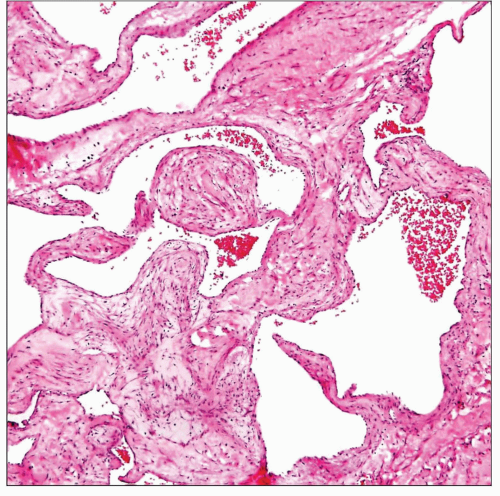
Hemangioma
Key Facts
Clinical Issues
Rare tumor
Affects broad age range, from newborns to old age
More frequent in children and young adults
Anterior and posterior mediastinum
Some cases may be diffuse and multifocal (hemangiomatosis)
Dyspnea
Cough
Chest pain
Benign lesions that usually produce symptoms through compression
Rarely invasive, but unencapsulated; may infiltrate mediastinal structures
Some cases may regress spontaneously
Most cases are cured by simple surgical excision
Microscopic Pathology
Capillary hemangiomas
Lobular growth pattern separated by thin fibroconnective tissue bands
Lobules composed of solid, cellular proliferation of endothelial cells with compressed vascular lumens
Rare mitotic figures can occasionally be found
Cavernous hemangiomas
Large, ectatic vessels filled with blood seen on scanning magnification
Stroma separating the vessels may contain prominent smooth muscle proliferation
Areas showing admixture of fibrosis, smooth muscle, and mature fat are commonly seen
Cellular proliferation can dissect focally into adjacent fibroadipose tissue
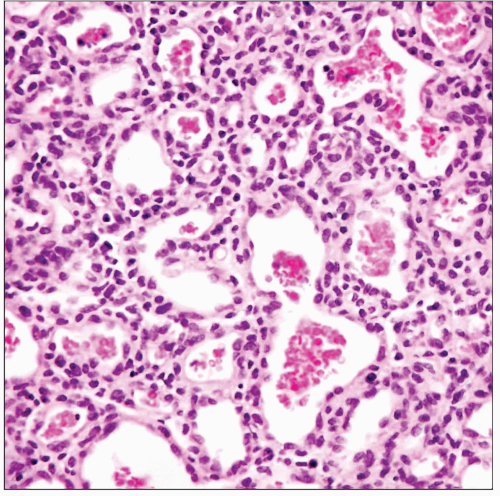 Capillary hemangioma of the mediastinum shows a tightly packed proliferation of small, capillary-sized vessels filled with red blood cells with little intervening stroma. |
TERMINOLOGY
Synonyms
Hemangiofibroma, angiomyoma, hemangiomyoma
Definitions
Benign neoplastic vascular proliferation
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Rare tumor
Age
Affects broad age range, from newborns to old age
More frequent in children and young adults
Gender
No gender predilection
Site
Anterior and posterior mediastinum
Some cases may be diffuse and multifocal (hemangiomatosis)
Presentation
Dyspnea
Cough
Chest pain
About 15% of patients may be asymptomatic, and lesion is discovered on routine chest x-ray
Incidental finding at autopsy
Natural History
Benign lesions that usually produce symptoms through compression
Rarely invasive, but unencapsulated; may infiltrate mediastinal structures
Some cases are associated with multiorgan, systemic involvement (hemangiomatosis)
Some cases may regress spontaneously
Treatment
Surgical excision
Sclerotherapy
Prognosis
Most cases are cured by simple surgical excision
Expectant approach may be warranted in children due to possibility of spontaneous regression
IMAGE FINDINGS
General Features
Location
Anterior mediastinum most common location
Posterior mediastinum in 1/4 of cases
Radiographic Findings
Smooth or lobulated mass with sharp borders
Phleboliths can be present in up to 10% of cases
MR Findings
T1 weighted images may show linear areas of high intensity from stromal fat
CT Findings
Often heterogeneous lesion with mixed attenuation
Phleboliths appear as small round or ring-like calcifications with central lucency
Central enhancement on CECT is very characteristic
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree