Ependymoma
Key Facts
Terminology
Neural neoplasm of possible intermediate malignant potential when in mediastinum
Etiology/Pathogenesis
Probably derived from paravertebral ependymal rests
Clinical Issues
Incidence
Ependymomas arising in mediastinum are rare
More common in adults with a wide range of ages
More common in posterior mediastinum
Symptoms
Cough
Chest pain
Dyspnea
Asymptomatic
Prognosis
Mediastinal ependymomas may follow a prolonged clinical course
Metastasis to lymph nodes may occur
Top Differential Diagnoses
Schwannoma
Neuroendocrine carcinoma
Metastatic melanoma
Diagnostic Checklist
Solid cellular proliferation
True ependymal rosettes
Pseudopapillary areas
Variable mitotic rate
TERMINOLOGY
Synonyms
Myxopapillary ependymoma
Definitions
Neural neoplasm of possible intermediate malignant potential when in mediastinum
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Pathogenesis
Probably derived from paravertebral ependymal rests
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Ependymomas in mediastinum are very rare
Age
More common in adults with wide range of ages
Gender
No gender predilection
Site
More common in posterior mediastinum
Presentation
Cough
Chest pain
Dyspnea
Asymptomatic
Treatment
Surgical approaches
Complete surgical resection
Prognosis
Mediastinal ependymomas may follow a prolonged and indolent clinical course
Metastasis to lymph nodes may occur
MACROSCOPIC FEATURES
General Features
Tumors are well circumscribed with glistening surface
On cut surface, they are solid, but cystic changes may be seen
Necrosis and hemorrhage may be seen
Tan to gray in color
Size
Variable size; may be > 7 cm in diameter
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
Histologic Features
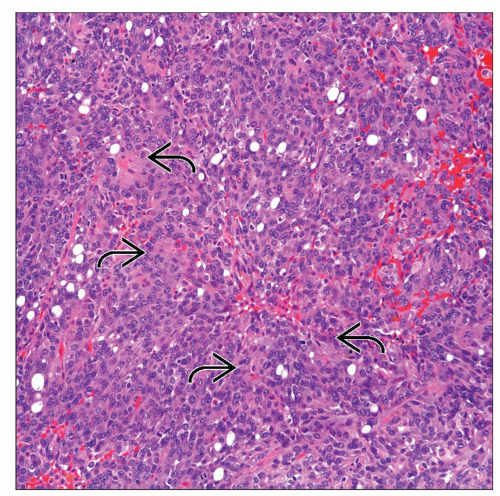
Solid, fairly uniform cellular proliferation that displays moderate atypia
Cells with finely stippled to vesicular chromatin
Perivascular pseudorosettes
Interanastomosing ependymal tubules
True ependymal rosettes and canals with ciliated cells
Pseudopapillary areas
Occasional psammoma bodies may be seen
Mitotic activity is variable and can range from 1 to > 5 x 10 HPF
Necrosis and hemorrhage may be present also in variable proportions, focal or extensive
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Schwannoma
Does not show increased mitotic activity
Does not show presence of true ependymal rosettes
Negative for GFAP
Neuroendocrine Carcinoma
Negative for GFAP and strongly positive for keratin
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree