Cough, chest pain, dyspnea, hemoptysis, and pleural effusion are most common presenting symptoms
Most common primary sites: Genital, gastrointestinal and genitourinary tracts, pancreatohepatobiliary tract, head and neck
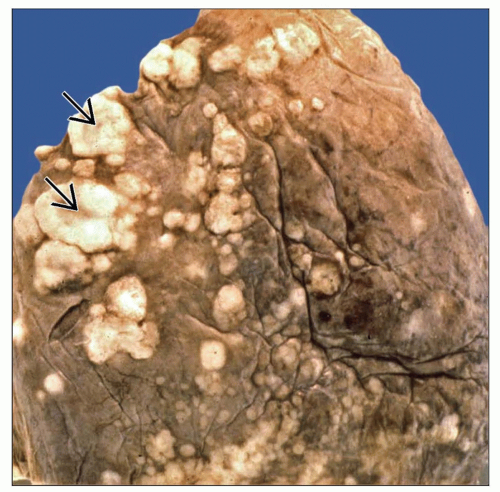
Most common locations are lower lobes in subpleural distribution
May vary from microscopic nodules to large nodules > 5 cm in diameter
Lesions are most commonly multiple and of varying sizes
Solitary “coin” lesion can be present in up to 9% of cases
Multiple bilateral nodules most commonly in peripheral, subpleural areas of lower lobes
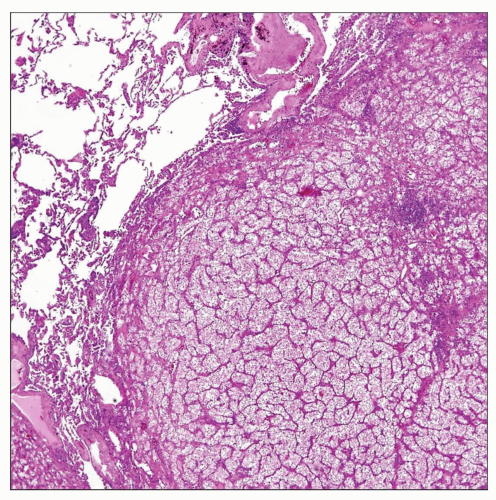
Tumor nodule formation composed of glandular or papillary structures, squamous islands, or poorly differentiated sheets of cells
Bronchioloalveolar (lepidic) pattern of growth with neoplastic cells lining alveolar spaces
Endobronchial pattern of growth with polypoid tumor mass filling the bronchial lumen
Miliary pattern of growth with diffuse small (< 0.5 cm) nodules diffusely studding the lung parenchyma
Lymphangitis carcinomatosa pattern characterized by plugging of peribronchial lymphatics by tumor cells
Tumor nodules appearing in the lung as a result of spread from another primary site
Majority of lung metastases occur via hematogenous route by spread through general circulation
Malignant tumors may also reach the lung through lymphatic dissemination
Less common mechanism of spread to the lung involves large vessel tumor emboli, especially via the pulmonary artery (liver and renal cancer)
Cough
Chest pain
Dyspnea
Hemoptysis
Pleural effusion
Cor pulmonale and pulmonary hypertension
Most common primary sites: Genital, gastrointestinal and genitourinary tracts, pancreatohepatobiliary tract, head and neck
Surgical approaches
Solitary metastatic nodules may respond well to surgical excision
Adjuvant therapy
Chemotherapy and radiation therapy are used for palliation of symptoms in advanced cases
Generally poor but may vary based on type of tumor, grade, and presence of other metastatic lesions
Patients with late metastases from low-grade indolent tumors (such as adenoid cystic carcinoma of salivary gland) may have good survival
Location
Most common locations are lower lobes in subpleural distribution
Size
May vary from microscopic nodules to large nodules > 5 cm in diameter
Morphology
Lesions are most commonly multiple and of varying sizes
Solitary “coin” lesion can be present in up to 9% of cases
Rounded contour is most likely to be associated with metastasis, as opposed to the “spiculated” appearance of primary lung cancer
CT is best imaging tool to characterize pattern and spread of disease
Multiple bilateral nodules of various sizes, most commonly in peripheral, subpleural areas in lower lobes
Endobronchial metastases may be polypoid and fill the lumen of the affected bronchus
Miliary pattern of metastases may resemble miliary tuberculosis
Pleural nodules show characteristic central umbilication
Histologic patterns of growth
Tumor nodule formation composed of glandular or papillary structures, squamous islands, or poorly differentiated sheets of cells
Bronchioloalveolar (lepidic) pattern of growth with neoplastic cells lining alveolar spaces
Endobronchial pattern of growth with polypoid tumor mass filling bronchial lumen
Miliary pattern of growth with diffuse small (< 0.5 cm) nodules diffusely studding lung parenchyma
Lymphangitis carcinomatosa pattern characterized by microscopic plugging of peribronchial lymphatics by tumor cells
May vary depending on type of tumor and degree of differentiation
Cells may be mucinous, clear, oncocytic, granular, signet ring, hobnailed, pleomorphic, or spindled
Primary lung carcinomas are usually TTF-1 positive, CK7 positive, and CK20 negative
TTF-1 may be negative in up to 40% of pulmonary primary tumors
Other tumors can also express CK7, including GI primary tumors, renal cell carcinomas, gynecologic neoplasms, and bladder carcinoma
Certain specific antibodies can be of value in identifying source of a primary lesion, including
PSA and PSAP for prostate cancer
CDX-2 for gastrointestinal tract primary cancers (colon, rectum, pancreas, biliary tract, etc.)
Hepar-1 (hepatocyte antigen) for hepatocellular carcinoma
Thyroglobulin for thyroid carcinoma
Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) antigen for renal cell carcinoma
Villin surface protein for colorectal cancer
WT1 for serous papillary carcinoma of ovary
Mammoglobin and estrogen and progesterone receptors for breast cancer
Immunohistochemistry for CDX-2 and CD20 are positive
Dirty necrosis, mucinous features, and cribriform growth pattern are commonly seen
Stains for TTF-1 are always negative
Sheets and islands of clear cells with abundant cytoplasm
“Blood lakes” (pools of red blood cells) are commonly present in center of tumor cell islands
Usually show low-grade nuclear features but may exhibit sarcomatoid features
Commonly associated with stromal desmoplasia and mucinous features
Immunohistochemistry is helpful because tumors are negative for TTF-1 and positive for CDX2
Subnuclear vacuolization, cribriform pattern, and squamoid “morules” are often present
Tumor cells are positive for ER/PR and negative for TTF-1
Clinical history of previous tumor elsewhere is indispensable for proper diagnosis
Comparison of lung lesion with histology of previous tumors is also of critical importance for definitive diagnosis
Correlation with endoscopic and imaging studies is critical to rule out occult malignancy
Multiple and bilateral nodules in lower lobes
Immunohistochemistry is most useful ancillary technique
Clinicopathologic correlation should always be carried out regardless of results of immunohistochemical stains
Immunohistochemistry | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree