Fungal Infections, Blood and Bone Marrow Features
Mohammad A. Vasef, MD
Key Facts
Terminology
Disseminated fungal organisms detected by morphologic review or special stains or by culture
Etiology/Pathogenesis
Barrier disruption due to chemotherapy
Host defense impairment
Organ transplant recipients
Patients with AIDS/other immunodeficiency
Prolonged neutropenia of any cause
Environmental contamination
Prolonged usage of broad spectrum antibiotics
Central venous line
Corticosteroids or radiation therapy
Microscopic Pathology
Well-formed or ill-defined granulomas can be identified in bone marrow biopsy sections
Sheets of histiocytes with intracytoplasmic fungal organisms without granuloma formation in immunocompromised patients
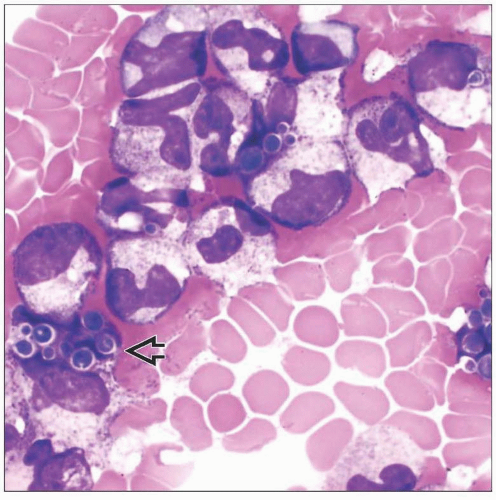
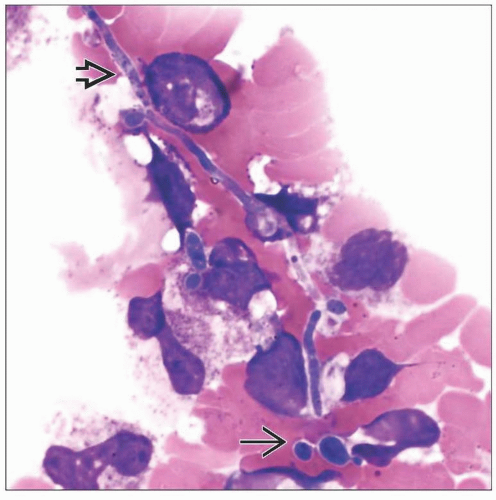
Fungal organisms are best detected on Wright-stained bone marrow aspirate smears
Special stains, including GMS &/or PAS, may be required for identification of organisms
Fungal organisms, such as Histoplasma and Candida, occasionally are seen as intracytoplasmic inclusions within neutrophils &/or monocytes in peripheral blood smears
Particularly in AIDS patients with low CD4 count
TERMINOLOGY
Synonyms
Systemic fungal infections
Definitions
Disseminated fungal organisms detected in blood or bone marrow morphologically or by special stains or via culture
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Pathogenesis
Host defense impairment
Patients at high risk for systemic fungal infections include
Bone marrow or organ transplant recipients
Patients with AIDS, human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), or other immunodeficiency-related states
Patients receiving potent chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or corticosteroids therapy
Other factors making patients susceptible to fungal infections
Prolonged neutropenia of any cause
Environmental contamination
Total parenteral nutrition
Prolonged use of broad spectrum antibiotics
Central venous catheters
Barrier disruption due to chemotherapy
CLINICAL ISSUES
Presentation
Fever of unknown origin in vast majority of patients
Prolonged neutropenia
Bone marrow or solid organ transplantation
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection
Radiation therapy
Corticosteroids therapy
Common systemic fungal infections involving peripheral blood &/or bone marrow in solid organ transplantation patients
Candida species
Histoplasma capsulatum
Aspergillus species
Zygomycosis
Poor prognosis without early aggressive treatment
Resistant to most antifungal agents
Common systemic fungal infections involving peripheral blood &/or bone marrow in patients with AIDS
Histoplasma capsulatum
Coccidioides immitis
Disseminated Pneumocystis jirovecii with bone marrow involvement (rare case reports)
Penicillium marneffei, mainly reported in China
Can be confused with Histoplasma capsulatum due to morphologic similarity
Laboratory Tests
Careful morphologic review of Wright-stained peripheral blood and bone marrow aspirate smears
Special stains for fungal organisms, including GMS and PAS on bone marrow biopsy sections
Bone marrow &/or blood culture
Fungal antigen detection in serum by RIA
Molecular methods, including PCR and nucleic acid sequence-based amplification (NASBA)
Treatment
Drugs
Amphotericin B
Itraconazole or posaconazole prophylaxis
Prognosis
High mortality rate associated with disseminated fungal infections in
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree