Malakoplakia
Key Facts
Clinical Issues
Most cases reported are associated with R. equi infection in AIDS patients or immunocompromised hosts
Presentation
Cough, fever, dyspnea
Microscopic Pathology
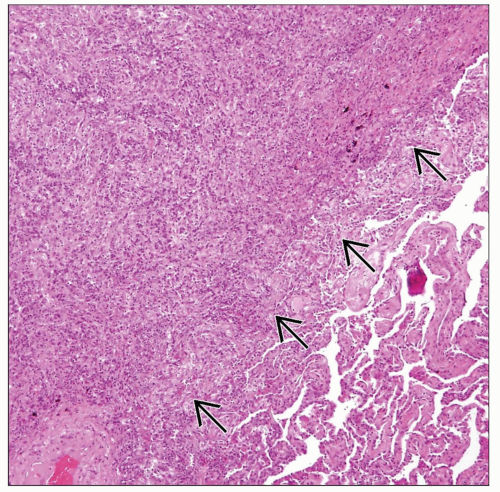
Sheets of histiocytes admixed with inflammatory cells, particularly plasma cells
Abscess formation with abundant fibrinopurulent exudate
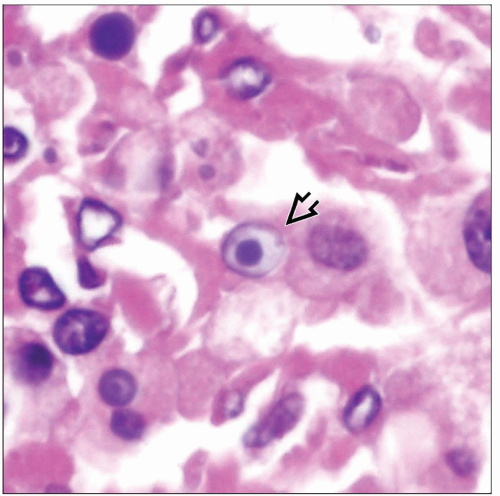
Histiocytes have large round to oval nuclei with vesicular chromatin and abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm
Scattered small calcific structures (Michaelis-Gutmann bodies) can be seen within histiocytes or in interstitium
Round to oval structures with concentric targetoid appearance
Small round to oval structures with glassy homogeneous appearance
Ancillary Tests
Michaelis-Gutmann bodies can be readily identified with alizarin red or von Kossa calcium stains
In case of R. equi infection, organisms can be stained with tissue Gram stains (Brown and Brenn stain; Brown and Hopps stain)
Michaelis-Gutmann bodies consist of large phagolysosomes that contain fragments of bacterial organisms on electron microscopy
TERMINOLOGY
Definitions
Distinctive chronic inflammatory process characterized by histiocytic proliferation admixed with microcalcifications (Michaelis-Gutmann bodies)
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Infectious Agents
Response to infection with Rhodococcus equi, E. coli, and Acinetobacter
R. equi is aerobic, usually Gram-positive coccobacillus of worldwide distribution found in soil and feces of animals, especially horses
Human infection is acquired through inhalation of contaminated soil
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Most cases reported are associated with R. equi infection in AIDS patients or immunocompromised hosts
Age
Adults between 30-60 years of age
Presentation
Cough
Fever
Dyspnea
Chest pain
IMAGE FINDINGS
Radiographic Findings
Dense single focus of parenchymal consolidation
Predilection for upper lobes of lung
Cavitation with thick walls simulating post-primary tuberculosis
Bilateral and multifocal pulmonary involvement may also occur
CT Findings
Large cavitary mass with thick fibrous capsule in upper lobes
MACROSCOPIC FEATURES
General Features
Lesions are more often solitary, although multifocal and bilateral lesions can sometimes be encountered
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree