Lobomycosis
Patricia J. Alvarez, MD
Francisco G. Bravo, MD
Key Facts
Etiology/Pathogenesis
Causative agent: Fungus Lacazia loboi
Habitat somewhere in rural environment
Introduced directly into dermis through injury
Clinical Issues
Disease of insidious character
Typical lesions are keloidiform nodules in ear, “keloids over keloids”
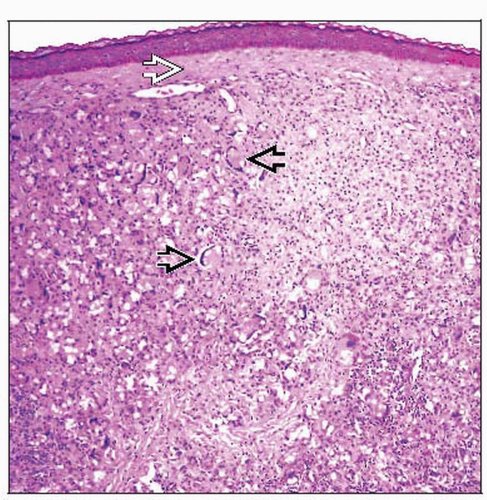
Microscopic Pathology
Granulomatous infiltrate with chains of rounded and hyaline cells with doubled birefringent membrane
Ancillary Tests
Diagnosis made by direct examination of fungus in tissue smear from lesion or by histopathology
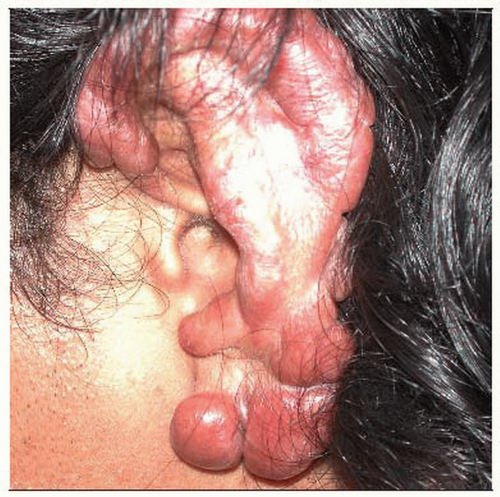 Lobomycosis clinically shows confluent keloidal lesions on the anterior region of the outer ear, which is a frequent location. |
TERMINOLOGY
Synonyms
Keloidal blastomycosis, Jorge Lobo disease, lacaziosis
Definitions
Chronic, granulomatous fungal disease caused by Lacazia loboi that affects skin and subcutaneous tissue
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Infectious Agents
Lacazia loboi is an intracellular agent known to cause disease in humans, salt water and fresh water dolphins
Soil and vegetation are likely sources of infection
L. loboi accesses skin by penetration or accidental trauma such as thorn prick or insect bite
Once in dermis, fungus is phagocytized, initiating slow-growing process of multiplication
Some suggest lymphatic dissemination, although hematogenous and contiguity are also hypotheses