Immunocytochemistry, Histochemistry, and Other Ancillary Techniques
Donna M. Coffey, MD
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Immunocytochemistry (ICC)
Immunohistochemistry (IHC)
In situ hybridization (ISH)
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR)
Flow cytometry (FC)
USE OF ANCILLARY STUDIES IN BODY FLUID SPECIMENS
Cell Block Preparations
If malignancy is suspected, histochemical, ICC, and other ancillary techniques can be performed on cell blocks to increase diagnostic accuracy
Histochemical stains and ICC can be done on cell blocks because multiple duplicate slides can be obtained
Other tests that can be performed on cell block include ISH and PCR
In addition, cell blocks show architectural features of tissue fragments, which can be compared with histopathologic sections
Sensitivity increases to 83-85% when ≥ 2 preparation methods are utilized (e.g., cytocentrifuge and cell block)
Traditionally, cell blocks are prepared from cell pellet using plasma thrombin clot or HistoGel method
ICC and molecular testing can also be performed utilizing Cellient cell blocks
INDICATIONS FOR HISTOCHEMICAL STAINS IN BODY FLUIDS
DDx of Reactive Mesothelial Cells/Mesotheliomas From Adenocarcinoma
Reactive mesothelial cells can have significant cytologic atypia and thus mimic carcinomas
Atypical features with intracytoplasmic vacuoles
Simulate signet ring adenocarcinoma
Malignant mesotheliomas can present as 3D clusters and papillary groups that simulate carcinomas
Histochemical stains that aid in DDx include mucicarmine stain and PAS diastase
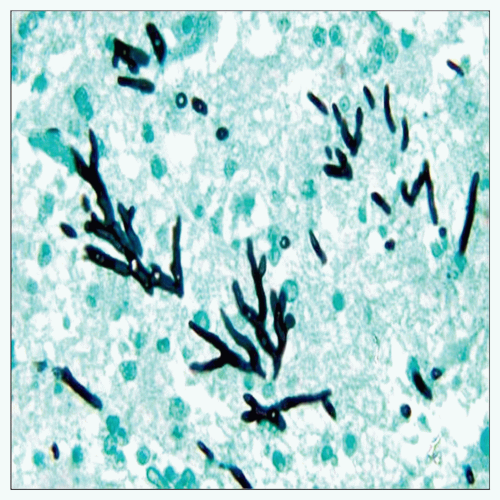
Detection of Infectious Organisms
GMS, AFB, Fite, and mucicarmine stains are some of the histochemical stains that can be used to detect mycobacterial or fungal organisms
ICC stains and molecular testing can be utilized to detect viral organisms
INDICATIONS FOR IHC STAINS IN BODY FLUIDS
DDx of Reactive Mesothelial Cells/Mesothelioma From Adenocarcinoma
Highly cellular specimens with atypical cytologic features can mimic adenocarcinoma
If malignancy is suspected, cell block is prepared to perform a panel of ICC stains
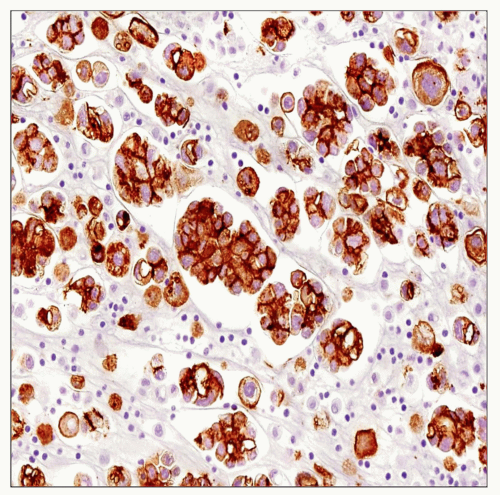
ICC is the most widely used ancillary method and has been shown to increase overall diagnostic accuracy
It is necessary to correlate cytomorphology with clinical history and radiologic findings to select the most appropriate ICC stains
Panel of ICC must include > 1 mesothelial and > 1 carcinoma markers
Some ICC are expressed in both mesothelial and epithelial cells
CK7, AE1/AE3, and EMA are expressed in both benign or malignant mesothelial cells and lung adenocarcinomas
AE1/AE3, CK5/6, and EMA are positive in both mesothelioma/reactive mesothelial cells and squamous cell carcinomas of lung
WT1 is expressed in peritoneal mesothelial cells and serous neoplasms of ovary
Determine Primary Site of Malignancy
ICC stains are helpful in determining possible primary site, especially in patients with occult primary and in patients with history of multiple primary malignancies
Consider cytomorphology, site of effusion, gender, and clinical history in order to perform most specific markers
General adenocarcinoma markers coupled with more specific markers are often helpful
Breast carcinomas: BRST2, mammaglobin, CK7
ER, PR, and HER2/neu can be used for diagnosis, prognostic/therapeutic considerations
Adenocarcinomas of lung: TTF-1, NAPSIN-A, CK7
Colon: CK20, CDX2, villin
Gastric: CK7, CDX2
Ovarian or peritoneal primary: pax-8, CA125, WT1
Renal cell carcinoma: pax-8, pax-2, CD10, RCC
Small cell carcinomas: CD56, TTF-1, synaptophysin
Melanoma: S100, Melan-A, HMB-45
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree