multinucleated giant cells.
The nodules may be surrounded by fibrosis.
Typically the nodules are small (<2.0 cm) and either interstitial or subpleural.
Large, confluent rheumatoid nodules are seen in Caplan syndrome.
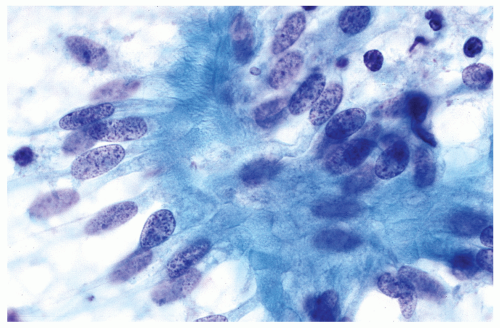 Figure 48.1 Fine-needle aspirate cytology showing a small granuloma with palisading histiocytes.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel
Full access? Get Clinical Tree
 Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

|