Histoplasmosis
Joseph Misdraji, MD
Key Facts
Etiology/Pathogenesis
H. capsulatum: Dimorphic fungus found in soil contaminated with bird or bat droppings
Clinical Issues
Endemic in Ohio and Mississippi River valleys
Disseminated infection is more likely in infants, AIDS patients with CD4 count below 150 cells per µL, patients on steroids or immunosuppressive drugs, or with TNF antagonists
Adrenal insufficiency is more common in disseminated histoplasmosis than with other fungal infections
Fungal culture of tissue or blood
Antibody assays include complement fixation and immunodiffusion assays
Antigen detection assays include enzyme immunoassay in urine, serum, or other body fluids
Microscopic Pathology
Portal and lobular lymphohistiocytic inflammation
Discrete granulomas in portal and lobular regions
Large numbers of yeast organisms in macrophages
Might have limited or no inflammatory response
Yeast are 2-4 µm, oval, with narrow-based budding
Ancillary Tests
GMS and PAS-diastase positive
Top Differential Diagnoses
Sarcoidosis: Similar epithelioid discrete granulomas
Leishmaniasis: Kinetoplast and GMS negative
Candidiasis: Larger yeast, more budding
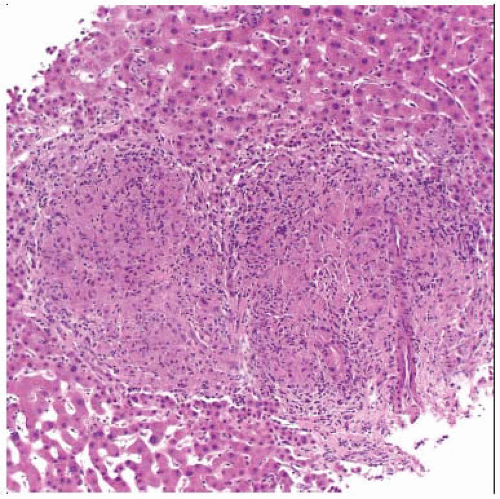 Liver biopsy in a patient with disseminated histoplasmosis shows large, coalescent, loosely formed granulomas. |
TERMINOLOGY
Definitions
Infection by fungus Histoplasma capsulatum
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Infectious Agents
H. capsulatum: Dimorphic fungus that exists as mycelial form at room temperature and as yeast form at body temperature
Found in soil, particularly when contaminated with bird or bat droppings
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Endemic in Ohio, Missouri, and Mississippi River valleys, Central and South America, and parts of eastern United States, southern Europe, Africa, and southeastern Asia
Outbreaks associated with demolition of buildings, moving soil, and spelunking
Disseminated histoplasmosis occurs in approximately 55% of infected immunocompromised patients and 4% of infected immunocompetent patients
Site
Liver is involved in up to 90% of cases of disseminated histoplasmosis
Presentation
Symptomatic acute disseminated infection
Occurs in immunosuppressed patients
Common symptoms include chills, fever, anorexia, weight loss, mucous membrane ulcers, and skin lesions
Hepatosplenomegaly and elevated liver enzymes, especially alkaline phosphatase
Chronic progressive disseminated histoplasmosis
Occurs in older patients without immunosuppression who are unable to control organism
Fever, night sweats, weight loss, fatigues, and oral ulcers are common
Adrenal insufficiency with destruction of adrenal glands
Can present as reactivation years after initial exposure and outside endemic area if cell-mediated immunity is compromised
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree