Diagnostic Entities |
Cytopathology Features |
See Figure(s) |
Small cell carcinoma; metastatic, from lung
(NEC) |
Neoplastic cells discrete, in loosely cohesive groups or in syncytial tissue fragments with no architectural patterns; cells small, round to oval, occasionally oblong to spindle shaped; nuclear membranes smooth to irregular; chromatin deep-staining and coarsely granular; nucleoli inconspicuous to absent; nuclear molding +; stretch artifacts +; mitoses +; karyorrhexis +; cytoplasm scant to indiscernible; cellular necrosis +; Immunoprofile: CK (AE1/AE3) +; CK 20-; neuroendocrine markers +; S100 protein -; LCA -; TTF-1 + |
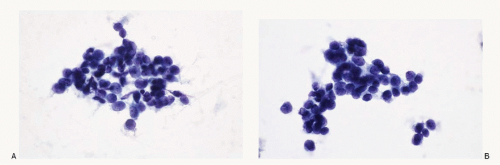
Figure 7.8 |
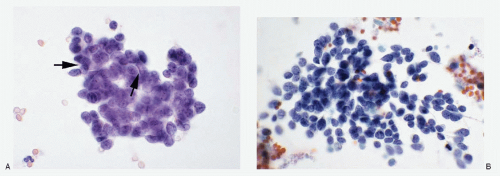
Merkel cell carcinoma |
Neoplastic cells discrete, in loosely cohesive groups with no architectural pattern; cells small, round to oval; nuclear membranes smooth to irregular; chromatin deepstaining, coarsely granular; nucleoli inconspicuous to absent; nuclear molding +; stretch artifacts +; mitoses +; karyorrhexis +; cytoplasm scant to indiscernible; necrosis +; Immunoprofile: CK20 +; neuroendocrine markers +; TTF-1 -; history of Merkel cell carcinoma helpful |
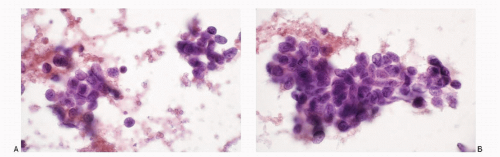
Figure 7.9 |
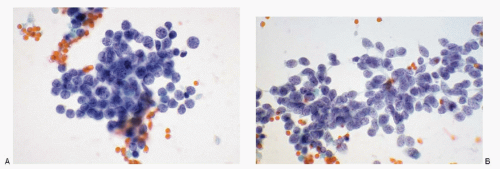
Poorly differentiated carcinomas |
Malignant cells isolated, in loosely cohesive groups or in syncytial tissue fragments with no architectural patterns; cells small, round, oval to cuboidal; occasionally oblong to spindle shaped; nuclear membranes smooth to irregular; chromatin deep-staining and coarsely granular; parachromatin clearing; nucleoli usually conspicuous; no nuclear molding; mitoses +; karyorrhexis +/-; cytoplasm variable, scant to indiscernible; cellular necrosis +; Immunoprofile: CK +; neuroendocrine markers -; S100 protein -; LCA – |
Figure 7.10 |
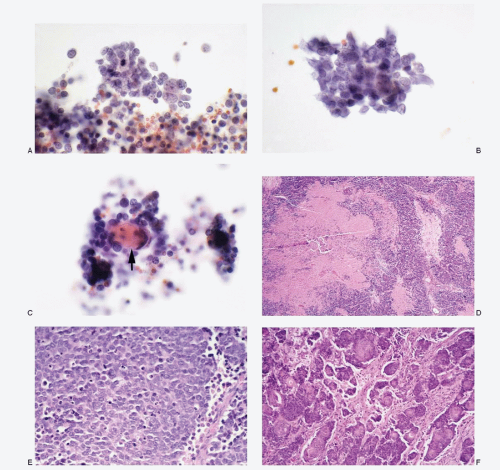
Basaloid squamous cell carcinoma |
Malignant cells isolated, in loosely cohesive groups or in syncytial tissue fragments with no architectural patterns; cells small, round, oval to cuboidal; occasionally oblong to spindle shaped; nuclear membranes smooth to irregular; chromatin deep-staining and coarsely granular; parachromatin clearing; nucleoli usually conspicuous; no nuclear molding; mitoses -; karyorrhexis +/-; cytoplasm variable, scant to indiscernible; cellular necrosis -; Immunoprofile: CK +; neuroendocrine markers -; S100 protein -; LCA -; p53 + |
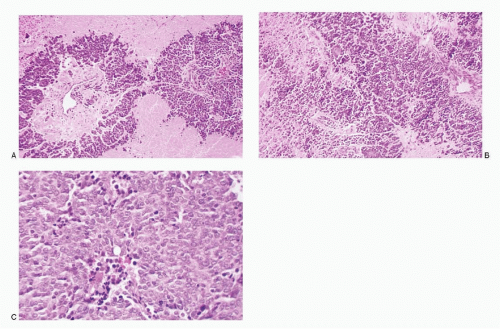
Figure 7.11 |
Adenoid cystic Carcinoma |
Neoplastic cells mostly in syncytial tissue fragments with intense crowding and overlapping, forming three-dimensional cell balls or in tight aggregates; cribriform pattern +/-; cylindrical cores of acellular, homogeneous hyaline material within the tissue fragments or in extracellular locations, staining intensely magenta pink with Romanowsky stain and pale green with Papanicolaou stain; neoplastic cells small with high N/C ratios; cell borders poorly defined; nuclei round to oval with smooth nuclear membranes; finely granular to compact chromatin; no nuclear molding; nucleoli inconspicuous to absent; no mitoses; no necrosis; background clean; bare nuclei +/-; Immunoprofile: CK +; S100 protein +; antibasement membrane antibody +; calponin +; p63 + |
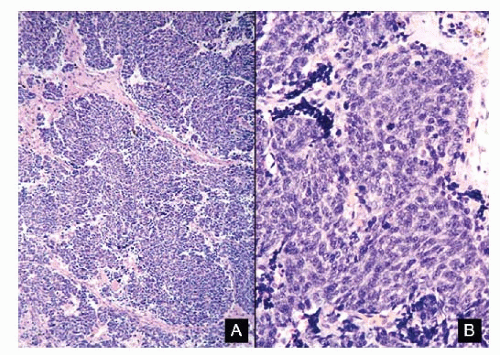
Figure 7.15 |
Basal cell adenocarcinoma |
Aspirate usually cellular; neoplastic cells discrete, in aggregates and in syncytial tissue fragments with or without branching and with crowding and overlapping of nuclei; peripheral palisading of nuclei may be present within the tissue fragments; cells small, uniform to slightly pleomorphic and enlarged; lymphocyte-like; high N/C ratios; scant to indiscernible cytoplasm; cell borders poorly defined; nuclei round to oval with smooth nuclear membranes; finely granular to compact chromatin; no nuclear molding; nucleoli inconspicuous to absent; no mitoses; no necrosis; background clean; bare nuclei +/-; Immunoprofile: CK +; S100 protein + |
Figure 7.13 |
Basal cell adenoma |
Aspirate usually cellular; neoplastic cells discrete, in aggregates and in syncytial tissue fragments with crowding and overlapping of nuclei; cells small, uniform, lymphocyte-like; high N/C ratios; scant to indiscernible cytoplasm; cell borders poorly defined; nuclei round to oval with smooth nuclear membranes; finely granular to compact chromatin; no nuclear molding; nucleoli inconspicuous to absent; no mitoses; no necrosis; background clean; Immunoprofile: CK +; S100 protein + |
Figure 7.12 |
Pleomorphic adenoma with a predominant basaloid cell pattern |
Small basaloid cells, mostly in syncytial tissue fragments or in tight aggregates, acinar pattern with hyaline globules +/-; cells small with high N/C ratios; poorly defined cell borders; round to oval nuclei with smooth nuclear membranes; coarsely granular to compact chromatin; nucleoli inconspicuous; scant cytoplasm; clean background; fibrillar stroma with aggregates of neoplastic cells in a diagnostic clue; Immunoprofile: CK +; S100 protein +; calponin +; p63 +; |
Figure 7.16 |
Cutaneous Basal Cell Carcinoma (from skin overlying salivary gland) |
Aspirate usually cellular; neoplastic cells discrete, in aggregates and in syncytial tissue fragments with or without branching and with crowding and overlapping of nuclei; peripheral palisading of nuclei may be present within the tissue fragments; cells small, uniform to slightly pleomorphic and enlarged; lymphocyte-like; high N/C ratios; scant to indiscernible cytoplasm; cell borders poorly defined; nuclei round to oval with smooth nuclear membranes; finely granular to compact chromatin; no nuclear molding; nucleoli inconspicuous to absent; no mitoses; no necrosis; background clean; bare nuclei +/- |
Figure 7.14 |
Reactive intraparotid lymph node |
Polymorphic lymphoid cell population with germinal center cells; tingible body histiocytes |
Figure 7.17 |
Malignant non-Hodgkin lymphoma |
Dissociated cell pattern; lymphoma cells discrete and in aggregates; small, monomorphic pattern with well to poorly defined cell borders; high N/C ratios; nuclei round to oval with smooth to irregular nuclear membrane; finely granular chromatin with parachromatin clearing; prominent nucleoli; cytoplasm variable but scant; no nuclear molding; mitoses +; karyorrhexis +; Immunoprofile: CK -; LCA +; B/T-cell markers +; neuroendocrine markers -; S100 protein – |
Figure 7.18 |