Molluscum Contagiosum
Talley Whang, MD
Chad Jessup, MD, MS
Martin C. Mihm, Jr., MD
Key Facts
Etiology/Pathogenesis
Caused by molluscum contagiosum viruses (poxvirus), transmitted by skin-to-skin contact
Clinical Issues
Primarily affects young children; in adults, considered STI; also affects immunosuppressed individuals
Dome-shaped papules with central umbilication; may number from a few to hundreds
Treatment: Watchful waiting (spontaneous resolution is the rule in healthy children); chemical, destructive, and immunologic methods
Microscopic Pathology
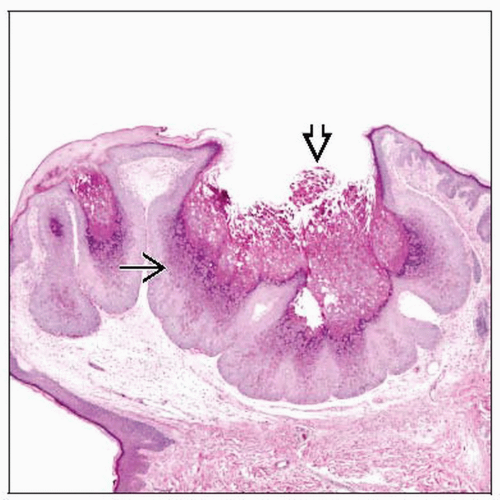
Hyperplastic epidermis with crater filled with distinct molluscum bodies (large, eosinophilic to basophilic intracytoplasmic inclusions that push aside nucleus)
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Molluscum contagiosum (MC)
Definitions
Infectious papules caused by poxvirus
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Infectious Agents
Caused by molluscum contagiosum virus (poxvirus), transmitted by skin-to-skin contact
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Age
Primarily affects young children, especially those with compromised epidermal barrier (i.e., atopic dermatitis)
In adults, molluscum is considered sexually transmitted and may coexist with other STIs
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree