Hidradenoma
Christine J. Ko, MD
Key Facts
Clinical Issues
Solitary dermal nodule
Microscopic Pathology
May be primarily composed of solid areas, cystic areas, or both
Classically does not connect to epidermis and is deep-seated
Solid areas composed of varying proportion of
Clear cells
Poroid cells
Squamoid cells
Rarely mucinous cells
Ducts with eosinophilic cuticles present in solid areas
Cystic areas lined by cuboidal cells, sometimes with evidence of decapitation secretion
Stroma between solid islands &/or cystic areas is prominently hyalinized
Well circumscribed
Necrosis usually absent
Prominent cytologic atypia not present
Mitoses not numerous
Top Differential Diagnoses
Metastatic renal cell carcinoma
Other clear cell tumors
Basal cell carcinoma
Squamous cell carcinoma
Other adnexal tumors
Lymphadenoma
Sebaceous adenoma
Cystadenoma
TERMINOLOGY
Synonyms
Clear cell hidradenoma, nodular hidradenoma, solid-cystic hidradenoma, cystic hidradenoma, eccrine acrospiroma, eccrine sweat gland adenoma, clear cell myoepithelioma, poroid hidradenoma, apocrine hidradenoma
Definitions
Benign tumor showing apocrine or eccrine differentiation
CLINICAL ISSUES
Presentation
Solitary dermal nodule
Treatment
Excision is generally curative
Prognosis
Benign
Low malignant potential; may rarely transform to hidradenocarcinoma
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
Histologic Features
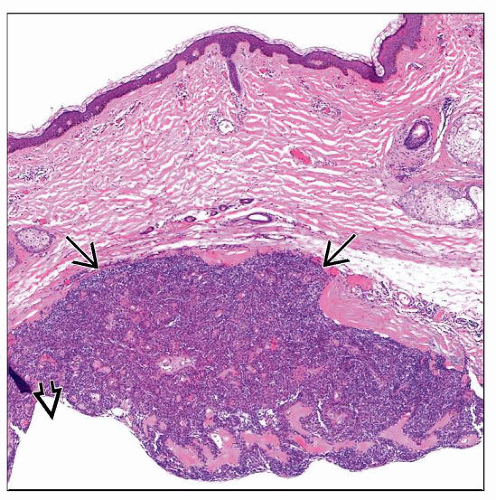
Well-circumscribed dermal-based tumor
Classically does not connect to epidermis and is deep-seated
May be primarily composed of solid areas, or cystic areas, or both
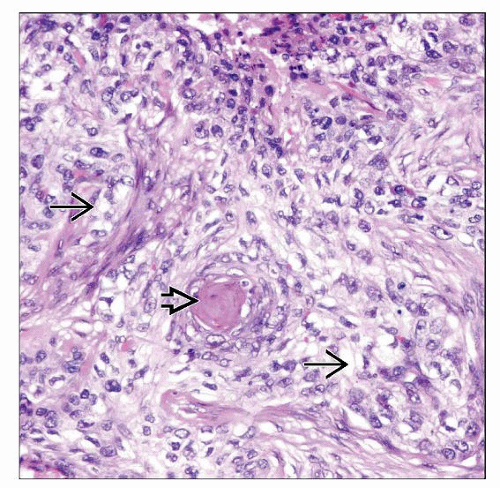
Solid areas composed of varying proportion of clear cells, poroid cells, squamoid cells, and rarely mucinous cells
Ducts with eosinophilic cuticles present in solid areas
Cystic areas lined by cuboidal cells, sometimes with evidence of decapitation secretion
Stroma between solid islands &/or cystic areas is prominently hyalinized appearing
Prominent cytologic atypia not present
Mitoses can be present, but usually not numerous
Necrosis usually absent
Generally does not show infiltrative pattern
Cytologic Features
Variable cell composition
Clear cells
Clear cytoplasm
Nuclei oval to round with small nucleoli
Contain glycogen and are PAS positive (diastase-sensitive)
Squamoid cells
Resemble keratinocytes with eosinophilic cytoplasm and well-demarcated cytoplasmic borders
Poroid cells
Basaloid cells with little cytoplasm
Nuclei have blue outlines and single nucleoli or occasionally multiple small nucleoli
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma
Composed of clear cells arranged in variably sized islands
Vascular pattern may be prominent
Often extravasated erythrocytes numerous
Generally does not show cystic areas
More commonly CD10 and EMA positive
Positive with renal cell carcinoma antigen (RCA)
Hidradenocarcinoma
Cellular, atypical nodular dermal-based tumor
Shows greater cytologic atypia and mitotic figures and often has infiltrative features
Clear Cell Basal Cell Carcinoma
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree