Neuroblastoma/Ganglioneuroblastoma
Key Facts
Terminology
Neuroblastoma (NB), ganglioneuroblastoma (GNB)
Differentiating neuroblastoma and immature ganglioneuroma both synonyms for GNB
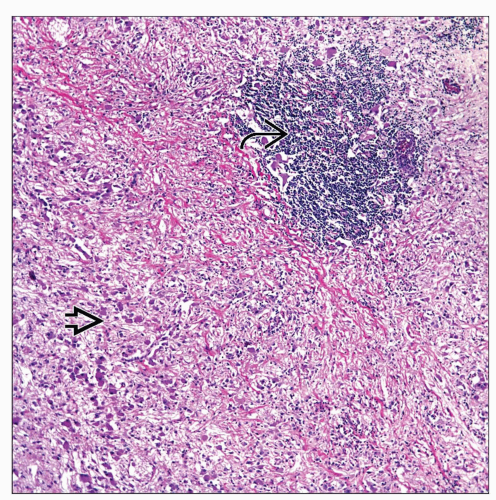
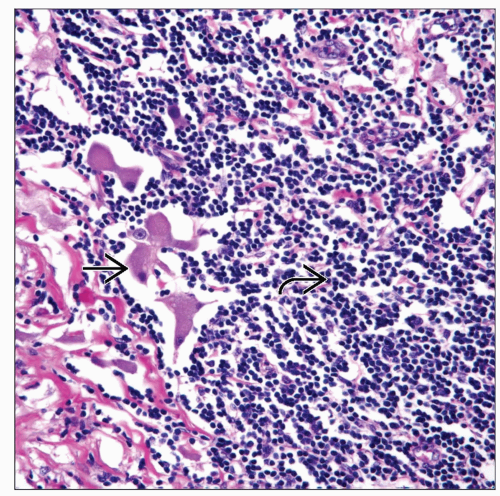
Malignant neoplasm composed of immature neural elements (NB) that may be admixed with ganglioneuromatous component (GNB)
Etiology/Pathogenesis
GNB is believed to represent a transitional tumor of sympathetic cell orgin
NB is a tumor believed to be of neural crest orgin
Clinical Issues
Tumor is more common in younger individuals
Usually in patients < 15 years of age
NB and GNB are usually in posterior mediastinum
Prognosis
Depends on clinical stage at time of diagnosis
Depends on degree of differentiation of tumor
Children appear to have more favorable outcome
Top Differential Diagnoses
Neuroblastoma
Ganglioneuroma (GN)
Rhabdomyosarcoma
Ewing sarcoma/PNET
Diagnostic Checklist
Small round blue cell tumor
Areas of neuropil
Presence of ganglion cells or precursors
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Neuroblastoma (NB), ganglioneuroblastoma (GNB)
Synonyms
Differentiating neuroblastoma and immature ganglioneuroma both synonyms for GNB
Definitions
Malignant neoplasm composed of immature neural elements (NB) that may be admixed with ganglioneuromatous component (GNB)
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Etiology
GNB is believed to represent a transitional tumor of sympathetic cell orgin
NB is a tumor believed to be of neural crest orgin
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Unusual tumors in mediastinal compartment
Age
Tumor more common in younger individuals
Usually in patients < 15 years old
Gender
No gender predilection
NB may be more commonly seen in male patients
Site
NB and GNB are usually in posterior mediastinum
Unusual cases may be in anterior mediastinum
Presentation
Chest pain
Paraplegia
Horner syndrome
Chronic diarrhea
Various congenital anomalies
Asymptomatic
Treatment
Surgical approaches
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree