Nephrogenic Fibrosing Dermopathy (Nephrogenic Systemic Fibrosis)
Cary Chisholm, MD
Key Facts
Etiology/Pathogenesis
Gadolinium administration prior to magnetic resonance (MR) imaging
Clinical Issues
History of renal failure is universally present
Dialysis not required prerequisite
Thickening and hardening of skin over days, weeks, or months
Papules and plaques over involved areas
Microscopic Pathology
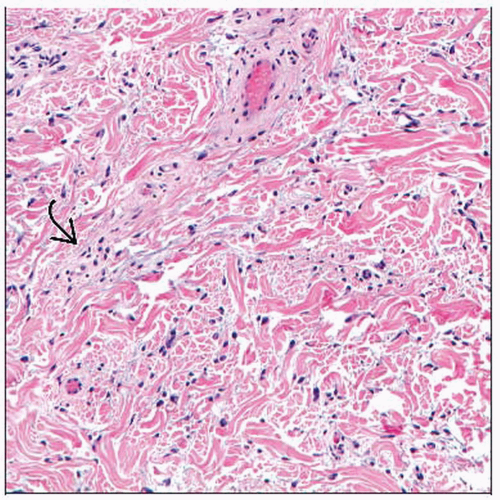
Fibrosis of dermis and subcutaneous septae
Increased numbers of fibroblasts
Spindled cells in between collagen fibers
Haphazard collagen bundles in affected deep dermis and adipose septae
Increased mucin deposition around fibroblasts
Increased histiocytes in between collagen bundles
Multinucleated giant cells may be seen
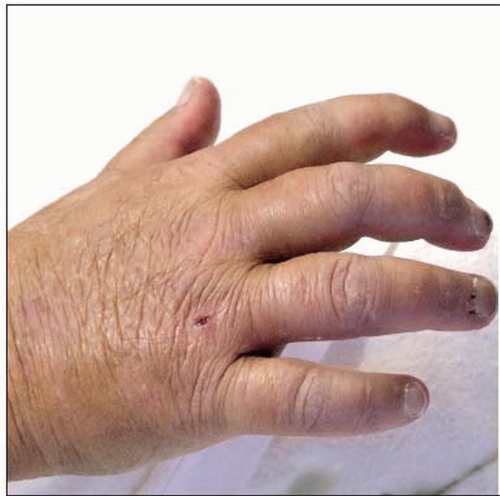 This patient is unable to open her hand due to indurated skin. She had been given gadolinium contrast months before. The skin is firm but not bound down as in scleroderma. |
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Nephrogenic fibrosing dermopathy (NFD)
Synonyms
Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis (NSF)
Definitions
Scleromyxedema-like dermatosis that affects only patients with renal failure
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Environmental Exposure
Gadolinium administration prior to magnetic resonance (MR) imaging
Gadodiamide (Omniscan) and gadopentetate (Magnevist) specifically
Have been given to virtually every reported patient prior to disease manifestation
Have been identified within lesional tissue
Stored in bone and slowly released over time