Hepatitis C
Kusa Terianm, MD
Key Facts
Terminology
Hepatitis, usually chronic, secondary to hepatitis C virus infection
Clinical Issues
Liver biopsy is performed to grade and stage disease and exclude other liver diseases
Grade indicates degree of necroinflammatory activity
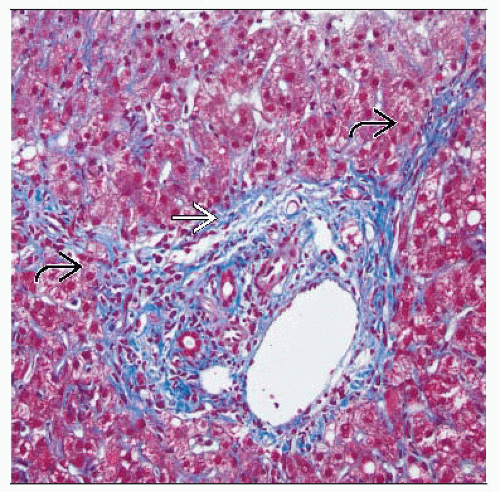
Stage indicates extent of fibrosis
Standard therapy is pegylated interferon-α in combination with ribavirin
Chronic HCV is slowly progressive disease, ultimately leading to cirrhosis, liver failure, and risk of hepatocellular carcinoma
Microscopic Pathology
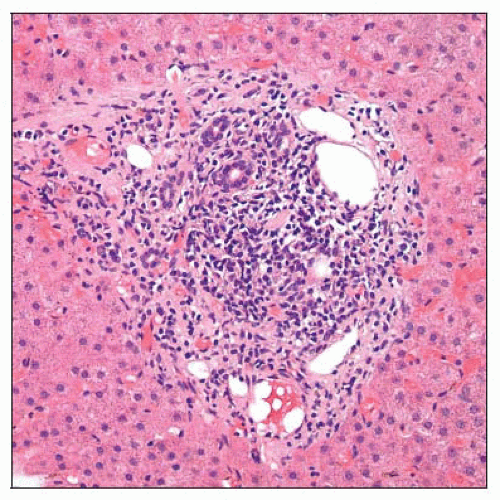
Variably dense portal inflammatory cell infiltrates composed mostly of lymphocytes
Periportal interface activity usually present but tends to be relatively mild
Scattered lobular collections of inflammatory cells with or without acidophil bodies
Progressive fibrosis begins in portal areas and extends outward in stellate fashion
Top Differential Diagnoses
HCV enters differential diagnosis for many forms of portal hepatitis
Can be confirmed or excluded by laboratory testing for hepatitis C antibodies (anti-HCV) or viral RNA
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Hepatitis C virus infection (HCV)
Definitions
Hepatitis, usually chronic, secondary to hepatitis C virus infection
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Infectious Agents
Enveloped, single-stranded RNA virus of Flaviviridae family
Positive-sense RNA encodes a single polypeptide
Polypeptide post-translationally cleaved to form structural, nonstructural, and envelope proteins
Inherent high mutation rate generates viral heterogeneity
6 viral genotypes and over 50 subtypes
Vary in geography, mode of transmission, and response to treatment
Modes of Transmission
Blood transfusion
Needlestick inoculation
Perinatal exposure probably occurs with low efficiency
Efficiency of sexual transmission is controversial but probably low
Pathogenesis
Virus is directly cytopathic and induces immunemediated cellular injury
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Worldwide seroprevalence of HCV antibodies (anti-HCV) estimated at 3%
Estimated 3-4 million persons infected in United States
Presentation
Fatigue
Nausea and anorexia
Depression and difficulty concentrating
May be asymptomatic
Laboratory Tests
Antibodies (anti-HCV) indicate exposure
Detection of HCV RNA indicates virus persistence
Liver biopsy performed to grade and stage disease and exclude other liver diseases
Natural History
Acute infection is often subclinical
Fulminant hepatitis is rare
Produces persistent (chronic) infection in 85% of infected persons
Defined as failure to clear virus in 6 months
Remaining 15% have self-limited infection
Treatment
Drugs
Standard therapy is pegylated interferon-α in combination with ribavirin