Metanephric Tumors Other than Metanephric Adenoma
Satish K. Tickoo, MD
Victor E. Reuter, MD
Key Facts
Terminology
Metanephric stromal tumor (MST), metanephric adenofibroma (MAF)
Metanephric adenofibroma: Biphasic tumor composed of metanephric adenoma-like epithelial and MST-like stromal components
Metanephric stromal tumor: Pure benign pediatric stromal tumor
Clinical Issues
Both tumors very rare
MAF: Mean age 72 months (range: 5 months to 36 years); MST: Mean age 2 years (range: 4 days to 15 years)
Hypertension may be presentation in some, particularly MST, because of JGAH
Polycythemia, in some metanephric adenofibromas
Macroscopic Features
Hemorrhagic and necrotic areas very rare
Microscopic Pathology
Stroma similar in both tumors
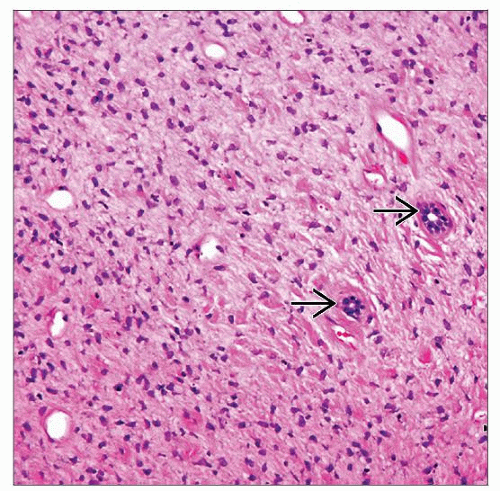
MSTs often show JGA hyperplasia within entrapped glomeruli; this feature not seen in MAF
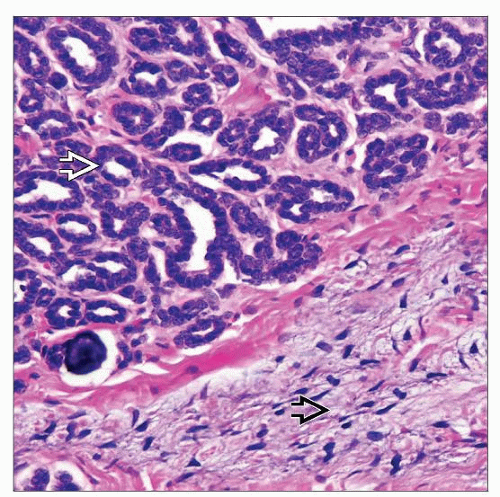
Epithelium in MAF usually mitotically inactive metanephric adenoma-like, with other rarer variant features
Stromal components immunoreactive for CD34, usually patchy
Top Differential Diagnoses
MST vs. congenital mesoblastic nephroma (CMN), classical variant
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Metanephric stromal tumor (MST), metanephric adenofibroma (MAF)
Definitions
Metanephric adenofibroma: Biphasic tumor composed of metanephric adenoma-like epithelial and MST-like stromal components
Metanephric stromal tumor: Pure benign pediatric stromal tumor
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Relationship with Wilms Tumor
Some believe metanephric tumors represent hyperdifferentiated Wilms tumors or intralobar nephrogenic rests (ILNR), due to
Presence of epithelial-predominant Wilms tumorlike areas in some MAF
Occurrence of ILNR in surrounding renal parenchyma in occasional case
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Both tumors very rare
< 70 MAFs reported in literature
MST < 1/10 as common as congenital mesoblastic nephroma, by itself a rare entity
Age
MAF: Mean age = 72 months (range: 5 months to 36 years); MST: mean age = 2 years (range: 4 days to 15 years)
Only very rare cases of MST reported in adults
Gender
MAF: M:F = 2:1; MST: Equally represented in both
Site
Both usually based in renal medulla
Presentation
Often asymptomatic and incidental findings
Hypertension may be presentation in some, particularly MST, due to juxtaglomerular apparatus hyperplasia (JGAH)
Hematuria may be another presenting symptom because of renal pelvis involvement
Polycythemia, in some MAF
Treatment
Surgical resection; adjuvant chemotherapy for MAFs that may be associated with Wilms tumor
Prognosis
Both lesions with benign outcome, regardless of presence of epithelial features in MAF
MACROSCOPIC FEATURES
General Features
Usually solitary, but rarely multifocal, particularly MST
Predominantly solid, with variable cystic components, usually with indistinct tumor borders
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree