Epithelioid Hemangioendothelioma
Key Facts
Terminology
Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma (EH)
Clinical Issues
Incidence
Unusual tumor in mediastinal compartment
May account for < 1% of all mediastinal tumors
May affect individuals ranging from 20 to > 60 years of age
Some series have reported slight male predominance for occurrence of this tumor
Symptoms
Chest pain
Cough
Dyspnea
Asymptomatic
Prognosis
Tumor may follow protracted course with recurrences
In some cases, it may follow rapid course with metastatic disease in or outside of thorax
Top Differential Diagnoses
Chordoma
Myxoid chondrosarcoma
Seminoma
Thymic carcinoma
Diagnostic Checklist
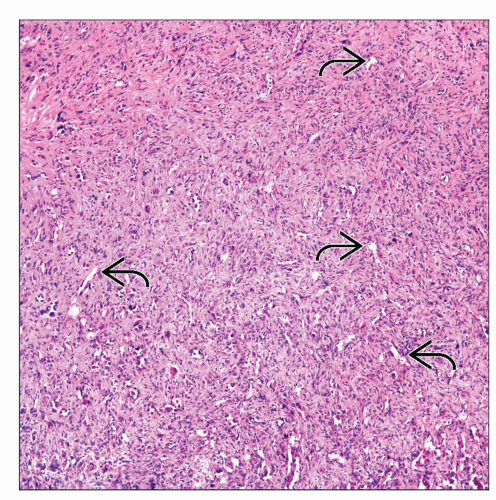
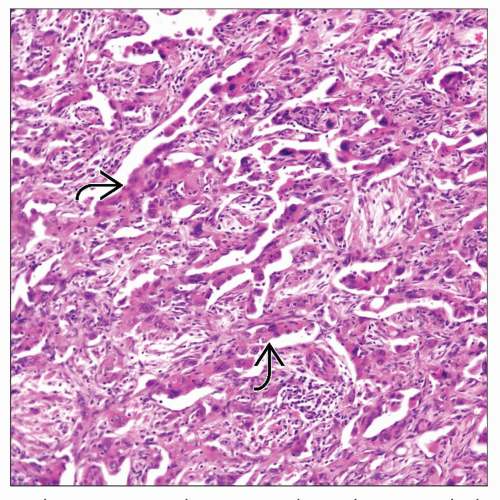
Cords of epithelioid cells
Low mitotic rate of no more than 1-2 × 10 HPF
Chondromyxoid stroma
Absent necrosis, and if present, it would be focal
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma (EH)
Definitions
Vascular neoplasm of intermediate malignant potential
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Etiology
Although well known to be tumor of vascular origin, its etiology is still unknown
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Unusual tumor in mediastinal compartment
May account for < 1% of all mediastinal tumors
Age
Wide range from younger patients < 20 years old to older patients > 60 years old
Gender
No apparent gender predilection
However, in some series of cases there has been slight male predominance
Ethnicity
No apparent ethnic predilection
Presentation
Chest pain
Cough
Dyspnea
Asymptomatic
Treatment
Surgical approaches
Complete resection of tumor
Adjuvant therapy
Radiation &/or chemotherapy may be considered depending on extent of tumor at time of diagnosis
Prognosis
Tumor may follow protracted course with recurrences
In some cases, may follow rapid course with metastatic disease within thoracic cavity or outside of thorax
MACROSCOPIC FEATURES
General Features
Well circumscribed, encapsulated
Some tumors may be locally infiltrative