Impetigo
Irina Margaritescu, MD, DipRCPath
Bruce R. Smoller, MD
Key Facts
Terminology
Definition
Acute, contagious superficial pyogenic infection of skin caused by staphylococci, streptococci, or both
Clinical Issues
Epidemiology
Peak incidence during summer and fall
Children affected most commonly
Face and extremities usually involved
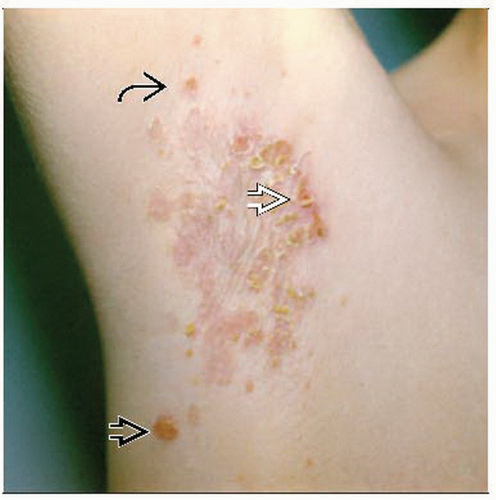
Non-bullous impetigo
Thin-walled vesicles on an erythematous base that rupture rapidly, forming honey-colored crusts
Bullous impetigo
Flaccid blisters and tender shallow erosions
Typically resolves with topical and oral antibiotics
Microscopic Pathology
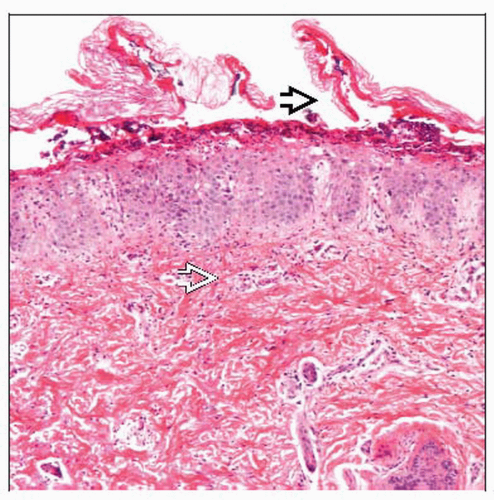
Non-bullous impetigo
Subcorneal pustule with a few acantholytic cells
Gram-positive cocci sometimes found in pustule or scale crust
Moderate superficial perivascular and interstitial mixed-cell infiltrate
Bullous impetigo
Subcorneal blister with a few neutrophils and some acantholytic cells
Rare or absent cocci
Sparse superficial perivascular inflammatory infiltrate
Ancillary Tests
Gram stain reveals gram-positive cocci
TERMINOLOGY
Synonyms
Pyoderma
Non-bullous impetigo
Impetigo contagiosa of Tilbury-Fox
Definitions
Acute, contagious, superficial pyogenic infection of skin caused by staphylococci, streptococci, or both
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Infectious Agents
Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus)
Gram-positive, nonmotile, non-spore-forming, catalase-positive cocci
Produce extracellular exfoliative exotoxins (exfoliatin A and B)
Streptococcus pyogenes (S. pyogenes)
a.k.a. group A β-hemolytic streptococci (GABHS)
Gram-positive, nonmotile, chain-forming, non-spore-forming, oxidase- and catalase-negative cocci
Pathogenesis
Staphylococcal pyodermas
Occur in individuals who are carriers of organism in axillary, inguinal, and perianal areas and anterior nares
Predisposing conditions include atopic dermatitis, diabetes mellitus, dialysis, intravenous drug use, and HIV infection
Insect bites, dermatophytoses, herpetic infections, varicella, abrasions, lacerations, and thermal burns also contribute to pathogenesis
Group A streptococcal pyodermas
Occur following colonization of skin from skin of another individual or from patient’s nasopharynx
Non-bullous impetigo
Currently S. aureus is prominent pathogen responsible for nonbullous impetigo
Accounts for 50-60% of cases
In past, S.aureus and S. pyogenes occurred with equal frequency
20-45% of cases are due to combination of S. aureus and S. pyogenes
S. pyogenes is still most common cause in developing countries
Bullous impetigo
Causative agent is gram-positive, coagulase-positive, group II S. aureus, most often phage type 71
S. aureus exotoxins cause loss of cell adhesion in superficial dermis, producing blisters in granular cell layer of epidermis
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree