Esophagitis and Barrett Esophagus
Blythe K. Gorman, MD
Key Facts
Clinical Issues
Endoscopic correlation is required
Clinical correlation is wise
Correlate with biopsy if available
Cytopathology
Reactive atypia may be marked in setting of esophagitis or ulcer
Smooth, uniform nuclei, normal N:C ratio, prominent nucleoli, streaming, no single atypical cells, no 3D clusters
If Barrett esophagus is diagnosed, report presence or absence of dysplasia
True goblet cells: Mucin vacuoles ≥ 3x size of nucleus
Morphologic overlap between reactive atypia and dysplasia
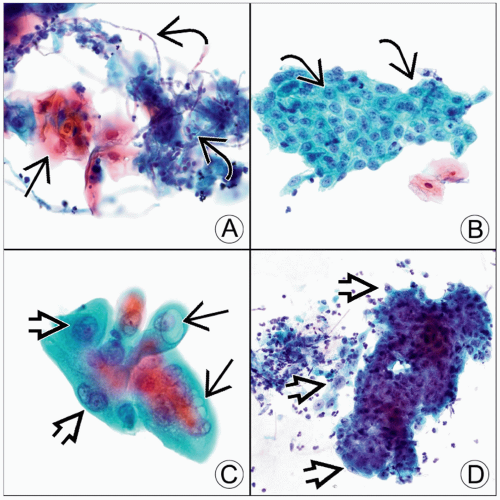 Pap-stained esophageal brushings are seen. (A) Candidal esophagitis shows reactive squamous cells
 , yeast, and pseudohyphae , yeast, and pseudohyphae  . (B) This reflux esophagitis has a flat, cohesive sheet of reactive cells. The nuclei . (B) This reflux esophagitis has a flat, cohesive sheet of reactive cells. The nuclei  have smooth contours, nucleoli, and fine chromatin. (C) Radiation esophagitis shows cells with cytoplasmic vacuoles have smooth contours, nucleoli, and fine chromatin. (C) Radiation esophagitis shows cells with cytoplasmic vacuoles  and a 2-tone cytoplasm. The nuclei are large with vesicular chromatin and a 2-tone cytoplasm. The nuclei are large with vesicular chromatin 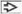 , and the N:C ratio is nearly normal. (D) Ulcerative esophagitis shows marked reactive atypia and neutrophils in the background. The nuclei are uniformly enlarged with prominent nucleoli and vesicular chromatin , and the N:C ratio is nearly normal. (D) Ulcerative esophagitis shows marked reactive atypia and neutrophils in the background. The nuclei are uniformly enlarged with prominent nucleoli and vesicular chromatin 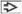 . .Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel
Full access? Get Clinical Tree
 Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

|