Inclusion Body Fibromatosis
Elizabeth A. Montgomery, MD
Key Facts
Terminology
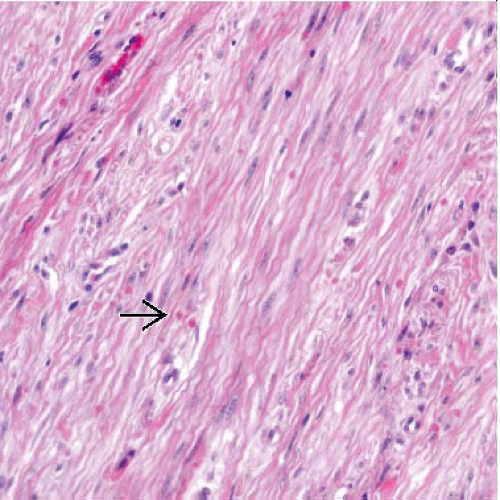
Nodular proliferation of benign fibroblastic and myofibroblastic cells with characteristic intracytoplasmic eosinophilic spherical inclusions
Clinical Issues
Broad-based or dome-shaped, nontender nodule over dorsal or lateral aspect of digits
Present in 1st 3 years of life
˜ 1/3 are congenital
Extradigital presentation in soft tissue is rare
Excellent overall prognosis
Tendency for local recurrence (60-75% of cases)
No evidence of aggressive behavior, metastatic potential, or malignant transformation
Observation recommended in absence of deformity and impairment
Macroscopic Features
Nodular firm mass covered by intact skin
Rarely exceeds 2 cm in diameter
Microscopic Pathology
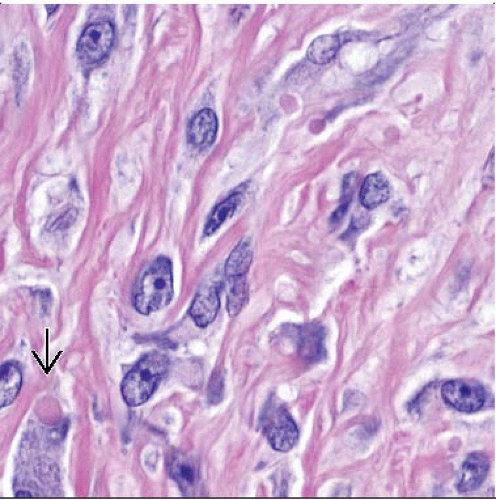
Sheets and fascicles of uniform myofibroblastic cells with intracytoplasmic eosinophilic spherical inclusions
Inclusions often perinuclear and stain bright red with Masson trichrome
Dense collagenous stroma
Overlying epidermis is often acanthotic with loss of rete ridges
Ancillary Tests
Masson trichrome
Inclusions stain bright red
TERMINOLOGY
Synonyms
Infantile digital fibromatosis
Digital fibrous tumor of childhood
Infantile digital fibroma
Reye tumor
Definitions
Nodular proliferation of benign fibroblastic and myofibroblastic cells with characteristic intracytoplasmic eosinophilic spherical inclusions
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Age
Present in 1st 3 years of life
˜ 1/3 are congenital
Site
Typically located over dorsal or lateral aspect of digits
Principle involvement of 2nd-5th digits
Thumb and great toe typically spared
Extradigital presentation in soft tissue is rare
Presentation
Broad-based or dome-shaped nodule
Nontender
Overlying skin is firm, stretched, and erythematous
Up to 2 cm in diameter
Functional impairment or deformity may be present
Natural History
12% of cases spontaneously involute over 2-3 years
Treatment
Options, risks, complications
Observation recommended in absence of deformity and impairment
Spontaneous involution reported
Surgical approaches
Complete surgical excision
60-75% of cases recur upon excision
Lower recurrence rates reported with wider surgical excisions
Surgical excision recommended with
Functional impairment
Continued growth
Cosmetic concerns
Removal by Mohs micrographic surgery without recurrence reported
Prognosis
Excellent overall prognosis
Tendency for local recurrence
60-75% of cases
No evidence of
Aggressive behavior
Metastatic potential
Malignant transformation
MACROSCOPIC FEATURES
General Features
Nodular firm mass covered by intact skin
Size
Rarely exceeds 2 cm in diameter
Range of 0.3-3.5 cm reported in large series
Median size = 1 cm
Gross Features
Solid, gray-white, cut surface
Lacks hemorrhage
Lacks necrosis
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree