Full-Length Practice Examination 1
This is the beginning of the first full-length practice examination.
To most closely simulate the actual examination, take this during an uninterrupted 5-hour block of time.
The answer key is located at the end of the examination.
QUESTION 1-1
A 76-year-old dialysis-dependent woman with a history of multiple prior abdominal operations presents to the emergency room with worsening abdominal pain. Workup raises your suspicions for ischemic bowel. She last underwent hemodialysis 3 days prior, and is currently uremic. How will you best prepare the patient for emergent celiotomy?
QUESTION 1-2
A 76-year-old man with aortoiliac occlusive disease undergoes percutaneous transluminal angioplasty of his left common iliac artery. What is the patency rate for patients who undergo angioplasty for iliac occlusive disease?
QUESTION 1-3
A 39-year-old female presents to the emergency department with complaints of watery diarrhea and upper abdominal pain for the past 2 weeks. On workup, she is found to have a small mass in the body of the pancreas on computed tomography scanning. Laboratory abnormalities include a hemoglobin of 8.7 mg/dL, white blood cell count of 10.1, hypokalemia, and a metabolic acidosis. She is subsequently scheduled to have an exploratory laparotomy. Intraoperatively, the mass is removed from her pancreas and multiple small nodules are found in her liver. Considering the most likely diagnosis, what are her best treatment options?
QUESTION 1-4
A 46-year-old woman comes to the emergency department complaining of acute right lower quadrant pain. How could appendicitis be differentiated from acute ileitis?
QUESTION 1-5
A 27-year-old male with idiopathic renal failure on hemodialysis is awaiting a kidney transplant. Multiple family members and friends have presented to the transplant center for evaluation of possible live donor transplantation. The recipient’s brother volunteers to donate his kidney and is found to have a favorable human leukocyte antigen (HLA) match. Which of the following conditions is least likely to be considered a contraindication for live kidney donation?
QUESTION 1-6
A 39-year-old male is referred to your clinic for treatment of a cecal mass diagnosed by surveillance colonoscopy. His father, paternal grandmother, and paternal uncle all developed colon cancer by their fifth decade. Mutation of which of the following genes is associated with this man’s disease?
QUESTION 1-7
A 68-year-old man presents with pain in his left leg. Examination and workup confirm diagnosis of a popliteal aneurysm. What is the most common complication that would result in the patient’s leg pain?
QUESTION 1-8
A 52-year-old woman presents to your clinic with a palpable thyroid nodule. Ultrasound shows a 3-cm lesion in the right thyroid lobe with solid and cystic components. Ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration (FNA) reveals a thyroid cancer. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
QUESTION 1-9
A 60-year-old man who suffers from chronic alcoholism is admitted to the hospital with an episode of acute pancreatitis. He suffered similar episodes in the past—all of which have resolved without complications. On laboratory studies, he is found to have an elevated serum amylase level. A computed tomography (CT) scan is performed which demonstrates a 4-cm pancreatic pseudocyst. What would be the best subsequent treatment?
QUESTION 1-10
Which of the following is a characteristic of Merkel cell carcinoma?
QUESTION 1-11
A 70-year-old man with ascites secondary to cirrhosis presents for elective umbilical hernia repair. Should he be offered repair of his hernia?
QUESTION 1-12
A 68-year-old man with atrial fibrillation presents to the emergency room with a cool, pulseless right foot. Sensation is intact. Duplex ultrasound of the right leg reveals multiple femoral stenoses and tibioperoneal thrombosis with poor tibial flow. What is the most appropriate management?
QUESTION 1-13
A 55-year-old woman presents to your clinic with the new diagnosis of tertiary hyperparathyroidism. Which of the following operations has she most likely previously undergone?
QUESTION 1-14
A 63-year-old man presents with a “gnawing” upper abdominal pain. He reports that he was diagnosed with a gastric ulcer years ago. Which of the following tests is most sensitive in diagnosing the patient with infection with Helicobacter pylori?
QUESTION 1-15
Which of the following is a characteristic of a cutaneous lymphatic malformation?
QUESTION 1-16
The fundamental goal of the American College of Surgeons National Surgical Quality Improvement Program (NSQIP) is:
QUESTION 1-17
A 73-year-old man has developed a pulseless left lower leg 8 days after experiencing a myocardial infarction (MI) requiring cardiopulmonary resuscitation. On examination, he has diminished sensation in his left foot. What is the most appropriate definitive treatment?
QUESTION 1-18
A 47-year-old woman presents with a rapidly enlarging 5-cm right breast mass without palpable axillary nodes. Fine-needle aspiration (FNA) is nondiagnostic. Core biopsy is performed and results are reported as equivocal, but suggestive of a phyllodes neoplasm. The appropriate next step in management is:
QUESTION 1-19
A 72-year-old man undergoes percutaneous transhepatic cholangiography (PTC) and percutaneous biliary drainage (PBD) for obstructive jaundice secondary to pancreatic cancer. Following the PTC/PBD, he develops melena and bright red blood is seen in the biliary drain. Laboratory work reveals a drop in hematocrit and increase in his liver function tests. What is the definitive treatment for this change in his condition?
QUESTION 1-20
During resection of a pelvic tumor, the left ureter is inadvertently transected below the level of the pelvic brim. The immediate treatment of this problem is:
QUESTION 1-21
Four weeks after a deceased donor kidney transplant, the recipient returns to the emergency department with bilateral lower-extremity edema. In spite of normal fluid intake, he reports that he has had minimal urine output over the past 18 hours. Serum creatinine is now elevated to 1.4 mg/dL from 1.0 mg/dL postoperatively. After failure to respond to a fluid challenge, an ultrasound is obtained. This reveals good perfusion, minimal hydronephrosis and, a 3- × 4- × 6-cm hypoechoic mass adjacent to the renal pelvis of the allograft. What is the most likely cause of the patient’s oliguria?
QUESTION 1-22
Eighteen months after undergoing an aortobifemoral artery bypass, a 74-year-old man presents with a painful swelling in his left groin. Ultrasound demonstrates a pseudoaneurysm at the site of the distal anastomosis with surrounding fluid. What is the likely underlying cause of this finding?
QUESTION 1-23
A 38-year-old woman is referred to your clinic after an elevated 24-hour urine cortisol measurement. She is not on any steroids. What is the most likely cause of this patient’s disease?
QUESTION 1-24
A 36-year-old woman underwent banding for an internal hemorrhoid 1 week ago. She contacts your office complaining of a small amount of blood on toilet paper after defecation, but denies pain or fever. The next step in her management is:
QUESTION 1-25
A 32-year-old male is brought to the emergency department after his left leg was pinned between two cars. Upon examination, his left leg is swollen and tense below the knee and you suspect compartment syndrome. Which nerve is most commonly injured during fasciotomy of the lower leg?
QUESTION 1-26
While visualizing the gallbladder during an elective laparoscopic cholecystectomy, the anesthesiologist informs you that the patient has a heart rate of 130, and a dropping blood pressure. What is the FIRST step in management?
QUESTION 1-27
Eighteen months after undergoing an aortobifemoral artery bypass, a 69-year-old woman presents with a draining, cellulitic wound in her right groin, with exposed polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) graft. What is the most likely pathogen infecting this graft?
QUESTION 1-28
A 40-year-old premenopausal woman is seen by her physician for evaluation of a breast nodule. Physical examination confirms the presence of a 1-cm movable mass; mammogram and ultrasound evaluation are both found to be consistent with a fibroadenoma. A core biopsy confirms this diagnosis. The lesion is excised at the patient’s request. Pathology results reveal a fibroadenoma with a small area of lobular carcinoma in situ (LCIS) in the surrounding breast tissue, focally extending to one margin. The next step in management is:
QUESTION 1-29
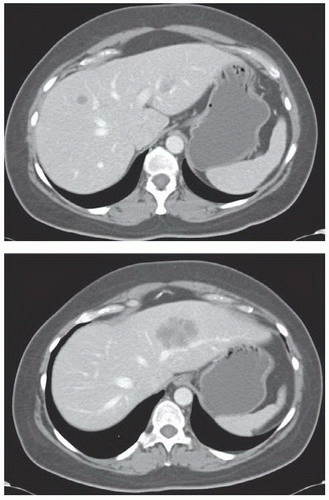
A 56-year-old man 2 years status post left colectomy for stage IIA colon cancer is now found to have rising carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) and two new lesions in the liver on follow-up CT scan (see scans below). There is no evidence of extrahepatic disease. How do you manage this patient?
|
QUESTION 1-30
A 56-year-old man presents to your clinic with a 5-mm wide lesion confined to the middle of his lower lip. Biopsy confirms squamous cell carcinoma. What is the most appropriate management?
QUESTION 1-31
A 26-year-old male is undergoing a nerve block for an outpatient orthopedic procedure on his left ankle. During injection of the superficial fibular nerve with lidocaine, he complains of tingling around his mouth and lips. What other symptom would be consistent with lidocaine toxicity?
QUESTION 1-32
A 64-year-old man undergoes endovascular repair of a 5.9-cm infrarenal abdominal aortic aneurysm with bilateral iliac artery involvement. The patient does well postprocedurally and is discharged home 4 days later. A 6-month follow-up CT reveals contrast extravasation into the aneurysm sac at the proximal aspect of the aneurysm and an interval increase in the aneurysm size to 6.3 cm. What type of endoleak is described, and what is the best management?
QUESTION 1-33
A 64-year-old postmenopausal woman with Estrogen Receptor Positive (ER+), stage I breast cancer presents following lumpectomy, and radiation therapy, now on therapy with tamoxifen. She asks about the risks of tamoxifen therapy. You tell her that:
 Tamoxifen has been linked to an increased risk of developing endometrial adenocarcinoma and uterine sarcoma
Tamoxifen has been linked to an increased risk of developing endometrial adenocarcinoma and uterine sarcoma Tamoxifen increases bone resorption, increasing risk of long bone and pelvic fractures due to osteoporosis
Tamoxifen increases bone resorption, increasing risk of long bone and pelvic fractures due to osteoporosisQUESTION 1-34
Workup for vomiting in a 46-year-old woman with Crohn disease reveals a stricture in the second portion of the duodenum. What is the best surgical management of this problem?
QUESTION 1-35
A 17-year-old male presents to the emergency department after a right shoulder injury sustained while playing football. Plain radiographs reveal the humeral head displaced medial to the glenoid fossa. Which nerve is most likely injured in this type of dislocation?
QUESTION 1-36
An obese woman who underwent a transabdominal hysterectomy 10 years ago presents for an elective ventral hernia repair. She undergoes hernia repair via a laparoscopic approach, to which she responds well initially. However, she develops a recurrent bulge 2 months later and presents to your office for counseling. What is the most common reason for recurrence after laparoscopic ventral hernia repair?
QUESTION 1-37
What is the most common cause of late death after heart transplant?
QUESTION 1-38
A 48-year-old male presents with persistent peptic ulcers that have been refractory to proton-pump inhibitors. His workup includes a positive secretin stimulation test. His underlying tumor is:
QUESTION 1-39
A 38-year-old male presents to the emergency department after attempted suicide via ingestion of oven cleaner. Upon rigid esophagoscopy, you observe erythematous, friable, mucosa with superficial, noncircumferential white ulcerations in the mid-esophagus. What degree of injury is this lesion?
QUESTION 1-40
A 32-year-old female requires a split-thickness skin graft after being involved in a car accident. A 12- × 6-cm site is harvested from her lateral thigh and is implanted on her scalp without complications. The healing rate at the donor site is most related to:
QUESTION 1-41
A 21-year-old male is brought to the trauma bay after sustaining a superficial stab-wound to the left shoulder. He reports that he received his full series of shots as a child, and received his last tetanus booster shot when he was 15. What should he receive for his tetanus prophylaxis?
QUESTION 1-42
A 72-year-old man is seen in clinic preoperatively to prepare for his upcoming femoral-tibial artery bypass for vascular insufficiency. The duplex scan demonstrates poor candidates for venous conduits, so the use of synthetic graft is anticipated. The long-term outcome for this patient could be improved by:
QUESTION 1-43
A 25-year-old male sustains a superficial gunshot wound to his left proximal, lateral thigh, near the anterior superior iliac spine. His initial neurologic examination in the emergency department reveals no motor deficits but numbness in the region of the left lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh. When should surgery for repair of the suspected nerve injury be performed?
QUESTION 1-44
A 40-year-old male former Australian lifeguard with a history of melanoma presents to the emergency department with a month-long history of abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting. What is the most likely cause for his symptoms?
QUESTION 1-45
Which of the following characteristics is an advantage of full-thickness skin grafts (FTSGs) over split-thickness skin grafts (STSGs)?
QUESTION 1-46
A 56-year-old male is ventilator dependent due to an open abdomen secondary to trauma. On the third day following his injury, he develops hypoxemia and tachypnea requiring an increase of the fraction of inspired oxygen (FiO2) and positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP). His partial pressure of oxygen in arterial blood (PaO2) increases minimally with these changes. Plain chest radiograph shows bilateral infiltrates and pulmonary artery occlusion pressure is 16 mm Hg. Which combination of features would support a diagnosis of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) over ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP)?
 Temperature 38.3°C, WBC = 12, minimal pleural effusion, increased protein on bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL), infiltrates not seen on chest radiograph
Temperature 38.3°C, WBC = 12, minimal pleural effusion, increased protein on bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL), infiltrates not seen on chest radiographQUESTION 1-47
A 28-year-old female professional violinist presents with headaches, neck pain, and hand clumsiness in her right hand. She also reports occasional numbness in the hand and right-sided chest pain. Which of the following is the likely cause of her symptoms?
QUESTION 1-48
A 72-year-old man with a history of diabetes and smoking presents with a 2-day history of excruciating pain in the right lower extremity. The patient states that the pain started while he was sitting in a chair, and that, unlike other pains he has had in the leg before, it was not relieved by elevation of the extremity. Physical examination shows a pale, cool, pulseless, and numb right foot and the calf is quite tender. No pedal Doppler signal is obtainable. The patient is taken to the operating room where on-table angiogram reveals occlusion of the superficial femoral artery. A right femoral below knee popliteal bypass is performed with restoration of the pulses. Postoperatively in the surgical intensive care unit, the resident notices severe swelling of the right lower extremity and loss of the dorsalis pedis pulse. The most likely etiology of the edema is:
QUESTION 1-49
A 22-week pregnant, 31-year-old woman received 7 days of ampicillin for a urinary tract infection. The patient developed diarrhea on day 5 of therapy, and stool is positive for Clostridium difficile toxin. How would you treat the patient?
QUESTION 1-50
You are performing a laparoscopic cholecystectomy on a 64-year-old woman with a history of cholelithiasis and vague abdominal pain. As you insert the camera through the supraumbilical trocar, you are surprised to find white cake-like tumor spreading from the left pelvis across much of the large intestine. You should:
QUESTION 1-51
A 2-year-old boy is brought to the emergency department by his mother. She reports that he has been inconsolable for the past 24 hours and has refused his feeds. Upon further questioning, the physician finds that the child has vomited twice and has not had a bowel movement. Examination reveals a slightly distended and diffusely tender abdomen, especially in the inguinal area, without signs of peritonitis. What should be your first step?
 Elevation of the child’s lower extremities with a pillow, followed by an attempt at manual reduction
Elevation of the child’s lower extremities with a pillow, followed by an attempt at manual reductionQUESTION 1-52
An 82-year-old man with a history of severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) presents with claudication and is found to have occlusive disease localized to the left common iliac artery. Which of the following procedures is the most appropriate for management of this patient’s disease?
QUESTION 1-53
A 47-year-old woman undergoes core-needle biopsy of a lesion found on routine mammography in the lower, outer quadrant of her right breast. Pathology is read as atypical ductal hyperplasia (ADH) of the breast. What is the most appropriate next step in this patient’s management?
QUESTION 1-54
A 43-year-old man presents to your clinic complaining of intermittent blood spotting on toilet paper for 2 weeks. Anoscopy reveals a 1-cm split in the anoderm posteriorly on the midline distal to the dentate line, lacking any hypertrophy or visible muscle fibers. What is the optimal management?
QUESTION 1-55
A 22-year-old male (65 kg) is seen in the emergency department after a motorcycle accident that resulted in significant head and maxillofacial trauma. Following initial evaluation and stabilization, he is admitted to the intensive care unit with lactated Ringer (LR) solution running at 125 mL/hr. During the first 60 hours of his stay, his urine output gradually declines to 25 mL/hr and his serum sodium drops from 136 to 127 mEq/L. His vital signs remain stable. Urine osmolarity is found to be 548 mOsm/L. Which of the following is the next best intervention?
QUESTION 1-56
A 45-year-old woman with a history of gallstones is admitted to the intensive care unit after diagnosis with acute pancreatitis with hemodynamic instability. Her admission laboratory values were remarkable for a number of abnormalities, including hyponatremia, hyperamylasemia, hyperlipasemia, and hyperlipidemia. What is the etiology of hyponatremia in pancreatitis?
QUESTION 1-57
A previously healthy 63-year-old woman began to complain of increased shortness of breath and chest pain while undergoing a root canal. After stopping the procedure, her symptoms resolved, and the oral surgeon resumed drilling. She began experiencing right facial pain and periorbital and neck swelling and subsequently complained of severe dyspnea. The patient’s blood pressure then became undetectable. An emergent ECG showed nonspecific ST wave changes. Her pulse oximeter revealed an oxygen saturation of 89% to 90% throughout the procedure. Immediate action should be?
QUESTION 1-58
A 34-year-old male Ukrainian immigrant is seen in clinic for a right-sided thyroid nodule, which shows no uptake on technetium scan. In 1986, he was living near the Chernobyl nuclear reactor during its melt-down. Given this history and probable etiology, what is the most likely diagnosis of his thyroid nodule?
QUESTION 1-59
A 54-year-old alcoholic man presents to the emergency department with severe substernal and epigastric pain after vomiting while drinking earlier that evening. Gastrografin esophagogram shows perforation of the distal esophagus with drainage into the left pleural space. What is the most appropriate treatment?
QUESTION 1-60
The appropriate treatment for an 8-year-old with a completely displaced supracondylar fracture of the humerus (Gartland type III) is:
QUESTION 1-61
A 42-year-old woman is in the intensive care unit immediately following removal of a left adrenal pheochromocytoma. Her blood pressure is 80/40 mm Hg. The most appropriate treatment of the patient’s hypotension is:
QUESTION 1-62
A 24-year-old man presents to the emergency department after sustaining two gunshots through his chest. Which of the following would suggest that he has lost 30% to 40% of his blood volume?
 HR >120, decreased blood pressure, very decreased pulse pressure, respiratory rate 30 to 40, urine output 5 to 15 mL/hr
HR >120, decreased blood pressure, very decreased pulse pressure, respiratory rate 30 to 40, urine output 5 to 15 mL/hrQUESTION 1-63
A 42-year-old woman presents with the presumed diagnosis of inflammatory carcinoma of her left breast. She is 8 weeks postpartum. What is the appropriate management?
 If the tumor responds to high-dose chemotherapy, continue with mastectomy, postoperative radiation, then possible further adjuvant therapy
If the tumor responds to high-dose chemotherapy, continue with mastectomy, postoperative radiation, then possible further adjuvant therapy If the tumor responds to high-dose chemotherapy, continue with radiation therapy, followed by surgical resection, then chemotherapy
If the tumor responds to high-dose chemotherapy, continue with radiation therapy, followed by surgical resection, then chemotherapyQUESTION 1-64
A 60-year-old man with a long history of smoking and heavy alcohol use undergoes a transhiatal esophagectomy for esophageal cancer. He does well and is discharged from the intensive care unit on the second postoperative day. However on the third day he develops a fever and malaise. A chest and neck CT scan demonstrates severe inflammation as indicated by stranding around, and wall thickening of, the gastric conduit but no intramural air. Which vascular supply to the stomach may have been compromised during the transhiatal esophagectomy?
QUESTION 1-65
On initial assessment the most important predictor of return of function in a patient with a severe head injury is:
QUESTION 1-66
A 7-week-old boy is referred with a 3-day history of projectile nonbilious vomiting. He appears dehydrated and, on abdominal examination, an olive-shaped epigastric mass is palpable. The most appropriate initial IV fluid regimen for resuscitation is:
QUESTION 1-67
A 67-year-old woman with long-standing diabetes presents to clinic stating that she has noticed some breakdown of the skin on the bottom of her right foot. Examination of the foot reveals a shallow ulcer overlying the area of the metatarsal heads with surrounding erythema. Radiograph of the foot reveals no bony involvement. How should you counsel her?
QUESTION 1-68
A 65-year-old female complaining of weakness, fatigue, and easy bruising, is found to have guarding and distention of her upper abdomen. She reports a history of taking prednisone and weekly epoetin-α. She feels her symptoms have become worse in the past year. What procedure would this patient need for definitive management of this condition?
QUESTION 1-69
You are called by the Intensive Care Unit (ICU) regarding a 45-year-old man intubated for ARDS for the past 3 weeks. Over the past 48 hours, he has developed increased abdominal distension. His last bowel movement was 4 days ago, and the ICU staff has attempted multiple enemas without result. An abdominal plain film has revealed diffuse dilation of the colon consistent with ileus, without an identifiable transition point. Your physical examination demonstrates a critically ill man with a rotund abdomen. There is no fluid wave or shifting dullness, just diffuse tympany. There is no stool in the rectal vault. How should you proceed with treatment?
QUESTION 1-70
For an oral squamous cell carcinoma with 4-mm depth of invasion without palpable lymph nodes, the appropriate surgical treatment entails:
QUESTION 1-71
A 45-year-old female is in the SICU 2 days postoperative from an orthotopic liver transplant for primary biliary cirrhosis. The patient’s condition has rapidly deteriorated, with signs consistent with fulminant hepatic failure. Ultrasound of the graft is most likely to reveal which of the following?
QUESTION 1-72
A 30-year-old man presents with facial swelling, engorged neck veins, and complaints of dizziness for the prior 3 months. Two years previously, he was diagnosed with unresectable malignant thymoma, but completed only two rounds of radiotherapy. How should you proceed with treatment?
QUESTION 1-73
A 42-year-old man presents with progressive fullness and abdominal cramping increasing in severity over the past 4 weeks. Computed tomography (CT) reveals a large intra-abdominal mass with multiple enlarged inguinal and cervical lymph nodes visible. Which of the following tests is diagnostic of this patient’s possible intra-abdominal lymphoma?
QUESTION 1-74
An 88-year-old woman presents from a nursing home with altered mental status and abdominal distension. She has a history of gallstones and has never had abdominal surgery. On examination, she is febrile and tachycardic and has a distended, tender abdomen that is tympanitic to percussion. A plain abdominal film demonstrates dilated loops of small bowel with air in the biliary tree. What is your proposed management?
QUESTION 1-75
The cerebral perfusion pressure (CPP) in a patient with head injury should ideally be greater than:
QUESTION 1-76
A 55-year-old man presents with a firm mass on his left thigh, which he noticed recently after bumping into a chair. The mass is painless, not discolored, and 5 cm in diameter. What is the next diagnostic test you should perform?
QUESTION 1-77
A 45-year-old woman was found on physical examination to have a right thyroid nodule. Ultrasound of the thyroid demonstrated a 2.5-cm hypoechoic nodule, which was identified as papillary thyroid cancer on fineneedle aspiration (FNA). What is the best next step in the management of this patient?
 Obtain Integrated Positron Emission Tomography and Computed Tomography (PET-CT) scan for complete staging
Obtain Integrated Positron Emission Tomography and Computed Tomography (PET-CT) scan for complete stagingQUESTION 1-78
A 35-year-old woman presents with complaint of a bloody discharge from the left nipple. Clinical breast examination confirms inducible discharge from a single duct in the left nipple and a small palpable mass near the inferior areolar margin. Bilateral mammogram and left ultrasound show a small density that appears to correspond to the palpable mass, which measures 8 mm by ultrasound and is solid. The lesion is amenable to ultrasound-guided core biopsy. Which of the following is correct?
 If core-needle biopsy confirms intraductal papilloma, then proceed to local excision with postoperative routine breast screening examination
If core-needle biopsy confirms intraductal papilloma, then proceed to local excision with postoperative routine breast screening examination If local excision shows DCIS, the patient can return to routine breast screening with no further intervention needed
If local excision shows DCIS, the patient can return to routine breast screening with no further intervention needed This is most likely a benign process, does not need to be biopsied, and should be followed with clinical breast examination and mammogram every 6 months
This is most likely a benign process, does not need to be biopsied, and should be followed with clinical breast examination and mammogram every 6 monthsQUESTION 1-79
A 54-year-old woman comes to clinic 3 weeks after undergoing a common bile duct exploration for biliary stones refractory to endoscopic management. She was left with a T-tube in place, which has been reliably draining bile until 2 days ago. Over the past 48 hours, she has noted increased right upper quadrant pain that is similar to her preoperative pain. You order a tube cholangiogram, which demonstrates a retained stone lodged in the common bile duct. How should you proceed?
QUESTION 1-80
A 78-year-old African American female with hypertension and diabetes mellitus falls in her kitchen and lacerates her right great toe. Three hours later, her family brings her to the emergency department because she has developed severe erythema migrating up her leg, fever to 40°C (104°F) and a marked change in her mental status. Examination of the wound reveals severe edema of the surrounding skin, marked erythema proceeding up the leg and crepitus to palpation. Her laboratory values show a lactate of 6.7 mmol/L. What is the most appropriate course of treatment?