|
Typical Clinical Features |
Microscopic Features |
Ancillary Investigations |
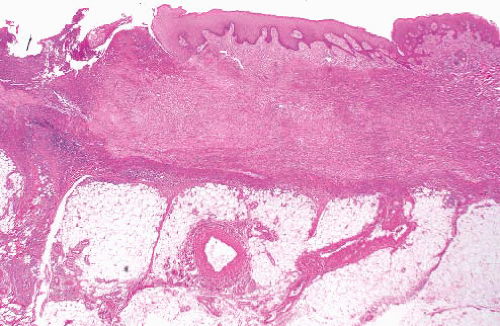
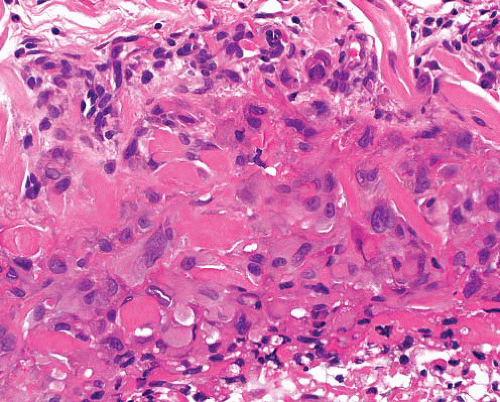
Epithelioid sarcoma |
Nonhealing ulcerated nodules, typically on hand or forearm, mainly first two decades
Proximal variant in young adults, in limb girdles, or axial in perineum, chest wall, pelvis, mediastinum |
Centrally necrotic granuloma-like lesions, mainly polygonal cells with mildly pleomorphic nuclei and abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm
Proximal variant has large cells with vesicular nuclei and prominent nucleoli, focal rhabdoid appearance |
CK+, EMA+, CD34+ (50%), SMA focal, INI1−, ERG±, S100 protein−, desmin− |
Extrarenal malignant rhabdoid tumor |
Children, young adults, head and neck, mediastinum, paraspinal, vulva, perineum |
Multinodular, central necrosis, sheets or cords of polygonal cells, vesicular nucleoli, large nucleoli, eccentric cytoplasm
Occasional fibrosis or myxoid stroma |
CK+, EMA+, CD34−, INI1− |
Epithelioid angiosarcoma |
Usually deep, mostly adults
Can arise in immunosuppression, or in course of other tumor (e.g., hemangioma, schwannoma, malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor) |
Sheets of polygonal cells, rounded vesicular nuclei, prominent nucleoli
Focal vasoformation, intracytoplasmic lumina
Geographic necrosis, old and recent hemorrhage |
CD31+, CD34+, ERG+, FLI-1+, CK±, EMA±, D240±, S100 protein−, desmin−, nuclear INI1+ |
Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma |
Deep lesions of soft tissues, lungs, and liver of adults |
Epithelioid cells in a chondromyxoid background, sometimes associated with a vessel
The cells infiltrate singly, in cords or small nests and do not form vascular channels, but individual cells can have intracytoplasmic lumina |
CD34+, CD31+, FLI-1+, CK±, VEGFR-3−, nuclear INI1+
t(1;3)(p36.3;q25), WWTR1-CAMTA1 fusion,
t(X;11)(p11.22;q13), YAP1-TFE3 fusion |
Epithelioid hemangioma |
Adults (20-40 y), head-neck region, single or multiple smooth papules or plaques (superficial)
Benign but can locally recur |
Lobular vascular proliferation surrounded by lymphoid cuff, often associated with damaged artery
Vessels lined by epithelioid endothelial cells, background eosinophils |
CD34+, CD31+, ERG+ in epithelioid cells |
Pseudomyogenic (epithelioid sarcoma-like) hemangioendothelioma |
Rare tumors of young adults
Extremities or trunk, in subcutis or deep soft tissue
Indolent behavior with local or regional recurrence |
Sheets, ill-defined nodules, fascicles of deeply eosinophilic cells in desmoplastic stroma but no overt vascular channel formation
Occasional cells with intracytoplasmic vacuoles suggesting vascular lumen formation |
CK+, CD31+, FLI-1+, CD34−, nuclear INI1+
t(7;19)(q22;q13), SERPINE1-FOSB fusion |
Epithelioid malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor |
Adults, F > M
Subcutaneous or deep, the latter usually associated with a nerve |
No capsule, nodules of cells in cords, nests or sheets
Cells have large nucleoli, eosinophilic cytoplasm, with occasional rhabdoid or clear cell change
Pleomorphism is rare
Spindle cell component is common |
S100 protein+, CD34±, INI1− (in about 50%). HMB45−, melan-A−, desmin− |
Epithelioid schwannoma |
Adults, superficial soft tissue of digits, ear, thigh, and on VIII cranial nerve |
Circumscribed, encapsulated
Cords of rounded cells, focal hyperchromatic nuclei, rare mitoses, thick-walled vessels
Epithelioid change can be focal in regular schwannoma |
S100 protein+ (diffuse), GFAP+, CK+ in some. Rim of EMA+ perineurial cells |
Epithelioid neurofibroma |
Very rare focal feature in typical neurofibroma in neurofibromatosis type 1 |
Clusters and cords of plump epithelioid Schwann cells |
S100 protein+, CK− |
Sclerosing perineurioma |
M > F, affects fingers, thumb, palm |
Cords and whorls of rounded or epithelioid cells in dense stroma, without atypia |
EMA+, claudin-1+, CD34±, CK−, betacatenin−, INI1+ |
Epithelioid inflammatory myofibroblastic sarcoma |
M > F, adults, intraabdominal (omentum or mesentery), recur and metastasize |
Atypical polygonal cells with prominent nucleoli in myxoid and inflammatory stroma including neutrophils, necrosis |
ALK+ (nuclear membrane), CD30+, desmin + t(2;2)(p23;q13), RANBP2-ALK fusion |
Epithelioid smooth muscle tumor |
Female genital tract, skin, subcutis especially head and neck, usually <2.5 cm |
Sheets of cells with distinct cell membranes, rounded nuclei, and eosinophilic, granular, or clear cytoplasm
Atypia, mitoses, necrosis, vascular invasion in epithelioid leiomyosarcoma |
SMA+, desmin+, h-caldesmon+, occasional CK+ (dot) |
Epithelioid gastrointestinal stromal tumor |
Related to wall of any part of alimentary tract (most commonly stomach, small intestine)
Also, in retroperitoneum, omentum |
Sheets of epithelioid or clear cells often a spindle component
Organoid pattern, occasional plasmacytoid, or rhabdoid change |
CD117+, DOG1+, CD34+, h-caldesmon +, SMA variable, desmin+ rarely, S100 protein+ rarely. CK+ in some after therapy
KIT or PDGFRA mutations |
Epithelioid pleomorphic liposarcoma |
Deep soft tissue, extremities, rarely retroperitoneum, rarely subcutis |
Sheets of clear or granular cells, admixed with pleomorphic lipoblasts
Usually focal, more typical tumor elsewhere |
S100 protein+, AE1/3+, melan-A+, SMA+ |
Angiomatoid fibrous histiocytoma |
Children, young adults, deep dermis or subcutis of upper limb, antecubital fossa, axilla, head and neck, trunk, groin |
Circumscribed, fibrous, and lymphoplasmacytoid cuff with germinal centers
Sheets of bland ovoid cells with scanty cytoplasm
Variable cystic blood-filled spaces without endothelial lining |
Desmin+ (60%), h-caldesmon+, EMA+, CD99+, CD68+, S100 protein−
t(2;22)(q33;q12), EWSCREB1 fusion,
t(12;22)(q13;q12) EWSATF1 fusion or
t(12;16)(q13;p11), FUSATF1 fusion |
Epithelioid myxofibrosarcoma |
Most subcutaneous, some subfascial
Extremities,
M = F |
Epithelioid cells with prominent nucleoli in myxoid stroma, pattern of short curved vessels |
CK−, EMA−, desmin−, S100 protein− |
Extraskeletal myxoid chondrosarcoma |
Deep soft tissues of extremities, slight male predominance |
Cords, sheets, and reticular pattern of uniform rounded cells with eosinophilic cytoplasm in hypovascular myxoid background |
S100 protein+, neuroendocrine markers+ in a subset
t(9;22)(q22;q12), EWSR1-NR4A3 fusion, t(9;17) (q22;q11), TAF1168-NR4A3 fusion, or t(9;15)(q22;q21), TCF12-R4A3 fusion |
Sclerosing epithelioid fibrosarcoma |
Deep soft tissue, limbs/girdles, head and neck
Can involve or arise in bone |
Multinodular, focal calcification
Cellular islands in dense fibrosis
Nests of ovoid cells, clear cytoplasm, or single files simulating carcinoma
Fibrosarcoma-like spindle cell areas in many cases |
Occasional and variable expression of bcl-2, EMA, CK, S100 protein
No specific immunophenotype
Some have genetic features of lowgrade fibromyxoid sarcoma including FUS-CREB3L2 and EWSR1-CREB3L1 fusions |
Carcinoma |
Usually metastatic deposit in skin or subcutis |
Cords and sheets of epithelioid cells with variable pleomorphism, sometimes with focal glandular formation |
CK+, EMA+, nuclear INI1+, CD34−
Other markers as indicated: PSA, thyroglobulin, calcitonin, hepar-1, CD56, chromogranin, WT1, GCDFP15, TTF-1, ER, PgR, etc. |
Epithelioid mesothelioma |
Pleural, peritoneal, paratesticular solitary or multiple masses or sheet-like proliferation
Can infiltrate organs |
Sheets of epithelioid cells, adenopapillary formations, necrosis |
CK5/6+, calretinin+, thrombomodulin+, D2-40+, desmin+ in some, CD34 and bcl-2−, BerEP4 and CEA−, nuclear INI1+ |
Melanoma |
Primary or metastatic |
Plump epithelioid cells in sheets, often with prominent nucleoli
Cytoplasm eosinophilic, sometimes rhabdoid
Anisocytosis and nuclear pleomorphism can be prominent, unlike in most epithelioid soft tissue tumors |
S100 protein+, melan-A+, HMB45+, INI1+, CK+ rarely |
Perivascular epithelioid cell tumor |
Intra-abdominal, soft tissue, or gynecologic locations |
Monotypic epithelioid type has sheets of granular or epithelioid cells
Malignant variants also have pleomorphism, multinucleation, and abnormal |
SMA+, HMB45+, melan-A+, desmin+ in some, CD117+ in some, S100 protein+ rarely, TFE3+ in some |
Anaplastic large cell lymphoma |
Skin or soft tissue involvement, the latter usually associated with advanced nodal disease |
Sheets of polygonal cells, prominent nucleoli, multinucleated forms
Can be spindled |
CD30+, ALK+ (or −), CD43+, CD45+, CD3+, TIA1+, t(2;5) (p23;q35), TMP3-ALK fusion |
Histiocytic sarcoma |
Very rare tumor occurring in skin, lymph nodes, gastrointestinal tract |
Sheets of epithelioid cells with eosinophilic cytoplasm and prominent nucleoli, binucleated or giant cells, necrosis
Marked neutrophilic or lymphocytic infiltrate |
CD45+, CD45RO+, CD68+, CD4+, lysozyme+, CD31+ |
Rhabdomyoma |
Extracardiac lesions occur in larynx, oral cavity, neck, female genital tract |
Adult type has large polygonal cells with voluminous granular cytoplasm, some with cross-striations.
Fetal type is myxoid or cellular with spindle cells and variable myotube formation, and some with cross-striation. |
Desmin+, myogenin+ (nuclear), MyoD1+ (nuclear) |
Granular cell tumor |
Skin, head and neck sites (tongue), viscera |
Infiltrative, cords and nests of cells with small nuclei, large amounts of coarsely granular cytoplasm, and distinct cell margins |
S100 protein+, CEA+, melanocytic and myoid markers negative |
|