Klebsiella Pneumonia
Key Facts
Terminology
Synonym
Friedlander pneumonia
Definition
Infectious condition caused by Gram-negative bacteria
Etiology/Pathogenesis
Klebsiella pneumoniae
Nonmotile, usually encapsulated bacillus
> 80 different types
Clinical Issues
Klebsiella pneumonia appears to be more common in
Hospitalized patients
Nursing homes
Alcoholics
Diabetics
Individuals with poor hygiene
Presentation
Fever
Cough
Hemoptysis
Chest pain
Malaise
Weight loss
Prognosis
Depends on setting in which illness occurs
May be fatal in 20-60% of patients
Treatment
Antibiotics
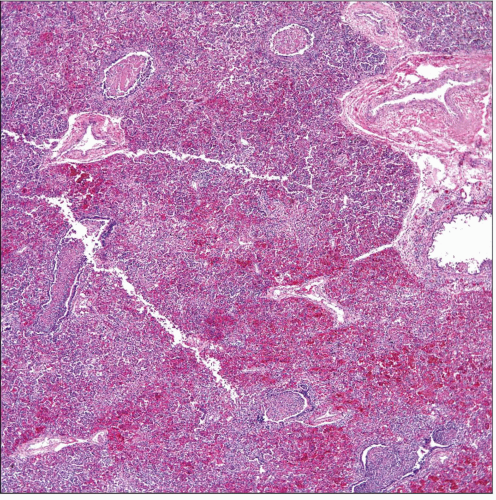 Low-power view of a section of lung parenchyma shows extensive areas of congestion and inflammation. Note the absence of alveolated tissue. |
TERMINOLOGY
Synonyms
Friedlander pneumonia
Definitions
Infectious condition caused by Gram-negative bacteria
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Infectious Agents
Klebsiella pneumoniae
Nonmotile, usually encapsulated bacillus
> 80 different types
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Klebsiella pneumonia appears to be more common in
Hospitalized patients
Nursing homes
Alcoholics
Diabetic patients
Individuals with poor oral hygiene
Age
More common in adults
Gender
No gender predilection
Ethnicity
No ethnic predisposition
Site
Posterior segment of the right upper lobe is more commonly affected
Presentation
Fever
Cough
Hemoptysis
Chest pain
Malaise
Weight loss
Laboratory Tests
Leukocytosis
Increased erythrocyte sedimentation rate
Cultures positive for Gram-negative bacilli
Treatment
Drugs
Antibiotics
Prognosis
Depends on setting in which illness occurs
May be fatal in 20-60% of patients
IMAGE FINDINGS
Radiographic Findings
Bilateral multifocal consolidations or cavitations
MACROSCOPIC FEATURES
General Features
Necrosis
Hemorrhage
Abscess formation
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
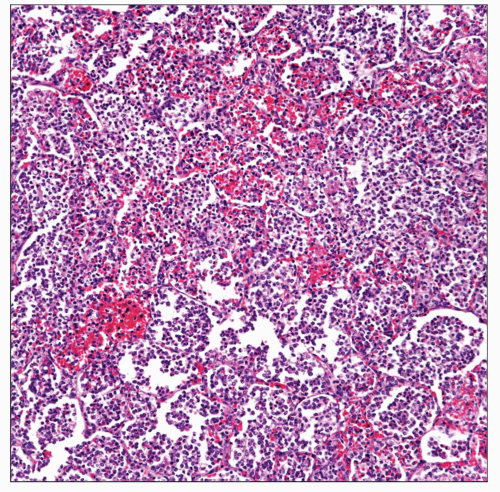
Histologic Features
Cytologic Features
Consolidation with acute inflammation
Cavitation
Abscess formation
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Bacterial Pneumonia
Gram stain distinguishes Gram-positive from Gram-negative pneumonia
Bacterial cultures help in identifying Klebsiella
Mucicarminophilic exudate appears to be more common in Klebsiella pneumonia
Pulmonary Tuberculosis
Although tuberculosis may show areas of cavitation, Gram stain is negative
Tuberculosis stains positive for acid-fast bacilli
Tuberculosis shows specific culture results