Idiopathic Sclerosing Mediastinitis
Key Facts
Etiology/Pathogenesis
Most cases are idiopathic
May be result of healed infection, such as tuberculosis or toxoplasmosis
May represent end stage of burned-out neoplasms, such as Hodgkin lymphoma or seminoma
May be secondary to autoimmune disorders, sarcoidosis, rheumatic fever, or drugs (e.g., methysergide)
Some cases thought to represent abnormal immune response due to delayed hypersensitivity reaction to infectious agents in susceptible individuals
Clinical Issues
Mediastinal mass or widening of mediastinum on chest x-ray and CT scan
Can show calcifications on imaging studies
Extensive subcarinal involvement most likely to lead to death due to encroachment of vital structures
Chronic course; may be self-limiting and regress spontaneously or progress to death due to respiratory compromise
Microscopic Pathology
Stage I: Edematous fibromyxoid tissue with fibroblastic spindle cells, eosinophils, mast cells, lymphocytes, plasma cells, and thin-walled blood vessels
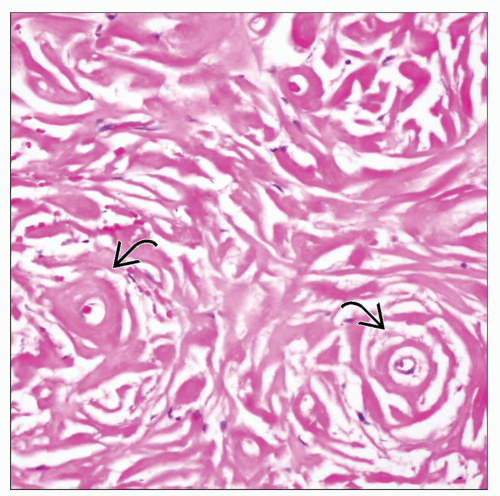
Stage II: Thick bands of dense collagen haphazardly distributed and containing scattered fibroblastic spindle cells, lymphocytes, and plasma cells
Stage III: Dense acellular collagen with scattered lymphoid follicles and occasional dystrophic calcifications
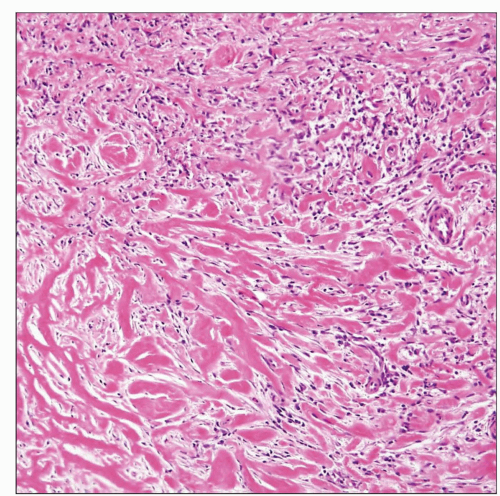 Histologic appearance of idiopathic sclerosing mediastinitis shows thick bands of keloidal collagen arranged in haphazard distribution (bottom) admixed with scattered inflammatory cells. |
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Idiopathic sclerosing mediastinitis (ISM)
Synonyms
Idiopathic fibroinflammatory lesion
Sclerosing mediastinitis
Inflammatory pseudotumor
Definitions
Chronic condition characterized by fibrous replacement of soft tissues in mediastinum, ± inflammation, of unknown etiology
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Pathogenesis
Most cases are idiopathic
May be result of healed infection, such as tuberculosis or toxoplasmosis
May represent the end stage of burned-out neoplasms, such as Hodgkin lymphoma or seminoma
May be secondary to autoimmune disorders, sarcoidosis, rheumatic fever, or drugs (e.g., methysergide)
Some cases thought to represent abnormal immune response due to delayed hypersensitivity reaction to infectious agents in susceptible individuals
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Age
Most often involves young individuals between 20-30 years of age
Gender
Slight female predilection
Ethnicity
Slight increase in African-Americans
Presentation
Cough
Shortness of breath
Fever
Superior vena cava syndrome in rare instances
Mediastinal mass or widening of mediastinum on chest x-ray and CT scan
Can show calcifications on imaging studies
Location can be in hilum, subcarinal, paratracheal, or anterior mediastinum
Treatment
Steroids
Surgery difficult and generally of limited benefit
Favorable response to antifungal agents has been observed in some cases
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree