Malignant Effusion, Mesothelioma
Donna M. Coffey, MD
Key Facts
Clinical Issues
Diffuse malignant mesothelioma (DMM) accounts for 1-4% of malignant pleural effusions and < 1% of malignant peritoneal effusions
DMM has 3 histologic patterns
Epithelial
Sarcomatous
Biphasic or mixed
Only epithelial and biphasic patterns exfoliate malignant cells in effusions
Cytopathology
Diagnosis can be achieved in up to 80% of cases if cytologic findings are combined with biopsy and history
Top Differential Diagnoses
Reactive mesothelial cells
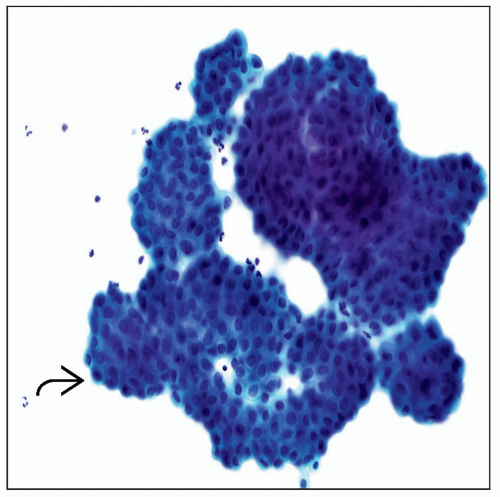
DMM effusions have large clusters or morulae
Malignant cells conserve a normal N:C ratio, but cytomegaly and some atypia are often present
Adenocarcinoma
DMM effusions show a morphologic continuum of cells from benign reactive cells to malignant cells, whereas adenocarcinomas contain a dual population of cells
Panel of immunohistochemical stains that includes ≥ 2 markers for mesothelial cells vs. carcinoma cells is often required
 Pap stain of a pleural effusion shows a highly cellular specimen with numerous large clusters of diffuse malignant mesothelioma (DMM) cells. Each cluster or morula contains hundreds of cells. |
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Diffuse malignant mesothelioma (DMM)
Localized malignant mesothelioma (LMM)
Well-differentiated papillary mesothelioma (WDPM)
Definitions
Effusions associated with DMM, which is a primary serosal malignancy that accounts for < 2% of all malignant effusions
CLINICAL ISSUES
Presentation
DMM is a rare primary serosal malignancy most commonly seen in male patients > 50 years with history of asbestos exposure
Most patients present decades after initial exposure to asbestos with history of pleuritic pain and shortness of breath
In cases of DMM, bloody or honey-colored and voluminous pleural effusions often occur
DMM accounts for 1-4% of malignant pleural effusions and < 1% of malignant peritoneal effusions
DMM and LMM most commonly arise in pleura while WDPM most often involves peritoneum of women
DMM has 3 histologic patterns: Epithelial, sarcomatous, and biphasic
Only epithelial and biphasic pattern exfoliate malignant cells in effusions
Grossly, DMM grows on pleural surfaces as masses or multiple nodules that eventually encase the lung
DMM is an aggressive tumor and most patients die of disease within 2 years of diagnosis
CYTOPATHOLOGY
Cellularity
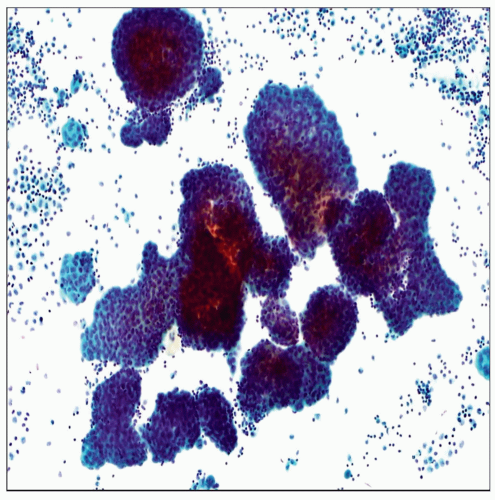
Effusions caused by DMM are highly cellular
Cellularity persists with multiple taps as opposed to reactive conditions
Pattern
Large clusters with scalloped borders, 3D morular groups, or numerous single cells
Cells
Cells of well-differentiated epithelial DMM often have deceptively bland cytologic features that recapitulate normal mesothelial cells
However, in most cases there is some cytomegaly compared with benign mesothelial cells