|
Typical Clinical Features |
Microscopic Features |
Ancillary Investigations |
Fat necrosis |
No typical features
Can be encountered in normal fat and in neoplasms with fat |
Fat with necrosis and many foamy macrophages, some multinucleated |
CD68+ in macrophages |
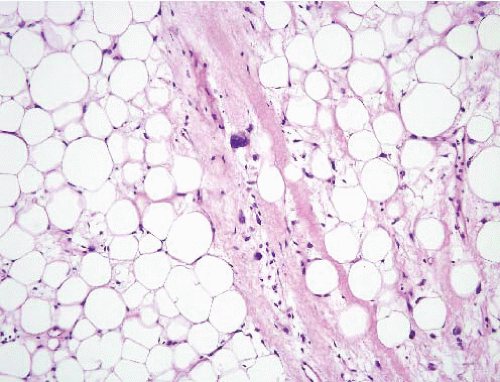
Fat atrophy |
Cachexia either from dieting, malignancy, or treatment for malignancy |
Lobulated fat with adipocyte shrinkage, capillaries appear more prominent |
Tumefactive extramedullary hematopoiesis |
Mass in patient with a myeloproliferative disorder, benign |
Trilinear hematopoiesis with erythroid hyperplasia and fat |
Lipoma with fat necrosis |
Usually superficial wellcircumscribed masses in adults (some intramuscular, rarely retroperitoneal) |
Has the appearance of mature fat
No hyperchomatic enlarged cells
Multinucleated histiocytes |
MDM2−, CDK4−, no MDM2 amplification, HMGA2 fusions |
Well-differentiated liposarcoma/atypical lipomatous tumor |
Deep tumors of adults >50 years |
Adipose tissue with scattered enlarged hyperchromatic nuclei, often found in fibrous septa |
MDM2+, CDK4+−, MDM2 amplification |
Spindle cell liposarcoma/fibrosarcoma-like lipomatous neoplasm |
Deep or superficial axial tissues of adults, possibly slight male predominance, favorable prognosis |
Spindle cells, primitive fat cells |
Lack of MDM2 amplification, lack of DDIT3 rearrangements, controversy concerning loss of RB protein |
Lymphedema in the morbidly obese |
Large subcutaneous-based mass in obese individuals, often with overlying skin changes |
Dilated lymphatic channels, edema, mildly atypical fibroblasts |
MDM2−, CDK4−, no MDM2 amplification, HMGA2 fusions |
Myxoid liposarcoma, low- and high-grade |
Deep soft tissues of extremities of young adults
Often metastasizes to other soft tissue sites as well as to lungs |
Monotonous small uniform rounded cells with abundant (low-grade) or minimal (highgrade) myxoid matrix
Rich network of delicate vessels becomes inconspicuous in high grade form
Lipoblasts |
S100 protein+ in some cases, DDIT3-TLS or DDIT3-EWS rearrangements |
Pleomorphic lipoma |
Superficial lesion of shoulder girdle, neck of middle-aged adults, M > F |
Same features as spindle cell lipoma with the addition of enlarged atypical multinucleated cells (“fleurette” cells) and lipoblasts |
CD34+, S100 protein+ in fat, abnormalities of 13q and 16q, MDM2−, CDK4−, no MDM2 amplification |
Chondroid lipoma |
Multiple anatomic sites, adults |
Lobulated lesion with fat, “bubbly” cells, chondroid matrix, lipoblasts, hypovascular |
S100 protein+, balanced translocation t(11;16)(q13;p12-13), C11orf95-MLK2 fusion |
Silicone granuloma |
Often in breast associated with ruptured implant |
Infiltrates between lobules and ducts, macrophages |
CD68+ |
Myelolipoma |
Usually in the adrenal gland of adults, F > M, association with obesity, hypertension, and diabetes |
Mixture of fat and trilinear hematopoiesis without erythroid hyperplasia |
t(3;21)(q25;p11) shown in one case |
Hibernoma |
Adults usually younger than 40 years (younger than patients with ordinary lipomas), thigh |
Lobulated lesion with prominent capillaries, varying amounts of mature fat cells, cells with fine vacuoles and cells with granular eosinophilic cytoplasm |
Abnormalities of chromosome 11q13 |
Lipoblastoma |
Proximal extremities of infants, benign |
Lobulated with mature fat and areas with lipoblasts and numerous capillaries (that can be indistinguishable from myxoid liposarcoma) |
Variable S100 protein+, amplification of PLAG1, rearrangements of HAS2 or COL1A2 |
Myxofibrosarcoma |
Superficial lesions in elderly adults |
Richly vascular myxoid lesion with pleomorphic cells |
None useful in differential diagnosis
Often CD34+, actin+ |
Extraskeletal myxoid chondrosarcoma |
Deep soft tissues of extremities, slight male predominance |
Uniform rounded cells with eosinophilic cytoplasm in hypovascular myxoid background |
S100 protein+, synaptophysin+, EWS-NR4A3 rearrangement |
Pleomorphic liposarcoma |
Deep soft tissue lesions in adults >50 years |
Pleomorphic lipoblasts in background that is either undifferentiated, epithelioid, or myxoid |
Can be CD34+, actin+, desmin+, focal S100 protein+
MDM2−, CDK4− |
Dedifferentiated liposarcoma |
Deep tumors of adults >50 years, typically retroperitoneal |
Areas of atypical lipomatous tumor/well-differentiated liposarcoma and juxtaposed zones of pleomorphic undifferentiated sarcoma |
MDM2+, CDK4+/−, MDM2 amplification |
Pleomorphic rhabdomyosarcoma |
Deep neoplasms in adults >50 years, usually proximal thigh |
Pleomorphic spindle cell neoplasm with cells with markedly eosinophilic cytoplasm |
Desmin+, myogenin+ (nuclear), MyoD1+ (nuclear) |
Pleomorphic undifferentiated sarcoma (malignant fibrous histiocytoma) |
Deep neoplasms in adults >50 years, usually proximal thigh |
Pleomorphic spindle cell neoplasm, often with storiform pattern |
Variable actin, desmin, MyoD1−, MDM2−, CDK4− |
Pleomorphic leiomyosarcoma |
Adults >50 years, deep extremities |
Defined as pleomorphic zones comprising two-thirds of the tumor, typical leiomyosarcoma in the remainder with fascicles of brightly eosinophilic cells with blunt-ended nuclei and paranuclear vacuoles |
Actin+, desmin+, calponin+, caldesmon+, myogenin−, MyoD1−, focal keratin in some cases |