Kaposi Sarcoma
Key Facts
Etiology/Pathogenesis
Commonly associated with HIV infection in patients with AIDS
Associated with human herpes virus 8 (HHV-8) infection
Clinical Issues
High incidence in homosexual men and intravenous drug abusers with AIDS
May also affect immunosuppressed patients and transplant patients
Cough
Dyspnea
Hemoptysis
20-40 years of age
Image Findings
Bilateral interstitial infiltrates with ill-defined nodularity
Discrete, localized intraparenchymatous mass that may be associated with a bronchus
Microscopic Pathology
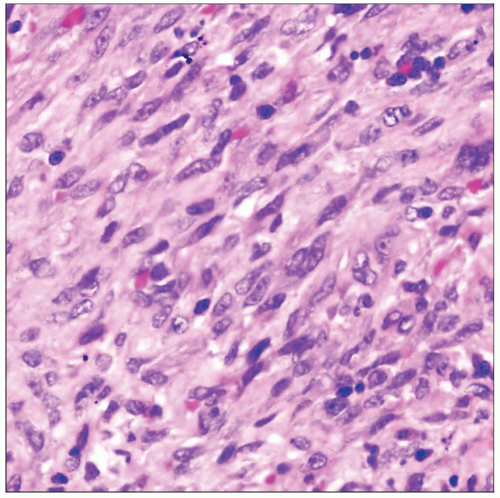
Monotonous spindle cell proliferation with fascicular growth pattern intersecting at right angles
Frequent anastomosing and slit-like vascular spaces containing abundant extravasated red blood cells
Spindle cells show mild to moderate cytologic atypia
Ancillary Tests
Spindle tumor cells are positive for CD34 and CD31
Tumor cells show strong nuclear positivity for HHV8 antibody
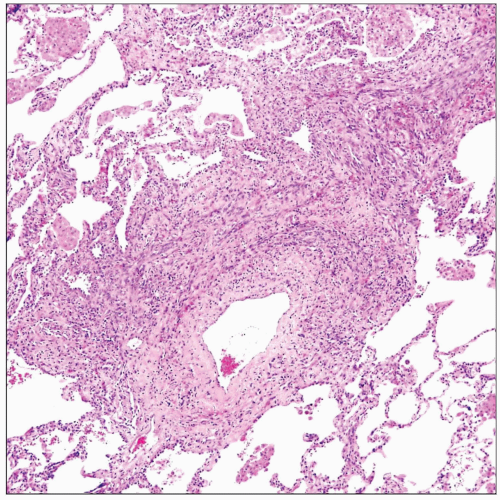 Scanning magnification in pulmonary involvement by Kaposi sarcoma shows characteristic perivascular distribution of the atypical spindle cell proliferation extending into adjoining alveolar septa. |
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Kaposi sarcoma (KS)
Definitions
Low-grade spindle cell sarcoma derived from vascular endothelial cells
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Pathogenesis
Commonly associated with HIV infection in patients with AIDS
Associated with human herpes virus 8 (HHV-8) infection
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
High incidence in homosexual men and intravenous drug abusers with AIDS
May also affect immunosuppressed patients and transplant patients
Age
20-40 years of age
Presentation
Cough
Dyspnea
Hemoptysis
Treatment
Adjuvant therapy
Combination chemotherapy (doxorubicin, bleomycin, and vincristine)
Radiation
Only used for palliation in advanced cases
Antiviral compounds
Zidovudine, interferon, and other antiviral compounds
Prognosis
Poor prognosis; most patients die within 2 years of diagnosis
Median survival is slightly better for responders to chemotherapy
IMAGE FINDINGS
General Features
Bilateral interstitial infiltrates with ill-defined nodularity
Discrete, localized intraparenchymatous mass that may be associated with a bronchus
Mediastinal lymphadenopathy
Bilateral pleural effusion
MACROSCOPIC FEATURES
General Features
Ill-defined, bluish-red intraparenchymatous nodules
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree