Liposarcoma
Key Facts
Clinical Issues
Rare tumor
Broad age range; from children to adults (mean age: 43 years)
Anterior and posterior mediastinum
Dyspnea
Chest pain
Recurrences in 33% of cases
Myxoid/round cell, dedifferentiated, and pleomorphic liposarcomas are associated with more aggressive behavior
Microscopic Pathology
Well-differentiated, lipoma-like liposarcoma/atypical lipomatous tumor
Myxoid/round cell liposarcoma
Dedifferentiated liposarcoma
Pleomorphic liposarcoma
Ancillary Tests
Lipoblasts and atypical cells in well-differentiated lipoma-like liposarcoma and dedifferentiated liposarcoma are positive for MDM2 and CDK4
Well-differentiated liposarcoma and dedifferentiated liposarcoma show amplification of MDM2 at 12q14-15 region
Myxoid liposarcoma shows TSL-CHOP translocation in t(12;16)(q13;p11)
Top Differential Diagnoses
Lipoma and thymolipoma
Low-grade spindle cell tumors
High-grade pleomorphic sarcomas
Small round blue cell tumors
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Liposarcoma (LS)
Synonyms
Atypical lipomatous tumor
Definitions
Malignant neoplastic proliferation of adipocytic cells
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Rare tumor
Age
Broad age range; children to adults (mean: 43 years)
Gender
Slight predilection for males
Site
Anterior and posterior mediastinum
More common in anterior mediastinum
Presentation
Cough
Dyspnea
Chest pain
Asymptomatic in up to 1/3 of patients
May be an incidental finding on routine chest x-ray or at autopsy
Treatment
Surgical excision
Prognosis
Depends on stage and histologic type
Recurrences in 33% of cases
Large, infiltrative, and unresectable tumors are associated with worse prognosis
Myxoid/round cell, dedifferentiated and pleomorphic liposarcomas are associated with more aggressive behavior
Round cell and pleomorphic liposarcomas are associated with distant metastases and high mortality
Well-differentiated liposarcomas can recur 15-20 years after initial diagnosis
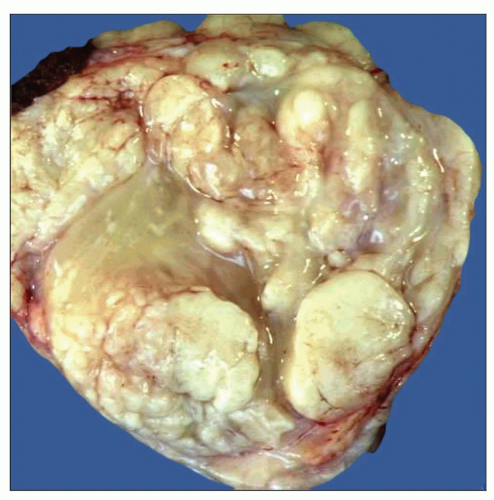
MACROSCOPIC FEATURES
General Features
Well-differentiated tumors are lobulated, well circumscribed, and thinly encapsulated with a soft, yellowish cut surface
Poorly differentiated tumors are irregular, infiltrative, with yellow-white firm cut surfaces and areas of hemorrhage and necrosis
Sections to Be Submitted
1 section per centimeter of largest tumor diameter
Additional sections must be submitted in tumors suspected of corresponding to dedifferentiated liposarcomas to identify lipogenic elements
Size
5-30 cm
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
Histologic Features
Well-differentiated, lipoma-like liposarcoma/atypical lipomatous tumor
Sheets of mature-appearing adipocytes ± scattered atypical lipoblastic cells
Areas of densely collagenized stroma containing atypical lipoblasts and spindle cells
Thymoliposarcoma is characterized by admixture of normal thymus with atypical lipomatous areas
Scattered lymphoid aggregates or lymphoid follicles
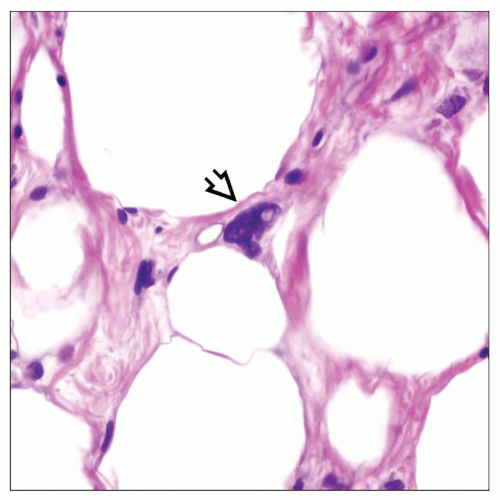
Myxoid/round cell liposarcoma
Scattered small, stellate or round cells embedded in abundant myxoid matrix
Prominent arborizing (“chicken wire”) vascular pattern of small branching vessels in stroma
Round cell variant characterized by increased cellularity with emergence of dense sheets of primitive, hyperchromatic small round cells
“Pulmonary-edema” pattern with dilated spaces filled with serum may be seen in these tumors
Dedifferentiated liposarcoma
Well-differentiated liposarcoma that shows emergence of nonlipogenic atypical spindle cell component
Low-grade dedifferentiated component shows bland-appearing spindle cell proliferation with low mitotic rate
High-grade dedifferentiated component shows pleomorphic tumor cells with atypical mitoses simulating malignant fibrous histiocytoma
Dedifferentiated component may be heterologous (i.e., rhabdo-, leio-, or osteosarcomatous)
Dedifferentiated component may show foci of spindle cells showing a distinctive whorling pattern that resembles meningioma
Pleomorphic liposarcoma
High-grade pleomorphic sarcoma with focal areas containing lipoblastic elements
Bizarre lipoblasts and multinucleated floret-type giant cells
Pleomorphic myxoid liposarcoma
Shows areas of myxoid liposarcoma admixed with pleomorphic tumor cells
More aggressive behavior than conventional myxoid liposarcoma
Rare morphologic variant more often seen in mediastinum
Cytologic Features
Majority of cells in well-differentiated liposarcoma resemble normal mature adipocytes
Well-differentiated liposarcoma may contain atypical, multinucleated adipocytes
Well-differentiated liposarcoma often contains floret-type multinucleated cells
Sclerosing areas in well-differentiated liposarcoma contain floret-type cells and bland-appearing spindle stromal cells
Lipoblasts may vary from small, signet-ring lipoblasts to multivacuolated adipocytes with multiple enlarged, atypical nuclei
Round cell liposarcoma shows primitive small round blue cells with scant cytoplasm
Pleomorphic liposarcoma contains bizarre, anaplastic and multinucleated atypical lipoblastic cells
ANCILLARY TESTS
Immunohistochemistry
Mature adipocytes are S100 protein positive
Lipoblasts and atypical cells in well-differentiated lipoma-like liposarcoma and dedifferentiated liposarcoma are MDM2 and CDK4 positive
Cytogenetics
Supernumerary ring and giant marker chromosomes are seen in well-differentiated and dedifferentiated liposarcoma
Random and nonrandom telomeric association can also be seen in well-differentiated liposarcoma
Characteristic t(12;16)(q13;p11) is present in > 90% of myxoid and round cell liposarcomas
t(12;16) in myxoid/round cell liposarcoma leads to fusion of CHOP and FUS genes with generation of a FUS/DDIT3 hybrid protein
Variant chromosomal translocation t(12;22)(q13;q12) is also present in myxoid liposarcoma in which DDIT3 fuses with EWS
No distinctive cytogenetic markers have been observed in pleomorphic liposarcoma
Molecular Diagnostics
FISH for MDM2 shows consistent amplification in 12q14-15 in well-differentiated and dedifferentiated liposarcomas
Neighboring genes such as CDK4, SAS, and HMGIC can also be amplified in well-differentiated and dedifferentiated liposarcomas
12q14-15 amplification is not observed in benign tumors and may serve to distinguish well-differentiated liposarcoma from lipoma
FISH for detection of FUS/DDIT3 fusion product is helpful in confirming diagnosis of myxoid/round cell liposarcoma
Amplification of MDM2 can be observed in about 1/3 of pleomorphic liposarcomas
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Lipoma and Thymolipoma
Mediastinal lipomas are small and well-circumscribed, completely encapsulated lesions
Absence of areas of sclerosis, lipoblasts, floret-type multinucleated cells, or signet ring lipoblastic cells
Thymolipoma shows admixture of mature adipose tissue with entrapped involuted thymic remnants
Low-Grade Spindle Cell Tumors
May be difficult to distinguish from low-grade dedifferentiated liposarcoma
Low-grade dedifferentiated liposarcoma is positive for MDM2 or CDK4
Low-grade spindle cell sarcomas of mediastinum lack well-differentiated adipocytic component
Solitary fibrous tumors are positive for CD34 and Bcl-2
Schwannomas and neurofibromas are S100 protein(+)
Spindle cell thymomas are positive for cytokeratin
Leiomyomas and low-grade leiomyosarcomas are positive for desmin and smooth muscle actin
High-Grade Sarcomas
May be difficult to distinguish from high-grade dedifferentiated liposarcoma or pleomorphic liposarcoma
Nonlipogenic high-grade sarcomas lack lipoblastic cells or well-differentiated adipocytic components
Small Round Blue Cell Tumors
May be confused with round cell liposarcoma
Small round blue cell tumors (Ewing/PNET, small desmoplastic round blue cell tumor, neuroblastoma, rhabdomyosarcoma) usually lack myxoid stroma
Ewing/PNET are positive for CD99 (c-mic2)
Small desmoplastic round blue cell tumors are polyphenotypic (positive for vimentin, cytokeratin, desmin, synaptophysin, EMA, and other markers)
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree