Ganglioneuroma
Key Facts
Terminology
Ganglioneuroma (GN)
Benign tumor of neural origin
Clinical Issues
Incidence
Tumor is more common in young patients
Location
More common in posterior mediastinum
Symptomatology
Chest pain
Horner syndrome
Shortness of breath
Neurofibromatosis
Treatment
Surgical resection
Prognosis
Good
Clinical features
Tumor is more common in younger patients
More common in posterior mediastinum
Shortness of breath
Symptoms
Shortness of breath
Chest pain
Horner syndrome
Neurofibromatosis
Top Differential Diagnoses
Schwannoma
Neurofibroma
Ganglioneuroblastoma
Solitary fibrous tumor
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Ganglioneuroma (GN)
Definitions
Benign tumor of neural origin
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Etiology
There is no definitive etiology for this neoplasm
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Unusual tumors representing a small percentage of mediastinal tumors
Age
More common in younger patients
Site
GN is more common in posterior mediastinum
Presentation
Shortness of breath
Chest pain
Horner syndrome
Neurofibromatosis
Treatment
Surgical approaches
Complete surgical resection
Prognosis
Good
MACROSCOPIC FEATURES
General Features
Well circumscribed and encapsulated
Firm, gray to yellowish
Cut surface shows whitish smooth or whorled appearance
Areas of necrosis and hemorrhage are generally absent
Size
Tumors vary in size from 1 cm to > 10 cm in greatest dimension
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
Histologic Features
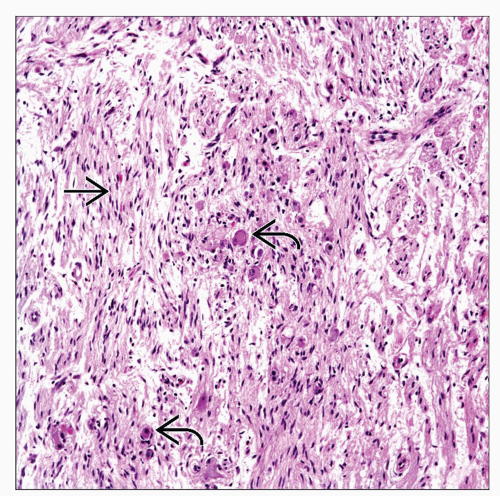
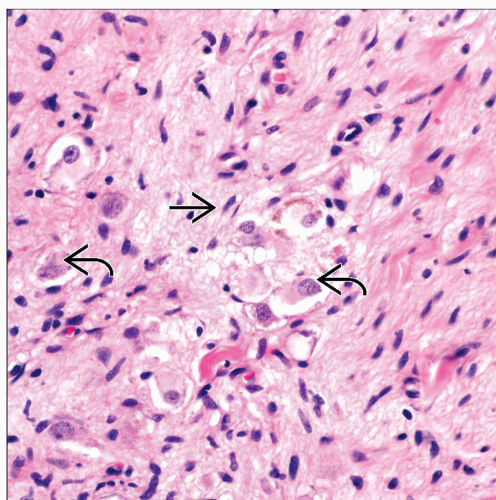
Mature ganglion cells embedded in loose fibrocollagenous or subtle spindle cell stroma
Proliferation of Schwann cells, nerve fibers, and ganglion cells
Nissl granules may be seen in some cases in ganglion cells
Cytologic Features
Mature ganglion cells
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Schwannoma
Classically shows Antoni A and B areas while these would be unusual in GN
It would be unusual for Schwannoma to show numerous ganglion cells
Neurofibroma
Spindle cell component of neurofibroma is similar to that of GN
Neurofibromas lack the presence of ganglion cells
Ganglioneuroblastoma
Shows neuroblastomatous component, which is absent in GN
Solitary Fibrous Tumor
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree