Kidney: Evaluation of Allograft Prior to Transplantation
SURGICAL/CLINICAL CONSIDERATIONS
Goal of Consultation
Determine if a cadaveric donor kidney is suitable for transplantation
Biopsy performed prior to implantation and evaluated by frozen section
Suitability of a kidney depends on the following
Pathologic features predictive of adequate renal function
˜ 40% of kidneys considered for transplantation under expanded criteria are rejected
Donor renal disease
Patients may not have been evaluated for renal disease prior to death
Donor neoplastic disease
Any suspicious focal lesions are biopsied
Implantation biopsy, zero-hour biopsy
Biopsy performed just after or just prior to implantation and evaluated on permanent sections
Used in clinical trials to determine baseline histologic features and any subclinical renal disease in donor kidney
Evaluate for evidence of antibody-mediated injury in presensitized recipient
Evaluate for evidence of donor disease in living donor (e.g., thin glomerular basement membrane nephropathy)
May be performed on either deceased or living donor kidneys
Change in Patient Management
Kidney will not be used for transplantation if determined to be unsuitable
Clinical Setting
Clinical criteria are used to select kidneys most likely to become functional allografts
Standard criteria donors (SCDs)
Donors not defined as expanded criteria donors
Expanded criteria donors (ECD)
All donors age > 60 years
Donors age 50-60 years and at least 2 of the following
Death from cerebrovascular accident
Hypertension
Serum creatinine (Cr) > 1.5 mg/dL
Increased risk of graft failure (relative hazard ratio: 1.70) and delayed graft function compared to SCD kidneys
Survival benefit for recipients of ECD kidneys compared to continued dialysis
Kidney Acceptance Criteria
Judgment of clinician based on pathology report and patient characteristics
Older patients or highly sensitized patients may benefit from kidney transplantation even if kidney is considered marginal
No absolute cutoff has been established for any pathologic criteria
Risk of overestimating damage and discarding useful kidneys
Double transplants are possible
2nd kidney transplant is performed if 1st graft function is suboptimal
SPECIMEN EVALUATION
Gross
Specimens are usually provided by the transplant team
Usually small wedge biopsies but can be a needle biopsy
Frozen Section
Entire specimen is used for frozen section
MOST COMMON DIAGNOSES
Preimplantation Biopsy
Sample adequacy
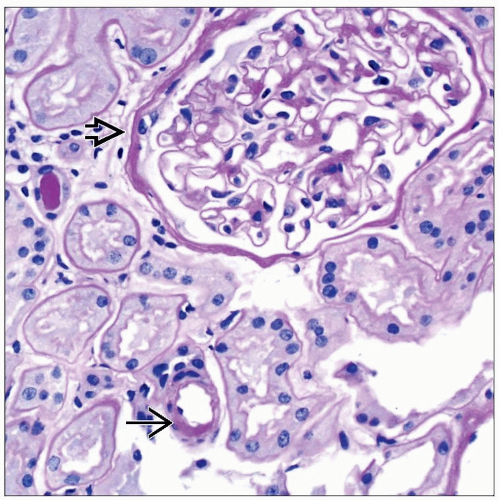
On donor biopsy, at least 25 glomeruli should be present, including from deep cortex
At least 2 arteries should be present
Some degree of chronic changes are present in many biopsies
Usually increase with donor age
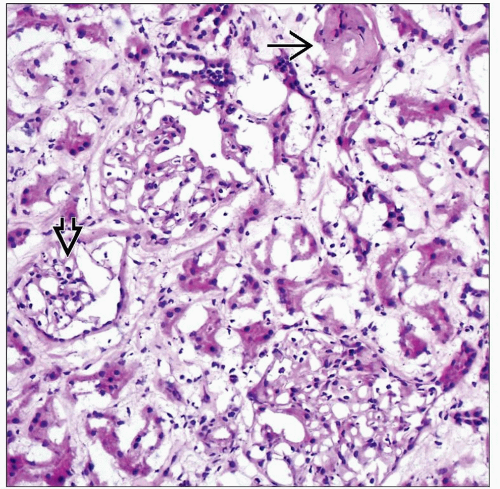
Percentage of globally sclerotic glomeruli important (global glomerulosclerosis)
If > 20% globally sclerotic glomeruli, higher incidence of delayed graft function (DGF) requiring transient dialysis, higher Cr at 3-24 months, variable effect on graft survival
> 20% global glomerulosclerosis has minimal effect on 1-year graft survival and only if donor Cr clearance is ≤ 80 mL/min (83% vs. 79%)
No absolute cutoff point for percent of global glomerulosclerosis has been determined
Sclerotic glomeruli are predominately in subcapsular cortex in arteriosclerosis and often overestimated in wedge biopsies
Strong correlation with age
Arteriosclerosis
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree