Diagnostic Entity |
Cytopathologic Features |
See Figure(s) |
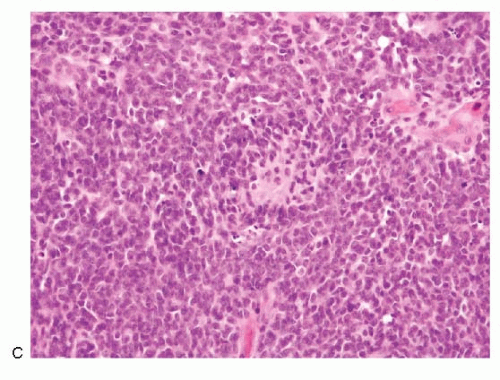
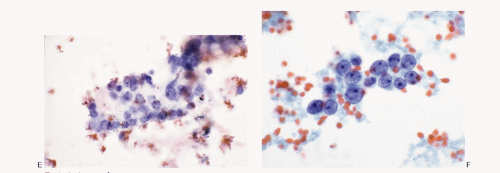
Olfactory neuroblastoma |
Monomorphic, small, round cells; dispersed cell pattern; pseudorosettes; uniform nuclei with salt-pepper chromatin pattern; nucleoli seen in high-grade tumors; carrot-shaped nuclei +/-; neurofibrillar stroma; immunoreactive to neuroendocrine markers, S100 protein (Schwann cells in stroma); neurofilament protein, protein gene product (pgp) 9.5 and occasionally to cytokeratin; CD99 – |
Figures 13.20A,B; 17.1,17.2 and 17.3 |
Neuroblastoma |
Monomorphic, small, round cells; dispersed cell pattern; Homer-Wright rosettes +; uniform nuclei with salt-pepper chromatin pattern; nucleoli seen in highgrade tumors; ganglionic differentiation +/-; neurofibrillar stroma (neuropil) +; immunoreactive to neuroendocrine markers, S100 protein (Schwann cells in stroma), pgp 9.5; negative to cytokeratin and CD99 – |
Figures 13.16; 16.3,16.4,16.5 and 16.6; 17.4A, B |
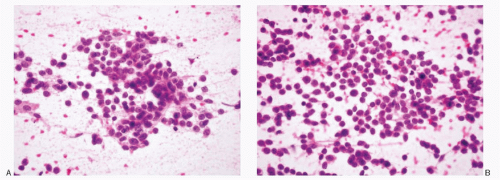
Ewing sarcoma/PNET |
Dispersed cell population; syncytial tissue fragments; Homer-Wright rosettes frequent; small to slightly larger cells; poorly defined cell borders; high N/C ratios; unipolar cytoplasmic tags or processes +/-; spindle forms in 10%-20% of the cases; round to oval; smooth to irregular nuclear membranes; chromatin fine to coarsely granular, salt-pepper type; micronucleoli +; mitoses +/-; molding +/-; scant, cytoplasm; CD99 +; neuroendocrine markers +; pgp 9.5 +; reciprocal translocation between the long arms of chromosomes 11 and 22 (t[11:22]q24:q12) |
Figures 13.28; 17.5A-C; 16.22,16.23 and 16.24 |
Rhabdomyosarcoma |
Cellular smears; small- to medium-sized uniform cells with poorly defined cell borders; scant cytoplasm with high N/C ratios; granular chromatin with nucleoli; no nuclear molding; strap cells +/-; Desmin and muscle-specific actin +; neuroendocrine markers -; CD99 -; specific translocation: t(2;13)(q35; q14) for alveolar type |
Figures 13.27; 16.13; 17.6A,B |
Pituitary adenoma |
Highly cellular; small round to polygonal cells; cell borders well to poorly defined; nuclei round, uniform with smooth nuclear membranes; coarsely granular chromatin; nucleoli -; mitoses absent; cytoplasm variable, scant to abundant; no cell processes; no necrosis; may form cords, ribbons or papillary structures, richly vascularized; granular background; neuroendocrine markers + |
Figures 10.2,10.3,10.4,10.5,10.6 and 10.7 |
In adult population: |
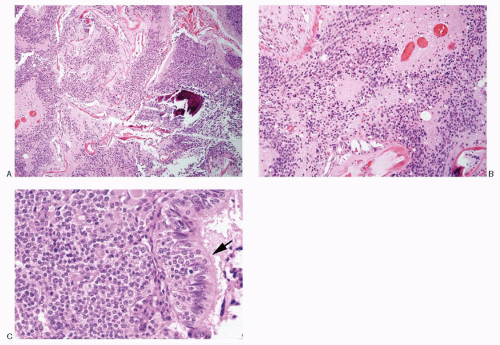
Sinonasal neuroendocrine carcinoma |
Small cells, with scant indistinct cytoplasm, occur singly and in syncytial tissue fragments without any architectural patterns; nuclear molding +; deepstaining compact chromatin; nucleoli not appreciated; mitoses +; necrosis +; neuroendocrine markers +; thyroid transcription factor (TTF-1) +; cytokeratin +; |
Figures 13.18A-C; 17.9A,B |
Sinonasal undifferentiated carcinoma |
Highly cellular, small- to medium-sized cells, discrete, in loosely cohesive groups and in syncytial tissue fragments; poorly defined cell borders; scant cytoplasm with high N/C ratios; granular chromatin with parachromatin clearing; nucleoli distinct; no nuclear molding; neuroendocrine markers -; cytokeratin +; EMA + |
Figures 13.19A-E; 17.8A,B |
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma |
Malignant cells isolated, in groups and in syncytial tissue fragments without any architectural patterns; the neoplastic cells are medium sized with granular chromatin, parachromatin clearing and nucleoli; non-neoplastic lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate +/-; Immunoprofile: CK +; neuroendocrine markers -; Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) + |
Figure 17.10A,B |
Basaloid squamous carcinoma |
Small basaloid cells either loosely cohesive or in syncytial tissue fragments with closely packed small cells, poorly defined cell borders, scant stroma and high N/C ratios; deep-stained nuclear chromatin; no nuclear molding; neuroendocrine markers -; cytokeratin +; p53 + |
Figure 17.11A-C |
Malignant non-Hodgkin lymphoma 1) B-cell type 2) peripheral T-cell type 3) extranodal NK/T-cell type |
Depends on the type; 1) B-cell or T-cell types; highly cellular; cells isolated; 2-1/2 to 3 times the size of normal lymphocytes; round nucleus; nuclear membrane irregularity +/-; granular chromatin; nucleoli prominent; mitoses +; cytoplasm scant; no cell processes; necrosis +; background may contain reactive astrocytes; lymphoid markers +; monoclonal population; cytokeratin and neuroendocrine markers – Extranodal natural killer (NK)/T-cell type; shows a polymorphous cell population composed of normal-appearing small lymphocytes, plasma cells, immunoblasts and atypical lymphocytes, mitoses +; Immunoprofile: CD56 +; EBV +; CD3+ |
Figure 10.10 |
Malignant melanoma |
Primary mucosal malignant melanoma, may present an undifferentiated small cell pattern; also present a pleomorphic cell pattern with spindle, plasmacytoid, epithelioid type cells+/-; melanin pigment +/-; Immunoprofile: strong reactivity with HMB 45, S100 protein and Melan-A; negative reactivity to neuroendocrine markers |
Figures 17.12 and 6.11C |
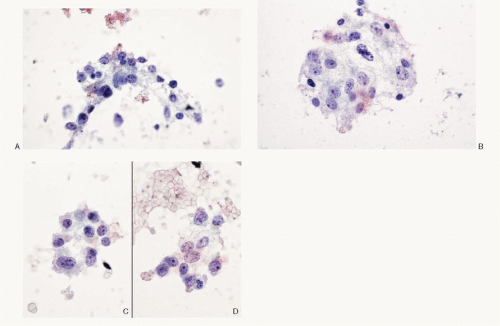
Paraganglioma |
Monomorphic cell pattern; cells discrete, or in loosely cohesive groups; neoplastic cells small to medium with occasional giant forms; round to plasmacytoid, uniform, round, eccentric nuclei; granular chromatin with salt-pepper appearance; sometimes compact; intranuclear inclusions +/-; cytoplasm variable; may be drawn into delicate process; eosinophilic cytoplasmic granules with Romanowsky stain; mitoses absent; neuroendocrine markers +; S100 protein + |
Figures 15.6; 15.7; 17.13A, B |